A censure motion is a formal statement of disapproval typically issued by a legislative body against a member for misconduct or unethical behavior. It serves as a public reprimand without removing the member from office, emphasizing accountability and ethical standards within governance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a censure motion impacts political careers and legislative processes.
Table of Comparison
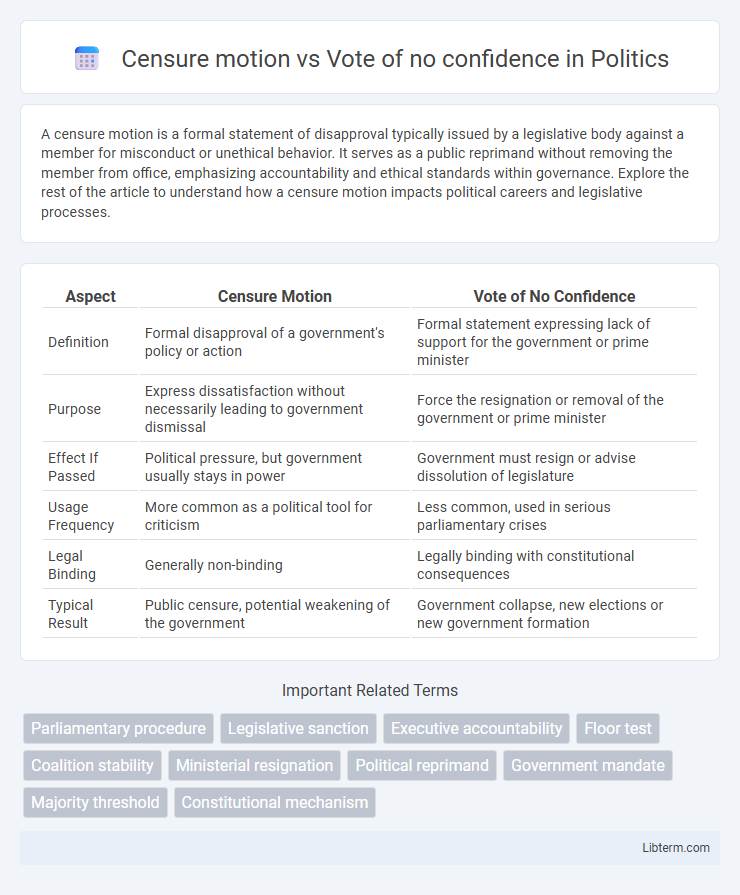
| Aspect | Censure Motion | Vote of No Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal disapproval of a government's policy or action | Formal statement expressing lack of support for the government or prime minister |
| Purpose | Express dissatisfaction without necessarily leading to government dismissal | Force the resignation or removal of the government or prime minister |
| Effect If Passed | Political pressure, but government usually stays in power | Government must resign or advise dissolution of legislature |
| Usage Frequency | More common as a political tool for criticism | Less common, used in serious parliamentary crises |
| Legal Binding | Generally non-binding | Legally binding with constitutional consequences |
| Typical Result | Public censure, potential weakening of the government | Government collapse, new elections or new government formation |
Introduction: Understanding Parliamentary Mechanisms
Censure motions and votes of no confidence are critical parliamentary tools used to express disapproval of government actions or leadership. A censure motion formally condemns specific conduct without necessarily threatening the government's stability, while a vote of no confidence directly challenges the ruling administration's legitimacy, often leading to its resignation or dissolution. These mechanisms play a pivotal role in maintaining accountability and ensuring democratic checks within legislative bodies.
Defining Censure Motion
A censure motion is a formal statement of disapproval passed by a legislative body against a member, typically signaling condemnation without removing them from office. Unlike a vote of no confidence, which challenges the entire government's legitimacy and can lead to its dissolution, a censure targets specific behavior or actions of an individual official. Censure motions serve as a political reprimand that holds members accountable while maintaining their position.
What is a Vote of No Confidence?
A Vote of No Confidence is a parliamentary procedure used to determine whether a government or individual still has the support of the majority in a legislative body. Unlike a censure motion, which is a formal reprimand without direct consequences on governance, a successful Vote of No Confidence typically results in the resignation of the government or dissolution of the assembly. This mechanism ensures accountability and can lead to significant political change by triggering new elections or a change in leadership.
Key Differences Between Censure Motion and Vote of No Confidence
A censure motion is a formal statement of disapproval without removing a member from office, primarily serving as a symbolic reprimand, whereas a vote of no confidence directly challenges the government's legitimacy and can lead to its dissolution or resignation. The censure motion targets individual actions or misconduct, while the vote of no confidence addresses overall government performance and policy failure. Unlike a censure, which does not affect the government's tenure, a successful vote of no confidence triggers political consequences such as cabinet reshuffles or new elections.
Legal Foundations and Constitutional Provisions
A censure motion and a vote of no confidence are parliamentary mechanisms grounded in constitutional provisions to hold the executive accountable. The legal foundation of a censure motion typically involves expressing formal disapproval of a government minister or the executive, without necessitating their removal, whereas a vote of no confidence directly challenges the government's majority and can lead to its dismissal. Constitutional frameworks specify the procedures, majority requirements, and implications for each, ensuring these tools operate within established democratic governance and rule of law principles.
Political Impact of Censure Motions
Censure motions serve as formal expressions of disapproval against government officials, impacting their political credibility and public image without necessarily resulting in their removal from office. Unlike votes of no confidence, which can lead to the government's collapse or resignation, censure motions primarily function to publicly reprimand and pressure officials, influencing political dynamics within legislatures. The political impact of censure motions often includes weakening the authority of targeted officials and shaping party strategies in parliamentary systems.
Consequences of a Vote of No Confidence
A Vote of No Confidence results in the immediate resignation or removal of the government or Prime Minister, often leading to the dissolution of the legislative assembly and triggering fresh elections. This motion directly challenges the legitimacy of the ruling administration, causing political instability and potential shifts in power. In contrast, a Censure motion serves as a formal disapproval without necessitating the government's resignation, primarily damaging reputation rather than authority.
Historical Examples: Censure Motions in Practice
Censure motions have served as formal expressions of disapproval in democratic legislatures, such as the 1917 censure of U.S. President Woodrow Wilson for his handling of World War I policies. Unlike votes of no confidence, which can dissolve governments as seen in the 1979 UK vote leading to Margaret Thatcher's premiership, censure motions typically do not remove officeholders but highlight significant political dissent. Historical cases from countries like India and Australia illustrate how censure motions function as tools for opposition parties to publicly challenge government actions without triggering immediate governmental change.
Notable Votes of No Confidence Worldwide
Votes of no confidence serve as a critical parliamentary tool to express a legislature's disapproval of the government, leading to potential resignation or dissolution; notable examples include the 1979 UK vote that toppled the Labour government and the 2018 Indian vote against the Narendra Modi administration. Unlike censure motions, which formally reprimand but rarely remove leaders, votes of no confidence carry binding consequences that can trigger leadership changes or elections. Countries such as Australia, Canada, and Germany have similarly witnessed impactful no-confidence votes, underscoring their global significance in maintaining governmental accountability.
Conclusion: Significance in Democratic Governance
Censure motions serve as formal expressions of disapproval without necessarily leading to government removal, preserving political stability while ensuring accountability. Vote of no confidence directly challenges the ruling party's legitimacy, potentially triggering government dissolution and new elections, thus reinforcing democratic responsiveness. Both mechanisms are essential in democratic governance for maintaining checks and balances between the legislature and the executive.
Censure motion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com