Integration streamlines workflows by connecting disparate systems and applications into a unified platform, enhancing data consistency and operational efficiency. It enables real-time information sharing, reducing manual errors and improving decision-making processes across your organization. Discover how effective integration can transform your business operations by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
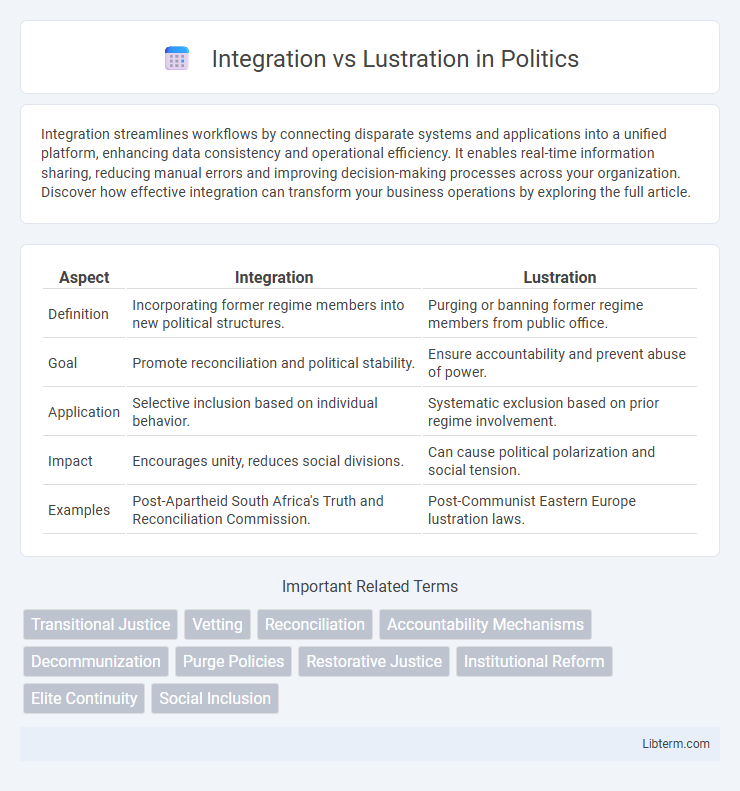
| Aspect | Integration | Lustration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating former regime members into new political structures. | Purging or banning former regime members from public office. |
| Goal | Promote reconciliation and political stability. | Ensure accountability and prevent abuse of power. |
| Application | Selective inclusion based on individual behavior. | Systematic exclusion based on prior regime involvement. |
| Impact | Encourages unity, reduces social divisions. | Can cause political polarization and social tension. |
| Examples | Post-Apartheid South Africa's Truth and Reconciliation Commission. | Post-Communist Eastern Europe lustration laws. |
Understanding Integration and Lustration: Definitions and Context
Integration involves incorporating individuals or groups into existing social, political, or organizational frameworks to promote unity and cooperation, while lustration refers to the process of purging or disqualifying certain people, often former regime affiliates, from positions of power to prevent abuses or conflicts of interest. Understanding integration requires analyzing mechanisms like reconciliation, inclusion policies, and transitional justice that aim for social harmony and stability. Lustration is contextualized within post-authoritarian or post-conflict societies where it serves as a tool for accountability, ensuring transparency and the rule of law during political transformation.
Historical Background: Roots of Integration and Lustration
Integration and lustration have roots in distinct historical contexts reflecting post-conflict societal restoration. Integration originates from post-World War II efforts to rebuild inclusive societies by promoting coexistence and social cohesion among diverse groups. Lustration emerged predominantly in Eastern Europe after the Cold War, involving the systematic vetting and exclusion of former regime collaborators from public office to ensure political transparency and democratic transition.
Key Principles of Integration Policies
Integration policies prioritize inclusive approaches that promote social cohesion by granting equal rights and opportunities to all community members, emphasizing participation, non-discrimination, and cultural recognition. Key principles include fostering mutual respect, facilitating access to education, employment, and public services, and encouraging active civic engagement. These policies seek to build diverse societies where individuals retain their cultural identities while contributing to a shared social framework.
Core Elements of Lustration Processes
Lustration processes primarily involve the systematic vetting and removal of individuals linked to previous regime abuses, focusing on political loyalty and past misconduct to restore public trust. Core elements include thorough background investigations, transparent legal frameworks, and clear criteria for eligibility or exclusion based on documented involvement in repression or corruption. These measures aim to ensure accountability, prevent the recurrence of abuses, and facilitate democratic consolidation within transitional societies.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Integration and Lustration
Case studies of integration and lustration reveal distinct approaches to transitional justice in post-conflict societies. Germany's lustration process after reunification focused on barring former East German Stasi officials from public office, emphasizing accountability and institutional cleansing. In contrast, South Africa's Truth and Reconciliation Commission highlighted integration by promoting forgiveness and national unity, allowing perpetrators to disclose crimes in exchange for amnesty, reflecting divergent global strategies to address past injustices.
Benefits and Challenges: Comparing Integration vs Lustration
Integration promotes societal cohesion by incorporating former regime members into new political, social, and economic systems, fostering reconciliation and stability. Challenges include potential compromises on justice and lingering mistrust among the population, risking incomplete accountability. Lustration enhances transparency and public trust by excluding individuals involved in past abuses but may provoke societal division, bureaucratic delays, and hinder national unity.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Integration and Lustration
Legal and ethical considerations in integration involve ensuring fair representation, protecting human rights, and fostering social cohesion without discriminating against former regime members. Lustration raises challenges related to due process, proportionality, and risk of political retaliation, demanding transparent mechanisms and safeguards against abuses. Balancing justice and reconciliation requires adherence to international legal standards while promoting societal healing and trust in institutions.
Societal Impact: Reconciliation, Justice, and Social Cohesion
Integration promotes long-term social cohesion by encouraging inclusive reconciliation and collective justice, fostering shared community values and trust among diverse groups. Lustration emphasizes accountability through purging individuals linked to past abuses, aiming to deliver justice but risking societal division and hindered reconciliation if applied excessively. Balancing integration and lustration mechanisms is essential to achieve sustainable social harmony and rebuild fractured societies with both justice and inclusion.
Policy Implementation: Best Practices and Pitfalls
Effective policy implementation in integration requires stakeholder engagement, clear communication channels, and adaptive strategies to manage cultural diversity and social cohesion. Lustration policies demand transparency, impartial vetting mechanisms, and respect for human rights to avoid political bias and social division. Balancing these approaches involves continuous monitoring, inclusive reforms, and safeguarding rule of law to ensure sustainable governance and public trust.
Future Prospects: Toward Effective Transitional Justice
Integration strategies emphasize reconciliation and social cohesion, fostering inclusive governance to prevent cycles of conflict. Lustration policies focus on accountability by vetting individuals linked to past abuses, ensuring justice and deterring future violations. Future prospects in transitional justice lean toward hybrid models combining both approaches, promoting healing while upholding the rule of law and securing sustainable peace.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com