A single-issue party focuses its entire political agenda on one specific topic or cause, seeking to influence policy and public opinion in that area. These parties often arise when traditional political groups overlook or underrepresent critical concerns. Discover how single-issue parties impact political landscapes and shape voter choices in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
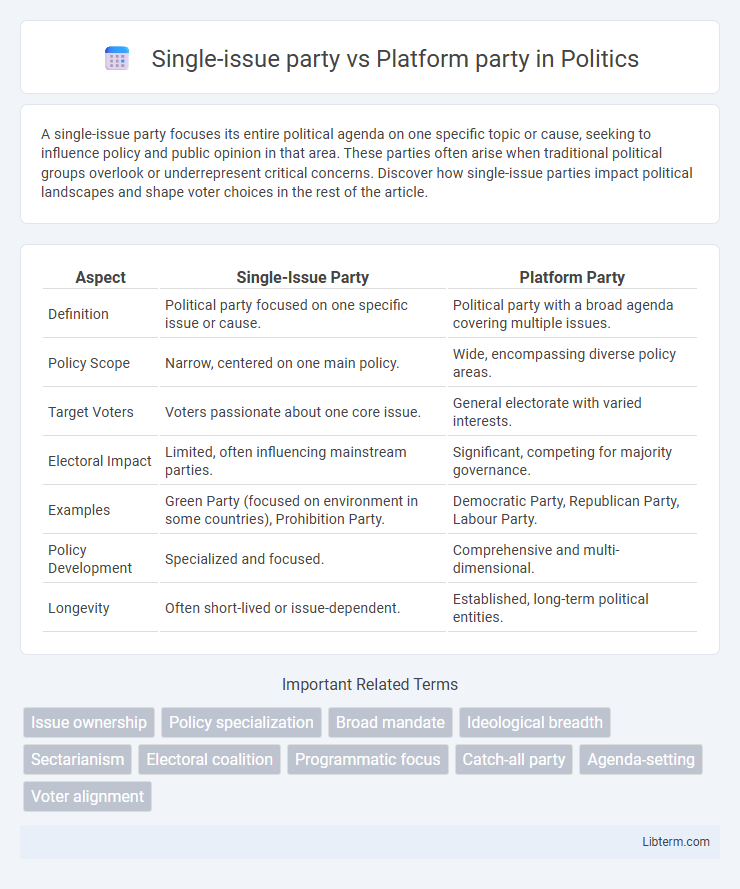
| Aspect | Single-Issue Party | Platform Party |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political party focused on one specific issue or cause. | Political party with a broad agenda covering multiple issues. |
| Policy Scope | Narrow, centered on one main policy. | Wide, encompassing diverse policy areas. |
| Target Voters | Voters passionate about one core issue. | General electorate with varied interests. |
| Electoral Impact | Limited, often influencing mainstream parties. | Significant, competing for majority governance. |
| Examples | Green Party (focused on environment in some countries), Prohibition Party. | Democratic Party, Republican Party, Labour Party. |
| Policy Development | Specialized and focused. | Comprehensive and multi-dimensional. |
| Longevity | Often short-lived or issue-dependent. | Established, long-term political entities. |
Introduction to Political Party Types
Single-issue parties concentrate exclusively on one specific policy area, such as environmental protection or tax reform, aiming to influence legislation in that domain. Platform parties represent a broad spectrum of policy positions, developing comprehensive agendas that address multiple societal issues, including healthcare, education, and economic development. Understanding the distinction between these political party types helps clarify their strategies in elections and governance.
Defining Single-Issue Parties
Single-issue parties focus exclusively on one specific topic, such as environmental protection or tax reform, aiming to influence policy in that particular area. Unlike platform parties, which address a broad range of political issues and offer comprehensive policy agendas, single-issue parties prioritize depth over breadth in their political goals. These parties often emerge to raise public awareness and pressure larger parties to adopt their core concerns.
Understanding Platform Parties
Platform parties are political organizations that develop comprehensive policy agendas addressing multiple social, economic, and political issues to appeal to a broad electorate. Unlike single-issue parties which concentrate on one specific cause, platform parties structure their policies into coherent platforms that reflect diverse voter interests and aim for sustainable governance. Understanding platform parties involves recognizing their role in shaping legislative priorities and coalition-building within multi-party systems.
Historical Examples of Single-Issue Parties
Single-issue parties, such as the Prohibition Party in the United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, focused exclusively on banning alcohol, influencing national policy despite limited electoral success. Another example is the British Anti-Corn Law League, which concentrated on repealing tariffs on grain, playing a pivotal role in shaping trade laws. In contrast, platform parties encompass broad policy agendas, aiming to address multiple issues to attract diverse voter bases.
Notable Platform Parties in History
Notable platform parties in history, such as the Democratic and Republican parties in the United States, have consistently offered comprehensive policy agendas addressing a wide range of social, economic, and foreign issues to appeal to diverse voter bases. Unlike single-issue parties, like the Prohibition Party focused solely on banning alcohol, platform parties develop multi-faceted solutions that evolve with changing political landscapes, enabling sustained electoral success and governance. This strategic breadth allows platform parties to build coalitions, influence legislation broadly, and maintain relevance across multiple election cycles.
Strengths of Single-Issue Parties
Single-issue parties excel in mobilizing voters passionate about a specific cause, creating heightened awareness and focused advocacy that can influence public policy. Their clear, concise agenda allows for targeted campaigning and resource allocation, often leading to significant impact within niche political arenas. These parties can act as catalysts for broader political change by pressuring larger platform parties to adopt their core issues.
Advantages of Platform Parties
Platform parties offer a comprehensive policy agenda addressing multiple issues, attracting a broader voter base and increasing electoral viability. Their inclusive approach facilitates coalition-building and long-term influence within legislative bodies. By integrating diverse interests, platform parties enhance governance stability and policy continuity.
Challenges Faced by Single-Issue Parties
Single-issue parties often struggle with limited voter appeal due to their narrow focus, making it difficult to address the diverse interests of the electorate. Their lack of comprehensive policy platforms limits coalition-building opportunities and reduces influence in parliamentary systems. These parties frequently face challenges in sustaining long-term relevance and expanding beyond their core issue in competitive political environments.
Limitations of Platform Parties
Platform parties often face the challenge of diluting their core message to accommodate diverse voter interests, leading to compromised policy stances. Their broad agendas can result in internal conflicts, making decisive action difficult and hindering effective governance. This diffusion of focus sometimes causes voter disengagement, as constituents struggle to identify clear priorities within the party platform.
Impact on the Political Landscape
Single-issue parties often drive public attention toward specific causes, influencing larger parties to adopt or address niche concerns, thereby reshaping political agendas. Platform parties present comprehensive policy solutions across multiple issues, appealing to broader electorates and stabilizing governance through diversified support. Together, these party types impact political landscapes by balancing focused advocacy with multidimensional policymaking, altering voter dynamics and legislative priorities.
Single-issue party Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com