Block voting is an electoral system where voters select a group of candidates rather than just one, often resulting in the majority party winning all the seats. This method can lead to disproportional representation and diminished minority influence in decision-making bodies. Discover how block voting impacts electoral fairness and what it means for Your voting power in the full article.
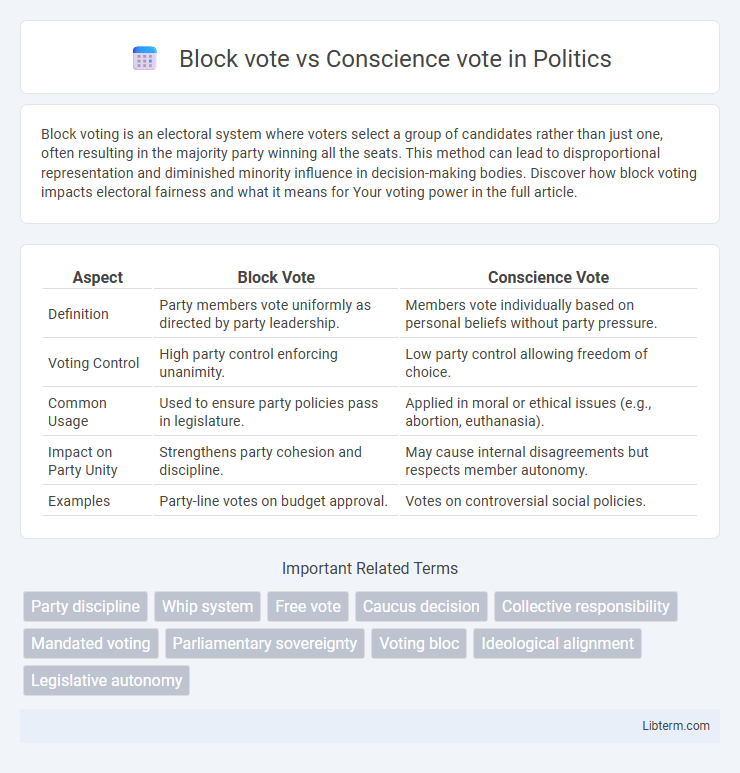
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Block Vote | Conscience Vote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Party members vote uniformly as directed by party leadership. | Members vote individually based on personal beliefs without party pressure. |
| Voting Control | High party control enforcing unanimity. | Low party control allowing freedom of choice. |
| Common Usage | Used to ensure party policies pass in legislature. | Applied in moral or ethical issues (e.g., abortion, euthanasia). |
| Impact on Party Unity | Strengthens party cohesion and discipline. | May cause internal disagreements but respects member autonomy. |
| Examples | Party-line votes on budget approval. | Votes on controversial social policies. |
Introduction to Voting Methods in Legislatures
Block voting is a method where legislators cast multiple votes equal to the number of seats available, often leading to a majority party winning all seats, which can diminish minority representation. Conscience voting allows legislators to vote based on personal beliefs rather than party lines, promoting individual judgment and ethical considerations in decision-making. These voting methods impact legislative dynamics by either reinforcing party dominance or encouraging independent policy choices.
Defining Block Vote
Block vote refers to a voting method where a group of delegates or members collectively cast their votes as a single unit, often reflecting party discipline or predetermined decisions. This approach contrasts with a conscience vote, where individuals vote according to their personal beliefs rather than party lines. Block voting is commonly used in legislative bodies to streamline decision-making and maintain party unity.
Understanding Conscience Vote
Conscience vote, also known as a free vote, allows legislators to vote according to their personal beliefs rather than party lines, reflecting individual moral judgment on sensitive or controversial issues such as euthanasia or same-sex marriage. Unlike block voting, where party members are expected to vote uniformly to maintain party discipline, conscience votes enable diverse perspectives within a legislative body, promoting democratic representation and respect for personal ethics. Understanding conscience votes is essential for analyzing parliamentary decision-making dynamics, legislative independence, and the balance between party unity and individual accountability.
Historical Context of Block and Conscience Voting
Block voting originated in early parliamentary systems as a method to streamline decision-making by requiring members to vote uniformly, often reflecting party discipline in the 19th century. Conscience voting emerged later as democratic ideals evolved, allowing legislators to vote based on personal beliefs rather than party lines, particularly gaining prominence during social and ethical debates in the 20th century. Historical shifts from rigid party control to greater individual autonomy illustrate the contrasting roles these voting practices play in legislative processes.
Mechanisms Behind Block Voting
Block voting operates through a mechanism where legislators cast their votes as a collective unit, often dictated by party leadership to ensure uniformity on key issues. This system emphasizes adherence to party lines, minimizing individual discretion to reinforce political cohesion and strategic legislative outcomes. In contrast, conscience voting allows members to vote independently based on personal beliefs, without party pressure.
The Role of Party Discipline in Block Voting
Party discipline plays a crucial role in block voting by ensuring parliamentary members cast their votes uniformly to support the party's official stance, thereby enhancing internal cohesion and strategic influence within legislative decisions. In contrast, conscience voting allows members to vote according to personal beliefs or constituency interests, often resulting in divergent outcomes that reflect individual autonomy rather than collective party control. The enforcement of party discipline in block votes strengthens policy implementation by minimizing dissent and maintaining the party's legislative agenda.
Advantages of Conscience Voting
Conscience voting allows representatives to make decisions based on personal beliefs and ethical considerations, promoting genuine democratic expression and accountability. This approach fosters diverse perspectives in legislative processes, enhancing the quality and legitimacy of decisions. It encourages integrity and trust between elected officials and their constituents, as votes reflect individual judgment rather than party pressure.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Voting Systems
Block vote systems face challenges such as the potential for majority domination, which can marginalize minority groups and reduce electoral fairness. Conscience vote mechanisms often attract criticism for undermining party discipline, leading to unpredictability in legislative outcomes and weakening cohesive policy agendas. Both systems struggle with balancing democratic representation and effective governance, highlighting persistent tensions between collective decision-making and individual accountability.
Impact on Legislative Outcomes
Block votes consolidate party members' decisions, often leading to predictable legislative outcomes by minimizing dissent and ensuring party-line voting. Conscience votes allow legislators to vote independently, increasing the likelihood of diverse viewpoints and potentially unpredictable or split decisions in lawmaking processes. The contrasting dynamics between block vote cohesion and conscience vote autonomy significantly shape the efficiency and representativeness of legislative decisions.
Future Trends in Parliamentary Voting Practices
Future trends in parliamentary voting practices indicate a decline in block votes as political parties embrace more transparency and individual accountability among members. Conscience votes are gaining prominence, reflecting increasing recognition of diverse personal convictions within legislative bodies. Digital voting technologies and AI-driven analytics are expected to further facilitate nuanced expressions of dissent and informed decision-making.
Block vote Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com