Issue-based politics focuses on addressing specific public concerns such as healthcare, education, and the environment, rather than relying on party loyalty or ideology. This approach encourages candidates to present clear solutions, enabling voters to make informed decisions based on policies that directly impact their lives. Discover how issue-based politics can transform your engagement in the democratic process by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
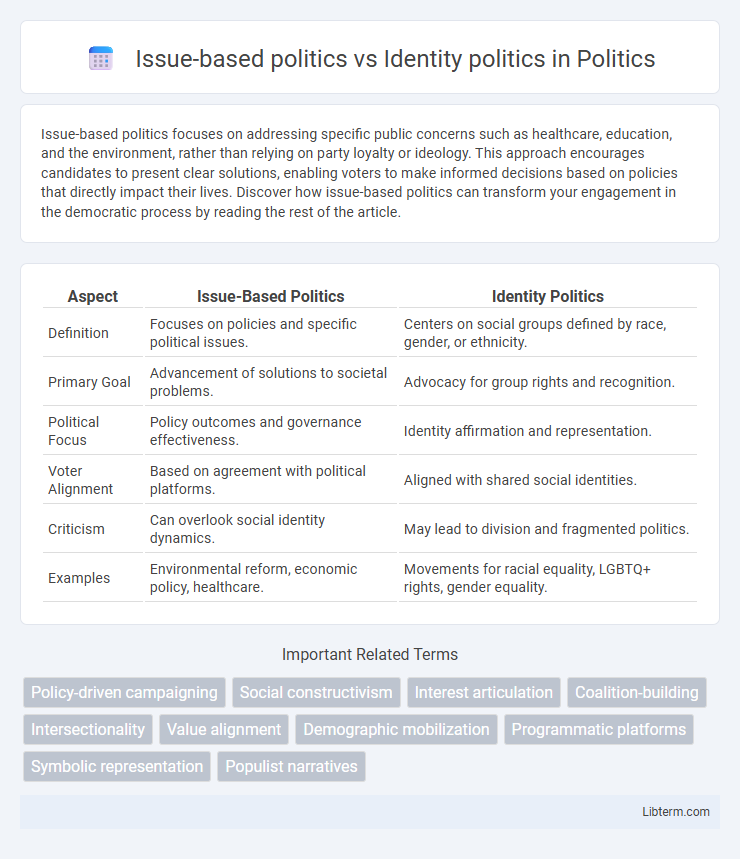
| Aspect | Issue-Based Politics | Identity Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on policies and specific political issues. | Centers on social groups defined by race, gender, or ethnicity. |
| Primary Goal | Advancement of solutions to societal problems. | Advocacy for group rights and recognition. |
| Political Focus | Policy outcomes and governance effectiveness. | Identity affirmation and representation. |
| Voter Alignment | Based on agreement with political platforms. | Aligned with shared social identities. |
| Criticism | Can overlook social identity dynamics. | May lead to division and fragmented politics. |
| Examples | Environmental reform, economic policy, healthcare. | Movements for racial equality, LGBTQ+ rights, gender equality. |
Introduction to Issue-Based and Identity Politics
Issue-based politics centers on policy debates and specific legislative agendas that directly impact social, economic, and environmental outcomes. Identity politics emphasizes the experiences and rights of particular groups defined by race, gender, ethnicity, or sexual orientation, shaping political alignment through shared social identities. Both frameworks influence voter behavior and party strategies, yet they diverge in focus between policy substance and group representation.
Defining Issue-Based Politics
Issue-based politics centers on addressing specific policy concerns such as healthcare, economic reform, and climate change by prioritizing pragmatic solutions over group affiliations. This approach emphasizes objective debate, evidence-driven decision-making, and cross-partisan collaboration to tackle societal challenges effectively. By focusing on concrete problems rather than identity markers like race, gender, or ethnicity, issue-based politics aims to unify diverse populations around shared goals.
Understanding Identity Politics
Identity politics centers on the shared experiences and social identities of groups based on race, gender, sexuality, or ethnicity, influencing political behavior and policy preferences. It emphasizes representation and recognition of systemic inequalities, shaping collective action around cultural and social identity markers. Understanding identity politics requires analyzing how these identity factors intersect with power structures and impact civic engagement and policy debates.
Historical Evolution of Political Approaches
Issue-based politics emerged prominently during the Enlightenment, emphasizing policy solutions, rational debate, and governance focused on economic, social, and legal reforms. Identity politics gained momentum in the late 20th century, rooted in civil rights movements that spotlighted race, gender, ethnicity, and cultural identity as central to political representation and advocacy. The historical evolution reflects a shift from collective policy-driven agendas to more personalized, group-specific demands shaping contemporary political landscapes.
Key Differences Between Issue-Based and Identity Politics
Issue-based politics centers on specific policy concerns such as healthcare, economy, and education, focusing debates on practical solutions and legislative outcomes. Identity politics emphasizes group affiliations like race, gender, ethnicity, or religion, advocating for the rights and recognition of particular social groups. The key difference lies in issue-based politics addressing universal policy matters, while identity politics prioritizes social identities and collective experiences.
Advantages of Issue-Based Politics
Issue-based politics prioritizes policy solutions and pragmatic problem-solving, promoting informed decision-making that directly addresses societal challenges such as healthcare, education, and economic inequality. This approach encourages collaboration across diverse groups by focusing on common goals rather than personal or group identities, enhancing political stability and effective governance. Emphasizing issues reduces polarization and helps voters evaluate candidates based on their platforms and track records, leading to more accountable and transparent democratic processes.
Benefits and Criticisms of Identity Politics
Identity politics empowers marginalized groups by amplifying their unique experiences and fostering solidarity for social justice movements. Critics argue it can lead to fragmentation, prioritizing group identity over shared societal goals and potentially exacerbating divisions. Benefits include increased political representation and policy focus on specific community needs, while criticisms center on limiting broader coalition-building and dialogue.
Impact on Democratic Participation
Issue-based politics emphasizes policy debates and promotes informed voting, leading to higher-quality democratic participation by encouraging citizens to engage with substantive challenges. Identity politics centers on social group affiliations, which can mobilize marginalized communities but may also fragment the electorate and polarize political discourse. The balance between these approaches shapes voter turnout, political representation, and the overall health of democratic institutions.
Case Studies: Global Examples
Issue-based politics centers on policy debates in countries like Germany, where coalition governments prioritize economic reforms and climate change policies. Identity politics prominently shapes electoral outcomes in the United States, exemplified by the impact of race and gender on voter mobilization in the 2020 presidential election. In India, identity politics intertwines with caste and religion, influencing regional party dominance and legislative agendas across states like Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
Future Trends in Political Engagement
Future trends in political engagement indicate a growing emphasis on issue-based politics as voters increasingly prioritize policy solutions over identity affiliations. Digital platforms enable targeted communication of specific policy issues, fostering informed debates around economic, environmental, and social challenges. However, identity politics remains influential in mobilizing marginalized communities, suggesting a hybrid approach will shape upcoming election strategies.
Issue-based politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com