Impeachment is a formal process in which a government official, including the president, is accused of unlawful activity, potentially leading to removal from office. It serves as a critical check and balance within the political system, ensuring accountability and preserving democratic integrity. Explore the detailed steps and implications of impeachment to understand its impact on Your government.
Table of Comparison
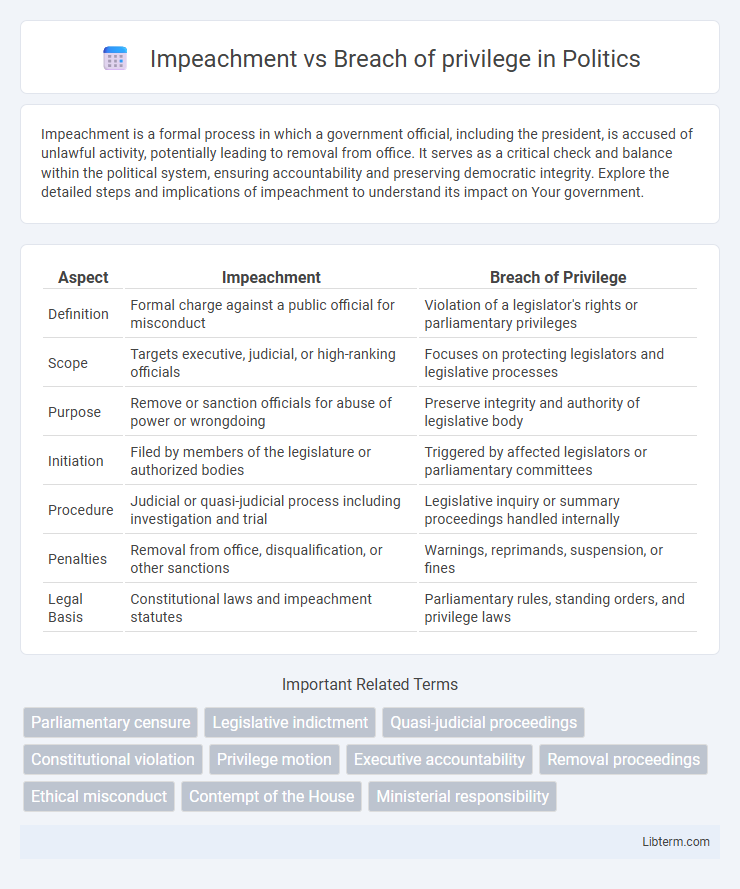
| Aspect | Impeachment | Breach of Privilege |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal charge against a public official for misconduct | Violation of a legislator's rights or parliamentary privileges |
| Scope | Targets executive, judicial, or high-ranking officials | Focuses on protecting legislators and legislative processes |
| Purpose | Remove or sanction officials for abuse of power or wrongdoing | Preserve integrity and authority of legislative body |
| Initiation | Filed by members of the legislature or authorized bodies | Triggered by affected legislators or parliamentary committees |
| Procedure | Judicial or quasi-judicial process including investigation and trial | Legislative inquiry or summary proceedings handled internally |
| Penalties | Removal from office, disqualification, or other sanctions | Warnings, reprimands, suspension, or fines |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional laws and impeachment statutes | Parliamentary rules, standing orders, and privilege laws |
Introduction: Understanding Impeachment and Breach of Privilege
Impeachment is a formal process used to charge and potentially remove public officials for misconduct, typically involving serious violations like corruption or abuse of power. Breach of privilege refers to actions that obstruct or disrespect the authority and functioning of a legislative body or its members, such as contempt or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. Both concepts serve to uphold accountability and integrity within government institutions but apply to different scopes of official conduct and legislative protections.
Defining Impeachment: Scope and Application
Impeachment is a constitutional process designed to address serious misconduct by high-ranking government officials, including the president, vice president, and federal judges, by charging them with offenses like treason, bribery, or other high crimes and misdemeanors. The scope of impeachment extends to removing officials from office and barring them from future public service, serving as a critical mechanism of checks and balances within the government. Unlike breach of privilege, which pertains to violations of parliamentary privileges affecting legislative proceedings, impeachment involves formal charges and trials conducted primarily by legislative bodies, such as the House of Representatives and the Senate in the United States.
What Constitutes Breach of Privilege?
Breach of privilege occurs when there is an act or omission that obstructs or impedes the functioning and authority of a legislative body or its members, such as refusing to answer questions, contemptuous behavior, or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. It primarily involves violations against the rights and immunities of lawmakers, ensuring their independence and effectiveness in fulfilling legislative duties. Unlike impeachment, which addresses misconduct or criminal acts by public officials, breach of privilege specifically protects parliamentary privileges and procedural integrity.
Legal Framework: Impeachment vs Breach of Privilege
Impeachment is governed by constitutional provisions outlining the removal process of public officials for crimes, misconduct, or violations of oath, emphasizing procedural due process within legislative bodies. Breach of privilege, rooted in parliamentary law, addresses offenses that obstruct or disrespect the authority and dignity of legislative institutions, typically handled internally by the same body without judicial intervention. The distinct legal frameworks differentiate impeachment as a formal judicial-political mechanism, while breach of privilege serves as an immediate disciplinary tool ensuring legislative order and authority.
Key Differences Between Impeachment and Breach of Privilege
Impeachment is a formal process used to charge and potentially remove public officials for misconduct, primarily involving crimes or abuses of power, while a breach of privilege refers to acts that violate the rights and immunities granted to members of a legislative body. Impeachment involves judicial procedures and requires evidence of serious offenses, whereas breach of privilege typically triggers internal disciplinary measures within the legislature without criminal prosecution. The scope of impeachment encompasses constitutional violations, while breach of privilege centers on protecting legislative functions and maintaining order within parliamentary proceedings.
Procedures Involved in Impeachment
Impeachment procedures involve a formal process initiated in the House of Representatives with the filing of a verified complaint, followed by a preliminary investigation by the House Committee on Justice. Upon determination of probable cause, the Committee drafts articles of impeachment, which the House votes on; a majority vote is required to impeach. The Senate then conducts a trial presided over by the Chief Justice, where a two-thirds vote is necessary to convict and remove the official from office.
Steps in Addressing a Breach of Privilege
Addressing a breach of privilege begins with the affected member raising the issue through a point of order or motion in the legislative chamber. The matter is then referred to the Committee on Privileges, which conducts an investigation and gathers evidence to determine the severity and intent of the breach. Depending on the committee's findings, the legislative body can impose sanctions ranging from reprimands to suspension, ensuring the protection of legislative integrity and member rights.
Case Studies: Historical Examples
The impeachment of President Andrew Johnson in 1868 exemplifies a prominent case study where constitutional authority was tested over alleged breaches of law and policy during Reconstruction. In contrast, the breach of privilege case involving Member of Parliament Vijay Mallya in India highlights parliamentary privilege invoked to address alleged contempt and misconduct within legislative processes. These historical examples underscore differing legal frameworks and institutional responses to accountability in executive and legislative branches.
Implications for Public Officials and Institutions
Impeachment serves as a constitutional mechanism to hold public officials accountable for serious misconduct, ensuring the protection of democratic governance and public trust. Breach of privilege involves violations of legislative authority or disruption of parliamentary proceedings, which can undermine institutional integrity and the effective functioning of government bodies. Both processes have significant implications, with impeachment leading to potential removal from office and breach of privilege triggering disciplinary actions that preserve legislative decorum and authority.
Conclusion: Assessing Accountability and Democratic Oversight
Impeachment serves as a constitutional mechanism for holding high-ranking officials accountable through a formal judicial process, ensuring democratic oversight by addressing serious misconduct. Breach of privilege pertains to violations of parliamentary rights and privileges, safeguarding legislative integrity and enabling swift disciplinary measures within the legislative body. Both mechanisms reinforce accountability but operate at different institutional levels to maintain the balance of power and protect democratic governance.
Impeachment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com