An unpledged elector is a member of the United States Electoral College who is not committed to voting for a specific presidential or vice-presidential candidate. These electors have the freedom to cast their vote according to personal judgment or political considerations rather than the popular vote results of their state. Learn more about the role and impact of unpledged electors in the U.S. presidential election process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
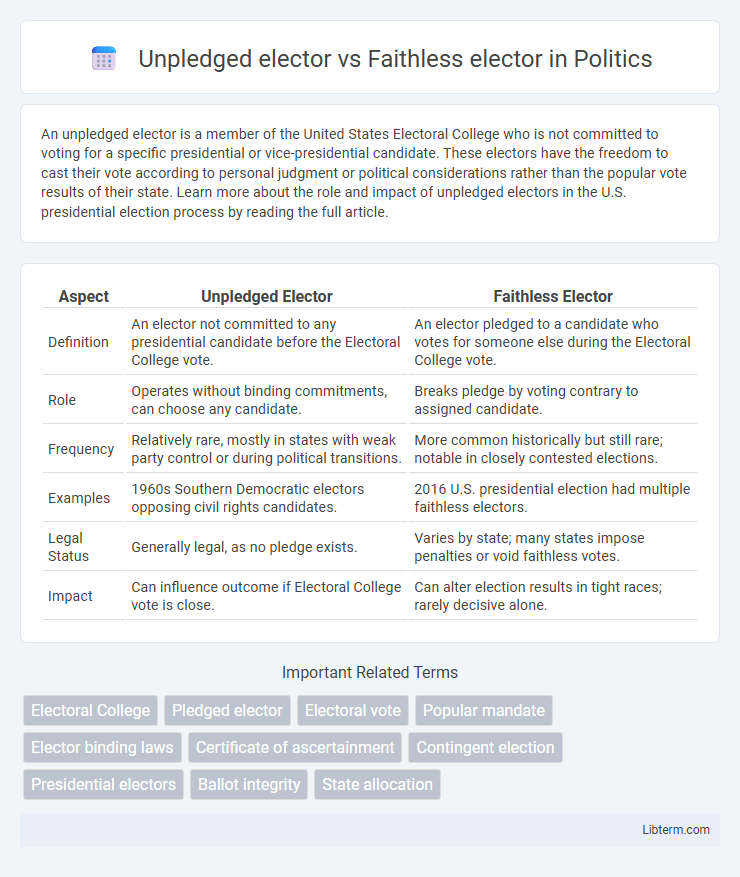
| Aspect | Unpledged Elector | Faithless Elector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An elector not committed to any presidential candidate before the Electoral College vote. | An elector pledged to a candidate who votes for someone else during the Electoral College vote. |
| Role | Operates without binding commitments, can choose any candidate. | Breaks pledge by voting contrary to assigned candidate. |
| Frequency | Relatively rare, mostly in states with weak party control or during political transitions. | More common historically but still rare; notable in closely contested elections. |
| Examples | 1960s Southern Democratic electors opposing civil rights candidates. | 2016 U.S. presidential election had multiple faithless electors. |
| Legal Status | Generally legal, as no pledge exists. | Varies by state; many states impose penalties or void faithless votes. |
| Impact | Can influence outcome if Electoral College vote is close. | Can alter election results in tight races; rarely decisive alone. |
Introduction to Electoral College: Unpledged vs. Faithless Electors
Unpledged electors in the Electoral College exercise independent judgment by not committing to any presidential candidate before the election, often selected in states with complex party dynamics or unique elector selection processes. Faithless electors, by contrast, pledge to support a specific candidate but cast their votes for someone else on the Electoral College voting day, potentially influencing tightly contested elections. Understanding the distinction between unpledged and faithless electors highlights nuances in the U.S. electoral system's function and the potential for unexpected outcomes in presidential elections.
Definitions: Unpledged Elector Explained
An unpledged elector is a member of the Electoral College who is not committed to voting for any specific presidential candidate prior to the election, allowing them to exercise independent judgment on Election Day. This contrasts with faithless electors, who break their pledged commitment by voting for a different candidate than their party's nominee. Unpledged electors often appear in states with party conventions or disputes, reflecting strategic electoral flexibility within the U.S. presidential election system.
Understanding the Faithless Elector
A faithless elector is a member of the U.S. Electoral College who does not vote for the presidential or vice-presidential candidate they pledged to support, differing from an unpledged elector who arrives without a binding commitment. Understanding the faithless elector involves recognizing the legal and political consequences they may face, as some states impose fines or other penalties for deviating from pledged votes. The phenomenon highlights tensions between individual elector discretion and the intentions of the popular vote in presidential elections.
Historical Context of Unpledged Electors
Unpledged electors historically emerged during the mid-20th century, particularly in Southern states resisting national party nominees on civil rights issues, most notably in the 1948 and 1960 presidential elections. These electors operated independently, refusing to commit to any candidate, contrasting with faithless electors who pledge support but later vote contrary to their commitment. The presence of unpledged electors highlighted regional political dissent and influenced electoral outcomes by withholding automatic support from major party candidates.
Notable Cases of Faithless Electors in U.S. History
Faithless electors in U.S. history have occasionally altered the expected Electoral College vote, such as in the 2016 election when seven electors cast ballots for candidates other than their pledged nominees, including cases in Washington, D.C., and Texas. Notable prior examples include the 1976 election, where one faithless elector voted for Ronald Reagan instead of Gerald Ford, and in 1836, when Virginia electors refused to vote for Martin Van Buren, influencing the election outcome. In contrast, unpledged electors are those chosen without a formal commitment to any candidate, seen notably in the 1960s Southern states to oppose civil rights platforms, reflecting distinct strategic roles in Electoral College dynamics.
Legal Consequences: State Laws on Elector Actions
Unpledged electors are permitted to vote for any candidate without violating state laws since they were not bound to any nominee when selected, whereas faithless electors break explicit pledges and may face penalties under state regulations, including fines or disqualification. Several states have implemented laws to penalize or replace faithless electors to uphold the integrity of the Electoral College vote, with the Supreme Court affirming states' rights to enforce such measures in Chiafalo v. Washington (2020). Legal consequences for faithless electors vary by jurisdiction but generally involve financial sanctions or removal and replacement by a substitute elector.
Impacts on Presidential Elections
Unpledged electors, often aligned with a political party without a commitment to any candidate, can influence presidential elections by creating uncertainty in the Electoral College outcome, potentially forcing contingent elections in the House of Representatives. Faithless electors deviate from their pledged vote, which can alter state results and challenge the legitimacy of the electoral process, though historically, their impact has been limited and rarely decisive. Both types undermine the predictability of presidential elections, highlighting vulnerabilities in the Electoral College system and prompting discussions on reform.
Public Perception and Media Coverage
Public perception of unpledged electors often views them as independent agents acting on principle, attracting nuanced media coverage that highlights their potential to influence elections in unpredictable ways. Faithless electors, who break their promise to vote for their party's candidate, face more negative media scrutiny, portrayed as betraying the democratic process and undermining voter trust. Media narratives emphasize faithless electors' rarity and controversy, whereas unpledged electors are discussed in the context of complex electoral dynamics and historical precedent.
Reform Proposals and Ongoing Debates
Reform proposals targeting unpledged electors emphasize binding Electoral College votes to state popular vote outcomes to reduce unpredictability, while suggestions for faithless electors include penalties or disqualification to uphold voter intent. Ongoing debates center around constitutional challenges and the balance between elector independence and democratic accountability, with some advocating for abolishing the Electoral College in favor of direct popular elections. Legislative efforts like the National Popular Vote Interstate Compact seek to address these issues by ensuring electors reflect the nationwide popular vote without violating states' rights.
Conclusion: The Future of the U.S. Electoral System
Unpledged electors and faithless electors both highlight vulnerabilities within the U.S. Electoral College system that challenge the direct reflection of voter intentions. As debates intensify over electoral reforms, future changes may include eliminating these elector roles to ensure a more consistent and representative presidential election outcome. Strengthening safeguards against elector unpredictability is essential for preserving electoral integrity and public trust in democracy.
Unpledged elector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com