Reservation systems streamline the process of securing a spot for events, accommodations, or transportation, ensuring availability and convenience. Efficient reservation management helps reduce errors, save time, and enhance customer satisfaction. Explore the rest of the article to discover how optimizing your reservation process can benefit you.
Table of Comparison
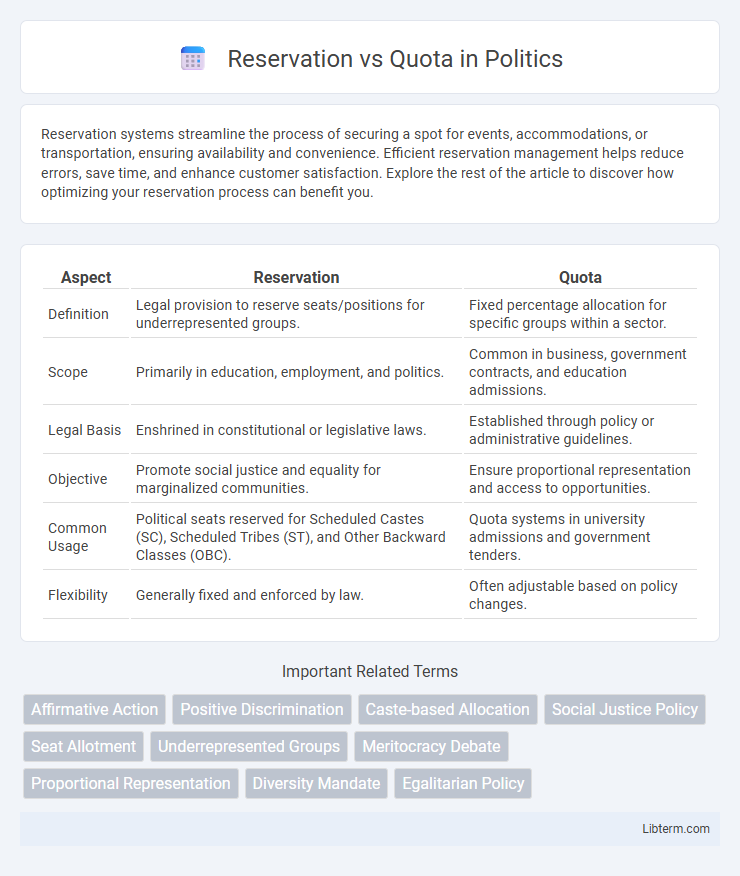
| Aspect | Reservation | Quota |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal provision to reserve seats/positions for underrepresented groups. | Fixed percentage allocation for specific groups within a sector. |
| Scope | Primarily in education, employment, and politics. | Common in business, government contracts, and education admissions. |
| Legal Basis | Enshrined in constitutional or legislative laws. | Established through policy or administrative guidelines. |
| Objective | Promote social justice and equality for marginalized communities. | Ensure proportional representation and access to opportunities. |
| Common Usage | Political seats reserved for Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC). | Quota systems in university admissions and government tenders. |
| Flexibility | Generally fixed and enforced by law. | Often adjustable based on policy changes. |
Understanding Reservation and Quota: Key Definitions
Reservation refers to the practice of setting aside a specific percentage of seats or positions in education, employment, or political representation for underrepresented or disadvantaged groups to promote social equality. Quota involves fixed numerical limits or allocations within a system to ensure proportional representation or access for particular communities or categories. Understanding these concepts is essential for grasping how social policies aim to balance opportunity and address historical inequalities through targeted distribution of resources and opportunities.
Historical Context: Origins of Reservation and Quota Systems
Reservation and quota systems originated as mechanisms to address historical social inequalities and discrimination faced by marginalized communities. The reservation system in India was introduced post-independence to ensure representation of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes in education, employment, and legislatures, based on the recommendations of the Mandal Commission and other social justice movements. Quota systems emerged globally in various sectors to promote diversity and equal opportunities, often influenced by civil rights movements and policies aimed at rectifying past exclusionary practices.
Purpose and Objectives: Reservation vs Quota
Reservation ensures representation of socially and educationally backward classes in education and employment to promote social equality and uplift marginalized communities. Quota allocates a fixed percentage of resources or opportunities to specific groups, primarily to maintain diversity or meet organizational goals. Both mechanisms aim to enhance inclusivity but differ in legal backing and application scope.
Legal Frameworks Governing Reservation and Quota
Legal frameworks governing reservation and quota systems differ by country but generally aim to ensure social equity and protect marginalized communities through constitutional provisions and specific legislation. Reservation policies often have constitutional backing, such as Article 15(4) and 16(4) of the Indian Constitution, which empower affirmative action for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes. Quota systems may be implemented through sector-specific laws or administrative orders, focusing on representation in education, employment, or political bodies to correct historical disadvantages and promote inclusivity.
Types of Reservation Policies Across Sectors
Reservation policies vary across sectors, including educational reservations for underrepresented communities in universities, job reservations in government and public sector units to enhance workforce diversity, and political reservations aimed at ensuring adequate representation of marginalized groups in legislative bodies. Each type of reservation targets specific social categories such as Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes, with eligibility criteria and percentage quotas defined by national or state legislation. Different sectors implement these policies to address historical inequalities and promote inclusive access to opportunities, influencing admission processes, recruitment, and electoral candidacy.
Quota Systems: Global Perspectives and Models
Quota systems function as policy tools designed to ensure equitable representation and resource allocation across marginalized groups, with models varying significantly worldwide based on social, economic, and political contexts. Countries like India implement caste-based quotas to address historical discrimination, while others, such as Norway and Rwanda, prioritize gender quotas to enhance women's representation in government and corporate sectors. These global perspectives highlight quota systems' adaptability in achieving diversity, inclusion, and social justice objectives tailored to specific demographic and cultural challenges.
Impact on Education and Employment Opportunities
Reservation policies in education and employment prioritize historically marginalized groups by allocating specific seats or positions, enhancing access to quality education and job opportunities for underrepresented communities. Quotas, while similar, often set fixed percentages that may limit flexibility but ensure minimum representation in competitive fields. The impact of these measures includes increased social inclusion, improved diversity, and the reduction of economic disparities among disadvantaged populations.
Social Equity and Inclusion: Reservation vs Quota Debate
Reservation ensures social equity by providing historically marginalized communities with guaranteed access to education and employment, addressing systemic inequalities. Quotas often serve as temporary targets rather than structural reforms, potentially leading to tokenism without resolving deeper social disparities. The Reservation vs Quota debate centers on long-term inclusion strategies versus short-term numerical representation in social justice policies.
Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Both Systems
Reservation and quota systems face criticism for perpetuating dependency and undermining meritocracy, which opponents argue can hinder social cohesion and economic progress. Quota systems often spark controversies related to fairness, as they may lead to reverse discrimination and resentment among non-beneficiary groups. Both policies encounter debates on their effectiveness in achieving true social equity, with critics claiming they sometimes entrench divisiveness rather than promote equal opportunity.
Future Trends and Reforms in Reservation and Quota Policies
Emerging trends in reservation and quota policies emphasize merit-based criteria combined with social justice measures to balance equality and efficiency. Future reforms are likely to incorporate dynamic assessment systems that periodically evaluate the socioeconomic status of beneficiaries to ensure targeted support. Technological advancements and data analytics will play a crucial role in monitoring the impact and effectiveness of reservation frameworks.
Reservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com