The executive council serves as the central decision-making body in many organizations and governments, responsible for implementing policies and overseeing administrative functions. It ensures that strategic goals are met and operational effectiveness is maintained. Explore the rest of the article to understand how an executive council can impact your organization's success and governance.
Table of Comparison
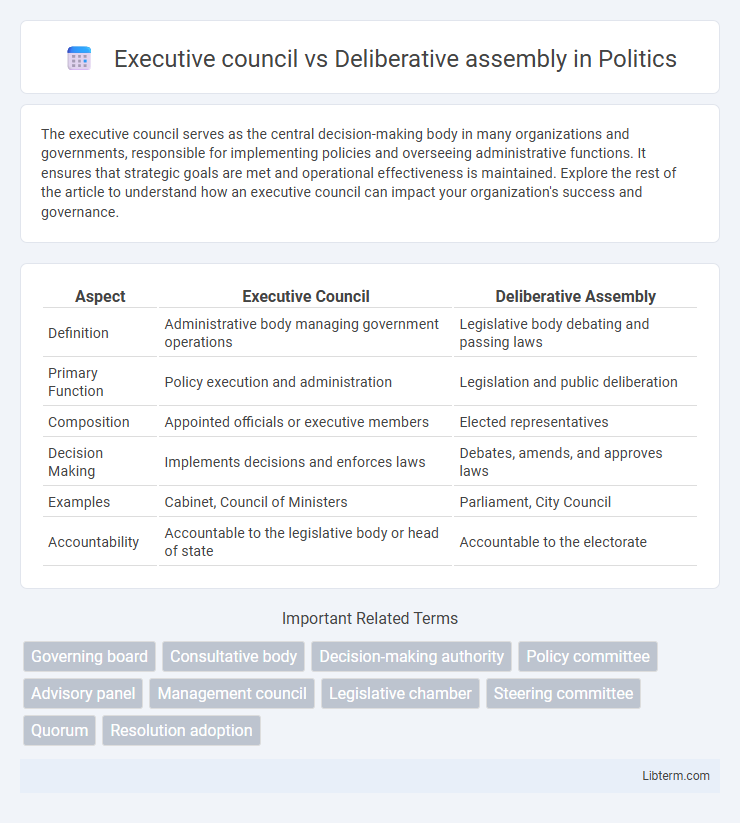
| Aspect | Executive Council | Deliberative Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Administrative body managing government operations | Legislative body debating and passing laws |
| Primary Function | Policy execution and administration | Legislation and public deliberation |
| Composition | Appointed officials or executive members | Elected representatives |
| Decision Making | Implements decisions and enforces laws | Debates, amends, and approves laws |
| Examples | Cabinet, Council of Ministers | Parliament, City Council |
| Accountability | Accountable to the legislative body or head of state | Accountable to the electorate |
Introduction: Executive Council vs. Deliberative Assembly
An Executive Council functions as the central decision-making body responsible for implementing policies and overseeing government operations, often comprising key ministers or officials. A Deliberative Assembly primarily serves as a forum for discussion, debate, and formulation of legislative proposals, representing a broader constituency of elected representatives. Distinguishing features include the Executive Council's focus on execution and administration versus the Deliberative Assembly's emphasis on legislative deliberation and consensus-building.
Definitions and Core Concepts
An Executive council is a governing body responsible for implementing policies and managing administrative functions within an organization or government, typically composed of key officials or executives. A Deliberative assembly is a formal gathering of members who debate, discuss, and make decisions through voting, serving as the primary legislative or decision-making forum. The core concept of an Executive council emphasizes execution and administration, while a Deliberative assembly focuses on discussion, representation, and collective decision-making.
Historical Background and Evolution
The Executive Council, rooted in colonial administrations during the 17th and 18th centuries, primarily functioned as an advisory body to the governor, evolving to gain limited legislative and administrative powers. Deliberative assemblies originated from medieval European parliaments, expanding significantly post-Enlightenment to embody representative democracy and broader legislative authority. Historical reforms in the 19th and 20th centuries further transformed these bodies, delineating the Executive Council's role in executive governance from the Deliberative Assembly's legislative and debating functions.
Structure and Composition Comparison
Executive councils typically consist of a small group of senior officials or ministers responsible for policy implementation and administrative decisions, often appointed by the head of government. Deliberative assemblies feature a larger, more diverse membership elected or selected to represent various constituencies, allowing for broad debate and decision-making on legislative matters. The executive council operates with a hierarchical structure focusing on executive authority, while a deliberative assembly functions through collective discussion and consensus-building among its members.
Primary Functions and Responsibilities
The Executive Council primarily implements policies, manages government operations, and makes administrative decisions to ensure effective governance. The Deliberative Assembly focuses on debating legislation, representing constituents, and making decisions through collective discussion to shape laws and public policy. While the Executive Council executes approved policies, the Deliberative Assembly serves as the platform for legislative oversight and democratic decision-making.
Decision-Making Processes
The Executive Council typically centralizes decision-making authority, enabling swift implementation of policies through a smaller group of appointed officials, while the Deliberative Assembly emphasizes collective debate and voting among elected representatives, ensuring diverse input and democratic legitimacy. Decision-making in an Executive Council is often streamlined, relying on consensus or majority within a limited membership, contrasted with the Deliberative Assembly's broader participation that can lead to prolonged discussions but more comprehensive consideration of issues. The effectiveness of each body depends on the decision context, with Executive Councils suited for urgent, strategic directives and Deliberative Assemblies ideal for inclusive policy formulation and public accountability.
Leadership and Representative Roles
The Executive council holds concentrated leadership authority, making key administrative decisions and implementing policies within an organization or government. In contrast, a Deliberative assembly emphasizes representative roles, where elected members debate, discuss, and vote on proposals to reflect the interests of their constituencies. Leadership in an Executive council is typically centralized and directive, while a Deliberative assembly fosters collective decision-making through member participation.
Impact on Governance and Policy
The Executive Council centralizes decision-making authority, enabling swift policy implementation but often limiting broader participatory input, which can lead to more streamlined governance yet reduced representational diversity. In contrast, the Deliberative Assembly emphasizes inclusive debate and diverse viewpoints, fostering comprehensive policy outcomes and democratic legitimacy but potentially slowing the decision-making process. Balancing these bodies affects governance efficiency and policy responsiveness, with the Executive Council driving agile actions and the Deliberative Assembly ensuring accountable and transparent government decisions.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Model
The Executive Council model offers streamlined decision-making and centralized leadership, enhancing efficiency in policy implementation but may limit diverse representation and reduce transparency. The Deliberative Assembly promotes inclusive debate and broad participation, fostering democratic legitimacy and diverse perspectives, yet it can result in slower decision processes and potential deadlock. Balancing the Executive Council's decisiveness with the assembly's inclusivity remains a critical challenge in governance structures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Model
Selecting the appropriate governance model depends on the organization's size, decision-making speed, and scope of authority required. Executive councils offer streamlined, efficient decision-making ideal for smaller, focused groups needing quick actions. Deliberative assemblies provide broader representation and thorough debate, better suited for larger organizations prioritizing inclusivity and diversity of opinion.
Executive council Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com