Social democracy promotes a political and economic system where social justice is achieved through democratic means, balancing market capitalism with government intervention to ensure equal opportunities and social welfare. It emphasizes policies like progressive taxation, universal healthcare, and labor rights to create a fairer society while maintaining individual freedoms. Explore this article to understand how social democracy impacts your community and the global political landscape.
Table of Comparison
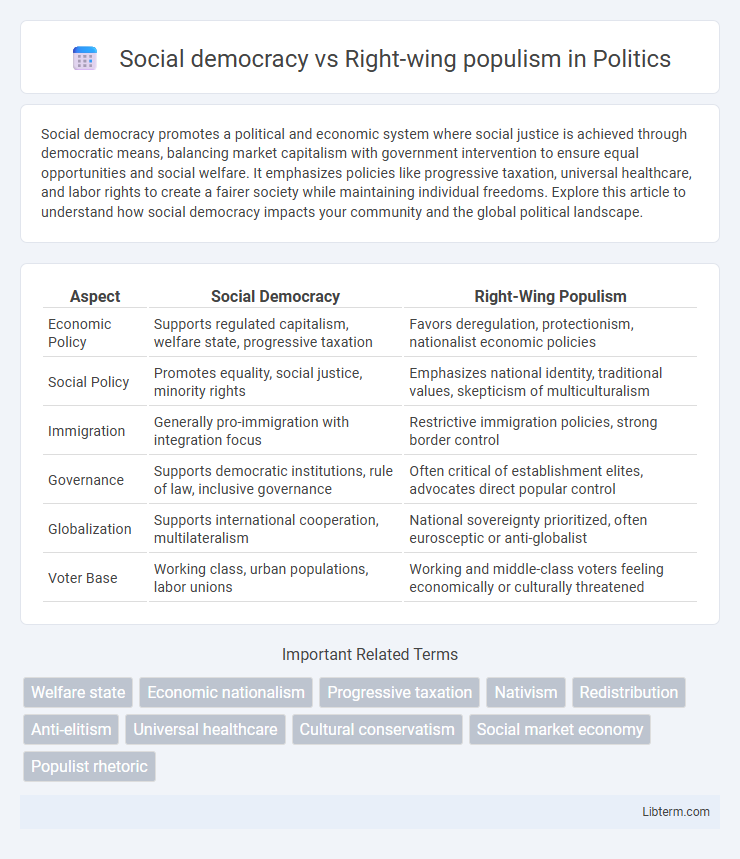
| Aspect | Social Democracy | Right-Wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Policy | Supports regulated capitalism, welfare state, progressive taxation | Favors deregulation, protectionism, nationalist economic policies |
| Social Policy | Promotes equality, social justice, minority rights | Emphasizes national identity, traditional values, skepticism of multiculturalism |
| Immigration | Generally pro-immigration with integration focus | Restrictive immigration policies, strong border control |
| Governance | Supports democratic institutions, rule of law, inclusive governance | Often critical of establishment elites, advocates direct popular control |
| Globalization | Supports international cooperation, multilateralism | National sovereignty prioritized, often eurosceptic or anti-globalist |
| Voter Base | Working class, urban populations, labor unions | Working and middle-class voters feeling economically or culturally threatened |
Defining Social Democracy and Right-Wing Populism
Social democracy is a political ideology advocating for a balance between market capitalism and social welfare, promoting policies such as universal healthcare, workers' rights, and income redistribution to achieve social justice and economic equality. Right-wing populism emphasizes nationalism, anti-immigration policies, and skepticism toward globalism, often appealing to popular discontent by prioritizing cultural identity and perceived threats to traditional values. Both ideologies diverge fundamentally in their approach to governance, social inclusivity, and economic management, shaping distinct political landscapes worldwide.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Social democracy emerged in the late 19th century as a response to industrial capitalism, advocating for social justice, workers' rights, and democratic socialism through gradual reforms. Right-wing populism traces its roots to early 20th-century nationalist and conservative movements, emphasizing nativism, anti-elitism, and traditional values amid economic or cultural crises. Both ideologies have evolved by adapting to contemporary political, economic, and social challenges, influencing global electoral landscapes and policy debates.
Core Ideological Principles
Social democracy centers on social justice, economic equality, and welfare state principles, advocating for government intervention to reduce inequality and provide universal social services. Right-wing populism emphasizes nationalism, anti-elitism, and strict immigration controls, often promoting traditional cultural values and skepticism toward globalization. These core ideological principles reflect fundamentally different views on governance, social cohesion, and economic policy.
Economic Policies Compared
Social democracy advocates for a mixed economy emphasizing social welfare programs, progressive taxation, and government intervention to reduce inequality and ensure public services. Right-wing populism promotes free-market principles with lower taxes, deregulation, and protectionist measures aimed at benefiting native industries and reducing immigration's economic impact. The economic policies of social democracy focus on wealth redistribution and social safety nets, whereas right-wing populism prioritizes national economic sovereignty and market-driven growth.
Social Policies and Welfare Approaches
Social democracy emphasizes expansive social policies and welfare programs aimed at reducing inequality through progressive taxation, universal healthcare, and comprehensive social safety nets, ensuring broad access to education, housing, and social security. Right-wing populism often critiques extensive welfare states, promoting restrictive social policies that prioritize nationalism, immigration control, and reduced government spending on social services to appeal to working-class voters. While social democracy supports inclusivity and redistribution, right-wing populism advocates for welfare chauvinism, limiting benefits primarily to native-born citizens.
Views on Immigration and Multiculturalism
Social democracy advocates for inclusive immigration policies emphasizing integration, social equality, and multiculturalism as strengths that enhance societal cohesion and economic growth. Right-wing populism often promotes restrictive immigration measures, viewing multiculturalism skeptically, framing it as a threat to national identity, social order, and cultural homogeneity. These opposing perspectives highlight contrasting priorities on cultural diversity, social policy, and national sovereignty within contemporary political debates.
Nationalism vs. Internationalism
Social democracy emphasizes internationalism by promoting global cooperation, social justice, and the protection of human rights across borders. Right-wing populism typically focuses on nationalism, advocating for sovereignty, cultural identity, and prioritizing the interests of the native population over international agreements. The tension between social democracy's inclusive global outlook and right-wing populism's exclusivist nationalism shapes contemporary political debates on immigration, trade, and foreign policy.
Political Parties and Influential Leaders
Social democracy is primarily represented by parties such as Germany's Social Democratic Party (SPD) and Sweden's Social Democrats, with influential leaders like Olaf Scholz and Magdalena Andersson advocating for extensive welfare states and progressive taxation policies. Right-wing populism is exemplified by parties like France's National Rally, led by Marine Le Pen, and Italy's League under Matteo Salvini, emphasizing nationalism, anti-immigration stances, and skepticism of the European Union. These political movements shape voter bases with social democrats appealing to working-class and moderate urban populations, while right-wing populists mobilize support through nationalist rhetoric targeting economic insecurities and cultural identity.
Impact on Democracy and Civil Liberties
Social democracy promotes a robust democracy by emphasizing inclusive governance, protection of civil liberties, and social justice through equitable policies and strong institutional checks. Right-wing populism often challenges democratic norms by concentrating power, restricting media freedom, and undermining minority rights, which can lead to weakened civil liberties and democratic backsliding. The contrasting approaches significantly influence the stability and quality of democracy, with social democracy fostering pluralism and rights protection, while right-wing populism may erode democratic institutions and individual freedoms.
Future Trends and Global Influence
Social democracy is expected to evolve with stronger emphasis on inclusive policies, digital governance, and sustainable development, maintaining significant influence in European and Scandinavian regions. Right-wing populism is likely to expand its appeal by leveraging nationalist rhetoric, immigration concerns, and economic protectionism, particularly in North America, Eastern Europe, and parts of Latin America. Global influence will depend on geopolitical shifts, economic crises, and social movements, with social democracy promoting international cooperation while right-wing populism often challenges multilateralism.
Social democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com