Unauthorized access poses significant risks to your digital security and personal information, potentially leading to data breaches and identity theft. Protecting your accounts with strong passwords and multi-factor authentication is essential to prevent unauthorized intrusions. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective strategies for safeguarding your digital presence.
Table of Comparison
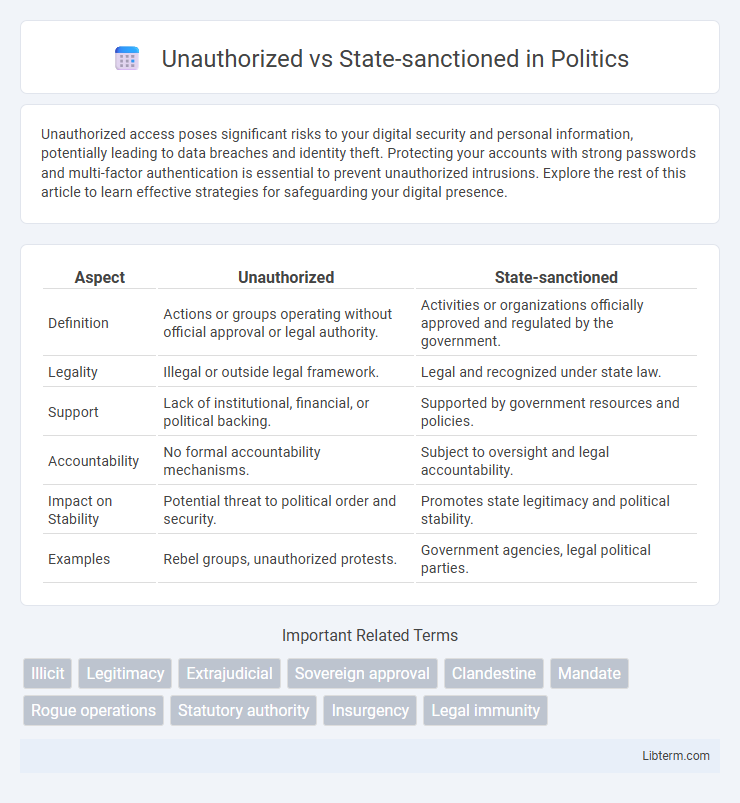
| Aspect | Unauthorized | State-sanctioned |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions or groups operating without official approval or legal authority. | Activities or organizations officially approved and regulated by the government. |
| Legality | Illegal or outside legal framework. | Legal and recognized under state law. |
| Support | Lack of institutional, financial, or political backing. | Supported by government resources and policies. |
| Accountability | No formal accountability mechanisms. | Subject to oversight and legal accountability. |
| Impact on Stability | Potential threat to political order and security. | Promotes state legitimacy and political stability. |
| Examples | Rebel groups, unauthorized protests. | Government agencies, legal political parties. |
Introduction to Unauthorized vs State-Sanctioned
Unauthorized actions occur without official approval or legal permission, often violating established laws or regulations. State-sanctioned activities are formally authorized and regulated by government authorities, ensuring legitimacy and compliance with legal frameworks. Understanding the distinction between unauthorized and state-sanctioned actions is crucial for analyzing legality, accountability, and governance in various contexts.
Defining Unauthorized Actions
Unauthorized actions are activities conducted without official approval or legal authority, often violating established laws, regulations, or policies. These actions can include unauthorized surveillance, data breaches, or unapproved use of government resources, posing risks to privacy and security. Distinguishing unauthorized actions from state-sanctioned ones hinges on the absence of formal consent or legal mandate granted by the relevant governmental entity.
Understanding State-Sanctioned Activities
State-sanctioned activities refer to actions officially approved or endorsed by government authorities, often supported by legal frameworks that legitimize their execution. These activities typically involve regulatory oversight, adherence to established laws, and are designed to promote public order, safety, or policy objectives. Understanding the legal basis and institutional approval behind state-sanctioned actions helps distinguish them from unauthorized activities, which lack official permission and often violate legal standards.
Historical Context: Unauthorized vs State-Sanctioned
Unauthorized actions often emerge from grassroots movements or dissenting groups challenging established power structures, usually lacking legal or official approval. State-sanctioned activities are legitimized by government authority, reflecting codified laws, policies, and institutional frameworks that maintain order and control. Historical context reveals how unauthorized acts, such as rebellions or protests, frequently prompt states to formalize previously informal practices or enforce stricter regulations to affirm their sanctioned status.
Legal Implications and Consequences
Unauthorized actions violate established laws, leading to criminal charges, fines, and potential imprisonment, reflecting the state's enforcement of legal boundaries. State-sanctioned activities are legally authorized, providing immunity from prosecution and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. The distinction impacts liability, legal accountability, and the scope of permissible conduct within jurisdictional parameters.
Ethical Considerations in Authorization
Unauthorized actions raise significant ethical concerns due to the lack of consent, which can lead to violations of individual rights and trust erosion within communities. State-sanctioned activities undergo legal vetting and often align with societal norms and regulations, ensuring accountability and transparency in decision-making processes. Ethical authorization balances the protection of public interest with respect for individual freedoms, requiring strict adherence to established laws and moral principles.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Unauthorized actions often lead to significant legal consequences, as seen in the Edward Snowden case, where leaking classified information without state approval resulted in charges of espionage. In contrast, state-sanctioned operations like the U.S. government's NSA surveillance programs, authorized under specific legislation such as the PATRIOT Act, demonstrate how legal frameworks can legitimize intelligence activities. These case studies highlight the critical distinction between unauthorized personal initiatives and officially approved governmental measures.
Impact on Society and Governance
Unauthorized actions often undermine societal trust and destabilize governance by fostering corruption and legal ambiguity. State-sanctioned measures, when transparent and lawful, reinforce institutional legitimacy and promote social order. The balance between enforcement and rights protection critically shapes public perception and democratic stability.
Navigating Gray Areas and Controversies
Navigating gray areas between unauthorized actions and state-sanctioned activities requires careful analysis of legal frameworks and jurisdictional boundaries. Controversies often arise from differing interpretations of legitimacy, sovereignty, and enforcement mechanisms, complicating accountability and international relations. Understanding nuanced political contexts and historical precedents is essential for resolving disputes and establishing clear regulatory policies.
Conclusion: Balancing Authority and Autonomy
Achieving a balance between unauthorized actions and state-sanctioned activities requires nuanced legal frameworks that respect individual autonomy while maintaining public order. Effective governance depends on clear distinctions in authority, ensuring state power does not infringe on personal freedoms without legitimate cause. Sustainable societal stability emerges when laws are enforced with transparency, accountability, and proportionality.
Unauthorized Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com