Consolidation enhances financial stability by merging multiple accounts, debts, or assets into a single entity, simplifying management and often reducing costs. This process can improve your credit score and provide a clearer overview of your finances. Discover how consolidation can streamline your financial life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
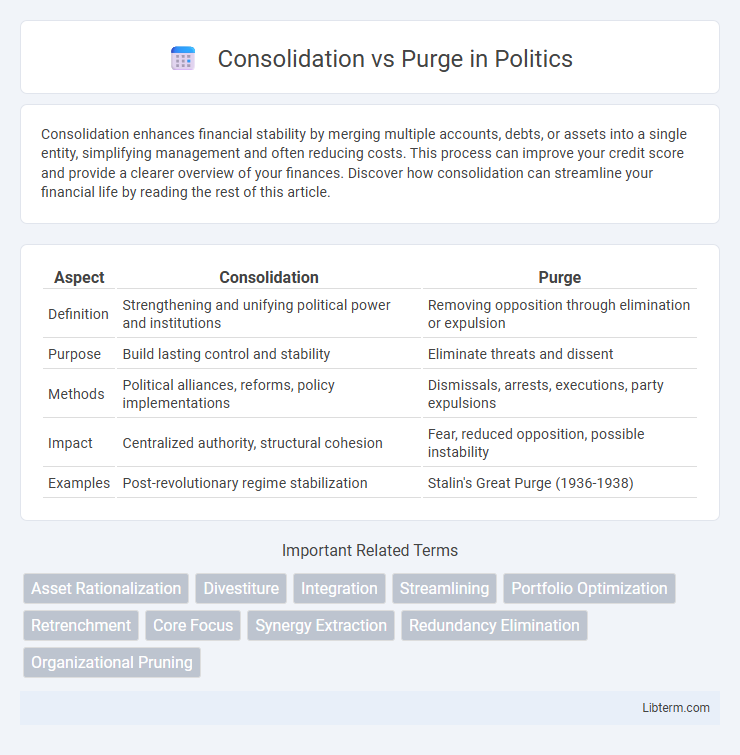
| Aspect | Consolidation | Purge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strengthening and unifying political power and institutions | Removing opposition through elimination or expulsion |
| Purpose | Build lasting control and stability | Eliminate threats and dissent |
| Methods | Political alliances, reforms, policy implementations | Dismissals, arrests, executions, party expulsions |
| Impact | Centralized authority, structural cohesion | Fear, reduced opposition, possible instability |
| Examples | Post-revolutionary regime stabilization | Stalin's Great Purge (1936-1938) |
Introduction to Consolidation and Purge
Consolidation involves merging data from multiple sources into a unified dataset to enhance data integrity and simplify analysis. Purge refers to the systematic removal of obsolete or redundant data to optimize storage performance and maintain database efficiency. Both processes are crucial for effective data management, ensuring accuracy and resource optimization in data warehouses and enterprise systems.
Defining Consolidation: Key Concepts
Consolidation involves merging multiple data sources or systems into a unified repository to improve data quality, reduce redundancy, and enhance accessibility. Key concepts include data integration, consistent data formatting, and centralized management for streamlined operations. This process supports better decision-making by providing a single source of truth from disparate datasets.
Understanding Purge: Core Principles
Purge involves the systematic removal of obsolete, redundant, or irrelevant data to enhance system efficiency and reduce storage costs. Its core principles emphasize data accuracy, compliance with regulatory standards, and secure deletion methods to prevent unauthorized recovery. Effective purge processes utilize automated tools and clear retention policies to maintain optimal data hygiene and operational performance.
Main Differences Between Consolidation and Purge
Consolidation involves combining multiple data sets or records into a single, unified entity to improve data management and reduce redundancy, whereas purge refers to the permanent deletion of obsolete or irrelevant data from the system to maintain data integrity and optimize storage. Consolidation enhances data accuracy and reporting by merging duplicates and harmonizing information, while purge focuses on removing unnecessary data to boost system performance and compliance with data retention policies. Both processes play crucial roles in database administration but serve distinctly different purposes: consolidation unifies data, and purge eliminates it.
Benefits of Consolidation Strategies
Consolidation strategies enhance data management by integrating fragmented datasets into a unified system, improving data accessibility and consistency. This approach reduces storage costs and streamlines data backups, leading to increased operational efficiency. By maintaining comprehensive and up-to-date information, consolidation supports better decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Advantages and Risks of Purge Approaches
Purge approaches optimize data storage by permanently removing obsolete or redundant information, resulting in improved system performance and reduced capacity costs. Key advantages include enhanced database efficiency, faster query response times, and compliance with data retention policies. Risks involve potential loss of critical data, challenges in data recovery, and inadvertent deletion of information that may be needed for auditing or regulatory purposes.
When to Choose Consolidation
Choose consolidation when data from multiple sources needs to be combined for comprehensive analysis or reporting, ensuring integrity and accessibility while maintaining all original records. Consolidation is ideal for organizations requiring unified datasets without losing historical details, supporting trend analysis and detailed audits. This approach optimizes storage by integrating data and facilitates improved decision-making through a single, coherent data repository.
When to Opt for Purge
Opt for purge when data retention requirements mandate permanent deletion of obsolete or irrelevant records to ensure compliance with legal or organizational policies. Purging is ideal for freeing up storage space and improving system performance by removing redundant or expired data that is no longer needed for operational purposes. Consolidation suits scenarios where integrating and summarizing data enhances reporting and analytics rather than eliminating it entirely.
Real-world Examples: Consolidation vs Purge
Consolidation involves merging multiple databases or datasets into a single, unified system, as seen in financial institutions combining customer accounts to streamline operations and improve data accuracy. Purge refers to the systematic removal of outdated or irrelevant data, such as healthcare providers deleting expired patient records to comply with privacy regulations and optimize storage. Companies like Amazon employ consolidation to integrate product inventories across warehouses, while using purging techniques to eliminate obsolete items from their databases to enhance performance and reduce costs.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing between consolidation and purge depends on data volume, retention policies, and system performance needs. Consolidation improves efficiency by merging data for easier access and analysis, while purge permanently deletes obsolete information to free storage and reduce costs. Evaluating organizational goals and compliance requirements ensures the optimal strategy balances data availability with resource management.
Consolidation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com