Restoration involves the process of returning something to its original condition, whether it's a historic building, artwork, or natural environment. Expert techniques and careful planning are essential to preserve authenticity while enhancing durability and aesthetics. Explore the rest of the article to learn how restoration can transform your valuable assets.
Table of Comparison
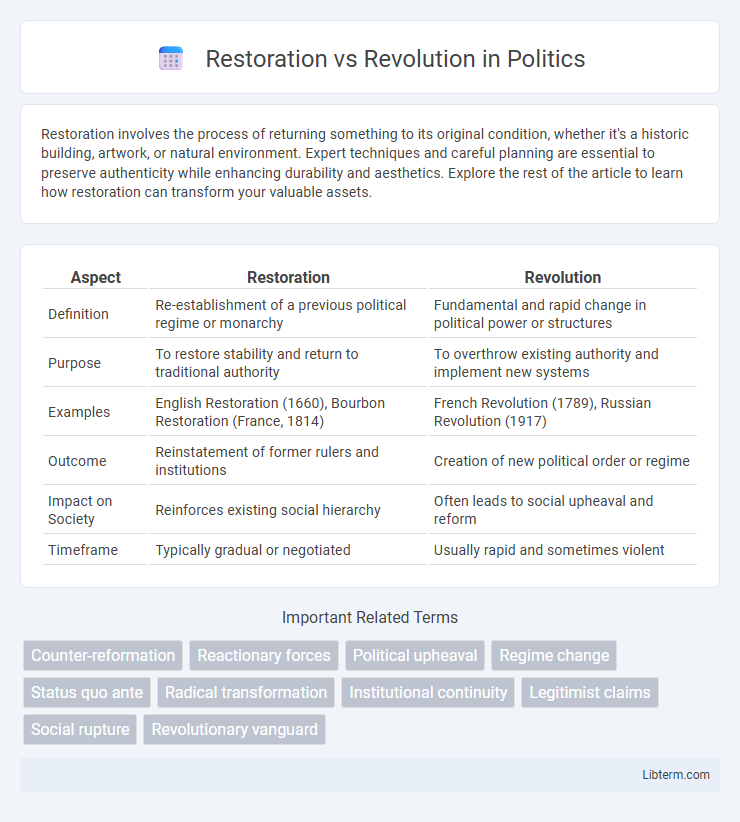
| Aspect | Restoration | Revolution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Re-establishment of a previous political regime or monarchy | Fundamental and rapid change in political power or structures |
| Purpose | To restore stability and return to traditional authority | To overthrow existing authority and implement new systems |
| Examples | English Restoration (1660), Bourbon Restoration (France, 1814) | French Revolution (1789), Russian Revolution (1917) |
| Outcome | Reinstatement of former rulers and institutions | Creation of new political order or regime |
| Impact on Society | Reinforces existing social hierarchy | Often leads to social upheaval and reform |
| Timeframe | Typically gradual or negotiated | Usually rapid and sometimes violent |
Understanding Restoration and Revolution
Restoration refers to the process of returning a system, government, or societal order to a previous state, often reinstating former institutions and traditional values after a period of change or upheaval. Revolution involves a fundamental and rapid transformation of political or social structures, driven by mass movements seeking to overthrow existing powers and establish new regimes. Understanding the distinction between restoration and revolution highlights the different approaches to change: one aims to preserve or revert to past frameworks, while the other pursues radical and foundational restructuring.
Historical Backgrounds: Restoration vs Revolution
Restoration refers to the period following the fall of revolutionary governments, aimed at re-establishing previous monarchies or traditional regimes, exemplified by the 1815 Congress of Vienna which sought to restore Europe's pre-Napoleonic order. Revolution signifies profound political and social upheaval, often characterized by the overthrow of established systems, such as the French Revolution of 1789 that dismantled the Ancien Regime and introduced republican ideals. Both movements shaped modern nation-states by either reaffirming existing power structures during restoration or radically transforming them through revolutionary change.
Key Differences Between Restoration and Revolution
Restoration emphasizes the revival of pre-existing political structures and traditions, seeking to reestablish previous authority and social order. Revolution involves a fundamental and often abrupt transformation of the political, social, or economic system, frequently overthrowing established institutions. Key differences include restoration's conservative aim to return to a former state versus revolution's radical goal to create a new system and the distinct methods used, where restoration typically uses negotiation or legal means, and revolution employs mass mobilization or conflict.
Major Examples of Restoration in History
The Restoration period in history is exemplified by key events such as the English Restoration of 1660, where the monarchy was reinstated under King Charles II following the Commonwealth period. Another notable example is the Bourbon Restoration in France (1814-1830), which restored the monarchy after the fall of Napoleon Bonaparte. These restorations aimed to reestablish traditional institutions and stabilize societies after revolutionary upheavals.
Landmark Revolutions That Changed Societies
Landmark revolutions such as the French Revolution of 1789, the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, and the Russian Revolution of 1917 fundamentally altered political, social, and economic structures, displacing monarchies and feudal systems with democracy, industrial capitalism, and communism respectively. These upheavals replaced existing orders with radical ideologies and new power dynamics, enabling the rise of modern nation-states and reshaping class relations. The profound societal transformations driven by these revolutions contrast sharply with restorations that aimed to reinstate pre-existing regimes, illustrating the far-reaching impact of revolutionary change on governance, labor, and cultural identity.
Motivations Behind Restoration and Revolutionary Movements
Restoration movements aim to reestablish political, social, or cultural systems perceived as legitimate or traditional after periods of disruption or upheaval. Revolutionary movements emerge from motivations to radically transform unjust or oppressive structures, driven by demands for equality, freedom, or systemic change. Both are propelled by contrasting desires: restoration seeks revival of past order, while revolution pursues creation of new paradigms.
Social and Political Impacts Compared
Restoration periods often aim to reinstate previous social hierarchies and political institutions, fostering stability but limiting progressive reforms. Revolutions tend to dismantle established structures, leading to rapid social transformation and the redistribution of power, though sometimes resulting in political instability. Comparative analysis reveals that restorations preserve tradition and continuity, while revolutions accelerate societal change and redefine governance frameworks.
Successes and Failures: Restoration vs Revolution
Restoration efforts often succeed in stabilizing political and social order by reinstating traditional institutions and preserving cultural continuity, but they frequently fail to address underlying systemic issues, leading to recurring unrest. Revolutions achieve significant breakthroughs by dismantling oppressive regimes and promoting radical reforms, yet they risk prolonged instability, violence, and the emergence of authoritarian successor states. Historical cases like the Bourbon Restoration in France illustrate limited progress and recurring conflict, whereas the French Revolution showcases both transformative success and the challenges of sustained governance.
Modern-Day Parallels and Relevance
Modern-day parallels between restoration and revolution are evident in contemporary political and social movements that seek either to reinstate traditional norms or to radically transform existing systems. Restoration efforts often emphasize preserving cultural heritage and institutional stability, whereas revolutionary movements drive rapid change to address perceived injustices or systemic failures. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for analyzing current global conflicts, policy reforms, and the balance of power between conservative and progressive forces.
Choosing a Path: Factors Influencing Societal Change
Choosing between restoration and revolution as paths for societal change depends on factors such as the urgency of grievances, the stability of existing institutions, and public support for reform. Restoration often appeals when social order and historical legitimacy are prioritized, while revolution is favored in contexts of systemic oppression and widespread dissatisfaction. Socioeconomic conditions, leadership dynamics, and external influences also critically shape the decision to pursue gradual reform or radical upheaval.
Restoration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com