Sovereignty issues arise when a nation's authority over its territory or governance is challenged by external forces or internal conflicts. These disputes often involve legal, political, and cultural dimensions that impact national identity and international relations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how sovereignty conflicts shape global dynamics and affect your country's sovereignty.
Table of Comparison
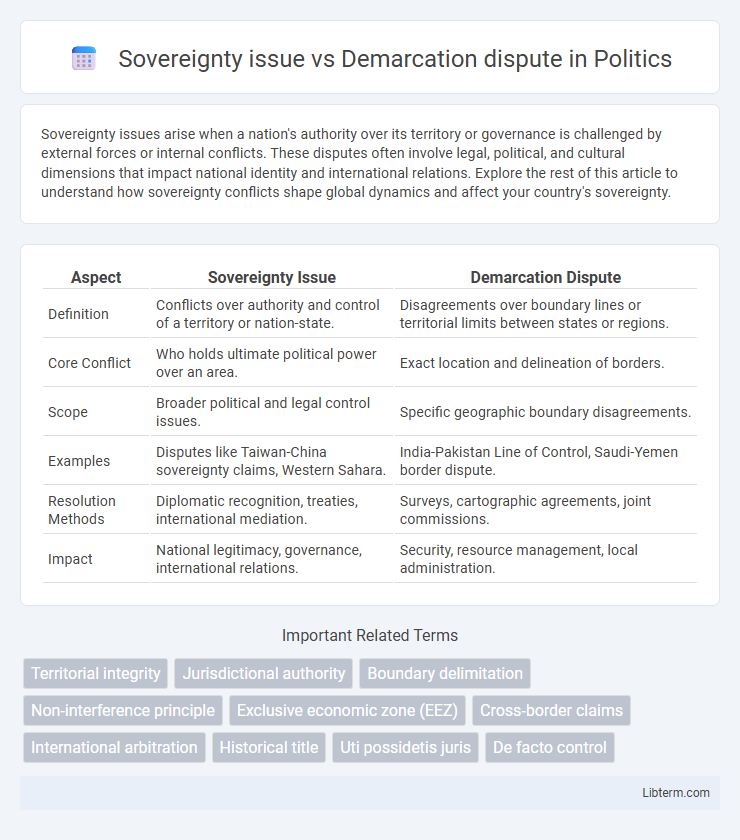
| Aspect | Sovereignty Issue | Demarcation Dispute |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conflicts over authority and control of a territory or nation-state. | Disagreements over boundary lines or territorial limits between states or regions. |
| Core Conflict | Who holds ultimate political power over an area. | Exact location and delineation of borders. |
| Scope | Broader political and legal control issues. | Specific geographic boundary disagreements. |
| Examples | Disputes like Taiwan-China sovereignty claims, Western Sahara. | India-Pakistan Line of Control, Saudi-Yemen border dispute. |
| Resolution Methods | Diplomatic recognition, treaties, international mediation. | Surveys, cartographic agreements, joint commissions. |
| Impact | National legitimacy, governance, international relations. | Security, resource management, local administration. |
Understanding Sovereignty: Definition and Context
Sovereignty refers to the supreme authority of a state to govern itself without external interference, encompassing political independence and control over a defined territory. It involves the legal and recognized right to exercise power within borders, often grounded in international law and historical claims. Understanding sovereignty is crucial in distinguishing it from demarcation disputes, which specifically address disagreements over the precise location of boundary lines between states rather than the legitimacy of territorial ownership itself.
What is a Demarcation Dispute?
A demarcation dispute refers to a conflict arising from the unclear or contested boundaries between distinct territories, regions, or administrative zones, often triggered by ambiguous or overlapping border definitions. Unlike sovereignty issues that question which state holds ultimate authority over a territory, demarcation disputes specifically address the precise lines that separate jurisdictions or property holdings. Accurate demarcation is essential for preventing conflicts, ensuring legal clarity, and managing resource distribution along borders.
Key Differences: Sovereignty Issues vs Demarcation Disputes
Sovereignty issues involve the fundamental question of which state has ultimate authority over a territory, often rooted in historical claims, national identity, and legal recognition under international law. Demarcation disputes center on the precise drawing and marking of boundaries already agreed upon by neighboring states but contested due to geographical ambiguities or differing interpretations of treaty language. Unlike sovereignty conflicts, demarcation disputes typically do not challenge state ownership but focus on the exact line separating territories.
Historical Evolution of Sovereignty Claims
Sovereignty claims often trace back centuries, rooted in historical treaties, colonial legacies, and evolving state boundaries that define authority over territories. Demarcation disputes arise when physical boundaries on the ground, such as rivers or mountain ranges, lack clear or agreed-upon markers, complicating the enforcement of sovereignty. The historical evolution of sovereignty claims influences contemporary demarcation conflicts by embedding legal, cultural, and political rights into territorial assertions.
Causes and Triggers of Border Demarcation Disputes
Border demarcation disputes primarily arise from unclear or poorly defined historical treaties, ambiguous cartographic representations, and lack of physical markers on the ground, which create overlapping claims between neighboring states. Sovereignty issues intensify when strategic resources, such as oil reserves, water bodies, or mineral-rich lands, are located within contested border areas, fueling nationalistic sentiments and government interests. Trigger events often include unilateral infrastructure projects, military patrols, or administrative actions perceived as encroachments, which escalate tensions and transform latent disagreements into active conflicts.
Case Studies: Prominent Sovereignty Conflicts
Sovereignty issues involve claims of ultimate authority over a territory, exemplified by the Kashmir conflict between India and Pakistan, where both nations assert exclusive control. Demarcation disputes revolve around disagreements on the precise boundary lines, as seen in the Ethiopia-Eritrea border conflict, which centered on unclear territorial delimitations despite agreed sovereignty. These prominent cases highlight how sovereignty conflicts often escalate when demarcation remains unresolved, impacting regional stability and international law enforcement.
International Law: Treaties and Principles Governing Boundaries
Sovereignty issues and demarcation disputes in international law revolve around the interpretation and implementation of treaties and established principles governing territorial boundaries. Treaties serve as binding legal instruments that define state boundaries, while principles such as uti possidetis juris, pacta sunt servanda, and effective control guide the resolution of conflicting claims. International courts and arbitration panels often rely on historical treaties, cartographic evidence, and the conduct of states to determine sovereignty and settle demarcation disputes.
Diplomatic Approaches to Resolving Disputes
Diplomatic approaches to resolving sovereignty issues and demarcation disputes often involve bilateral negotiations, confidence-building measures, and third-party mediation to establish mutually acceptable boundaries. These methods prioritize peaceful dialogue, legal frameworks such as international treaties, and adherence to principles of international law to prevent escalation. Engaging regional organizations and international courts can further legitimize solutions and promote long-term stability in contested territories.
The Impact on Local Populations and Economies
Sovereignty issues and demarcation disputes significantly affect local populations through restricted access to resources and heightened security tensions, often resulting in disrupted livelihoods and increased displacement. Economies in contested regions suffer from investment uncertainties, trade interruptions, and damaged infrastructure, which hinder sustainable development and exacerbate poverty levels. Effective resolution mechanisms directly contribute to stabilized communities, revitalized economic activities, and improved governance at the local level.
Future Trends: Managing and Preventing Border Disputes
Future trends in managing sovereignty issues and demarcation disputes emphasize the integration of advanced geospatial technologies such as satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for precise border mapping. Implementation of multilateral diplomatic frameworks and international legal mechanisms, including arbitration through the International Court of Justice (ICJ), demonstrates increasing effectiveness in preventing escalations. Enhanced regional cooperation and real-time data sharing platforms are expected to promote transparency and proactive conflict resolution among neighboring states.
Sovereignty issue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com