Voter intimidation undermines the democratic process by coercing or threatening individuals to influence their voting decisions, which can lead to decreased electoral participation and unfair election outcomes. Laws and regulations are in place to protect your right to vote freely without fear of intimidation or harassment at polling stations. Explore the rest of the article to understand how voter intimidation occurs and the steps you can take to safeguard your voting rights.
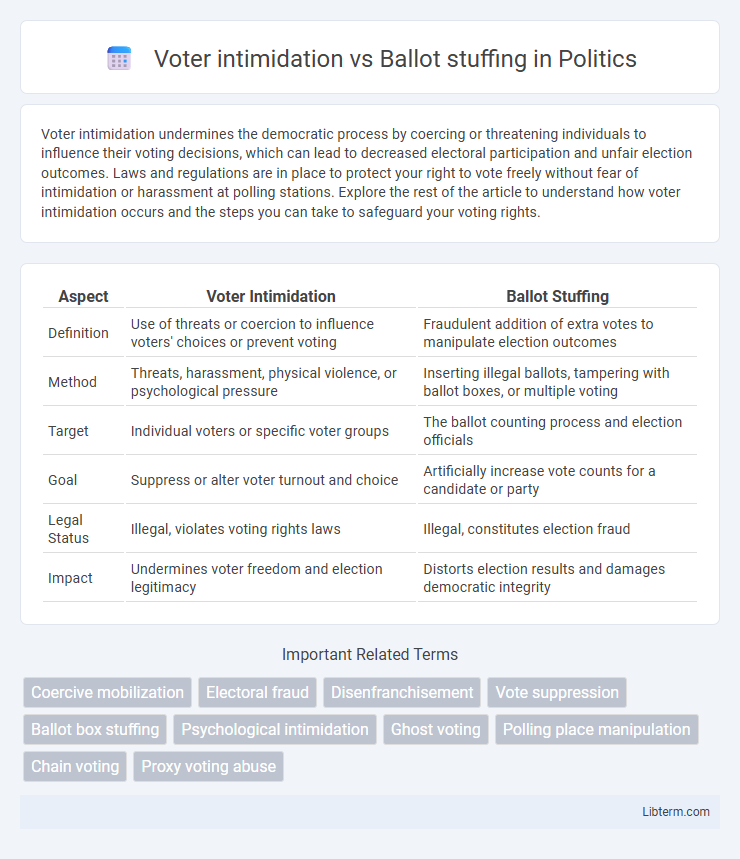
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Voter Intimidation | Ballot Stuffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of threats or coercion to influence voters' choices or prevent voting | Fraudulent addition of extra votes to manipulate election outcomes |
| Method | Threats, harassment, physical violence, or psychological pressure | Inserting illegal ballots, tampering with ballot boxes, or multiple voting |
| Target | Individual voters or specific voter groups | The ballot counting process and election officials |
| Goal | Suppress or alter voter turnout and choice | Artificially increase vote counts for a candidate or party |
| Legal Status | Illegal, violates voting rights laws | Illegal, constitutes election fraud |
| Impact | Undermines voter freedom and election legitimacy | Distorts election results and damages democratic integrity |
Understanding Voter Intimidation: Definition and Examples
Voter intimidation involves coercing or threatening voters to influence their choices or deter them from voting, often through verbal threats, physical presence, or misinformation at polling stations. Unlike ballot stuffing, which entails illegally adding fraudulent votes to the tally, voter intimidation undermines the electoral process by suppressing genuine voter participation. Recognizing examples such as aggressive behavior near polling sites or distributing misleading information is crucial for safeguarding free and fair elections.
Ballot Stuffing Explained: Tactics and Impact
Ballot stuffing involves illegally adding multiple ballots into the voting box to fraudulently increase vote counts for a candidate or issue, often orchestrated through coordinated actions by poll workers or supporters. This tactic undermines the integrity of elections by distorting genuine voter preferences and can lead to contested results and decreased public trust. High-profile cases of ballot stuffing have prompted electoral reforms and stricter monitoring measures to safeguard democratic processes.
Key Differences Between Voter Intimidation and Ballot Stuffing
Voter intimidation involves coercing or threatening voters to influence their choices or prevent them from voting, often through physical presence, verbal threats, or misinformation. In contrast, ballot stuffing is the fraudulent act of submitting multiple ballots or tampering with ballot boxes to artificially inflate vote counts in an election. The key difference lies in voter intimidation targeting individual voter behavior and free choice, while ballot stuffing directly manipulates election outcomes through illegal vote accumulation.
Historical Cases of Voter Intimidation Worldwide
Historical cases of voter intimidation worldwide reveal tactics such as threats, physical violence, and coercion aimed at suppressing voter turnout or influencing election outcomes, with notable instances in apartheid-era South Africa and Jim Crow United States. Ballot stuffing, by contrast, involves the fraudulent addition of illegitimate votes to inflate totals, as seen in elections in Russia and Zimbabwe. Understanding voter intimidation highlights the systemic manipulation of democratic processes through fear rather than direct vote tampering.
Notable Incidents of Ballot Stuffing in Elections
Notable incidents of ballot stuffing have marred elections worldwide, undermining democratic integrity and trust in the electoral process. In the 2018 Zimbabwean general elections, reports surfaced of ballot boxes being stuffed with fake votes to favor the ruling party, while Russia's 2011 parliamentary elections saw numerous allegations of ballot stuffing, leading to widespread protests against alleged voter fraud. These high-profile cases highlight the persistent challenge election commissions face in securing transparent and credible voting systems against fraudulent vote inflation tactics.
Legal Consequences for Voter Intimidation and Ballot Stuffing
Voter intimidation and ballot stuffing are serious election offenses with distinct legal consequences. Voter intimidation involves threats or coercion to influence a voter's choice, punishable by criminal charges such as fines and imprisonment under federal laws like the Voting Rights Act. Ballot stuffing, the illegal act of submitting multiple votes, leads to severe penalties including felony charges, disqualification of election results, and potential incarceration under both state and federal election fraud statutes.
Technology’s Role in Preventing Election Fraud
Technology plays a crucial role in preventing voter intimidation by enabling secure voter identification through biometrics and blockchain-based authentication systems, which ensure only legitimate votes are cast. Advanced surveillance tools and AI-powered monitoring platforms detect and deter suspicious activities at polling stations, reducing the risk of ballot stuffing through real-time anomaly detection and tamper-evident electronic voting machines. Election management systems also integrate cryptographic audits and transparent reporting protocols, strengthening overall election integrity and public trust.
The Effects on Democracy: Comparing Both Threats
Voter intimidation undermines the democratic process by coercing or threatening individuals to influence their voting choices, leading to reduced voter turnout and skewed election results. Ballot stuffing distorts democracy by artificially inflating vote counts, compromising the integrity of election outcomes and eroding public trust in electoral systems. Both threats weaken democratic legitimacy, but voter intimidation directly impacts voter participation, while ballot stuffing attacks the accuracy of vote tabulation.
How to Identify and Report Election Irregularities
Voter intimidation often involves threats, coercion, or misinformation aimed at discouraging or controlling voter participation, identifiable by witness testimonies or suspicious interactions at polling locations. Ballot stuffing is detected through evidence of multiple ballots cast fraudulently in favor of a candidate, such as sudden vote surges or mismatched ballot counts. Reporting election irregularities requires documenting the incident with detailed descriptions, collecting witness statements, and promptly contacting election officials or watchdog organizations for investigation.
Strengthening Election Integrity: Best Practices and Solutions
Voter intimidation undermines election integrity by coercing or threatening voters to influence their choices, while ballot stuffing involves fraudulent addition of votes to alter outcomes. Strengthening election integrity requires implementing robust voter identification systems, increasing transparency through independent monitoring, and deploying secure, tamper-evident voting technologies. Legal frameworks must be enforced rigorously to deter intimidation and fraud, complemented by comprehensive voter education and training for election officials.
Voter intimidation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com