Local businesses play a crucial role in strengthening community ties and boosting the economy by providing personalized services and unique products tailored to your neighborhood's needs. Supporting local vendors helps preserve cultural heritage and fosters sustainable growth within your area. Discover more about the benefits of shopping local in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
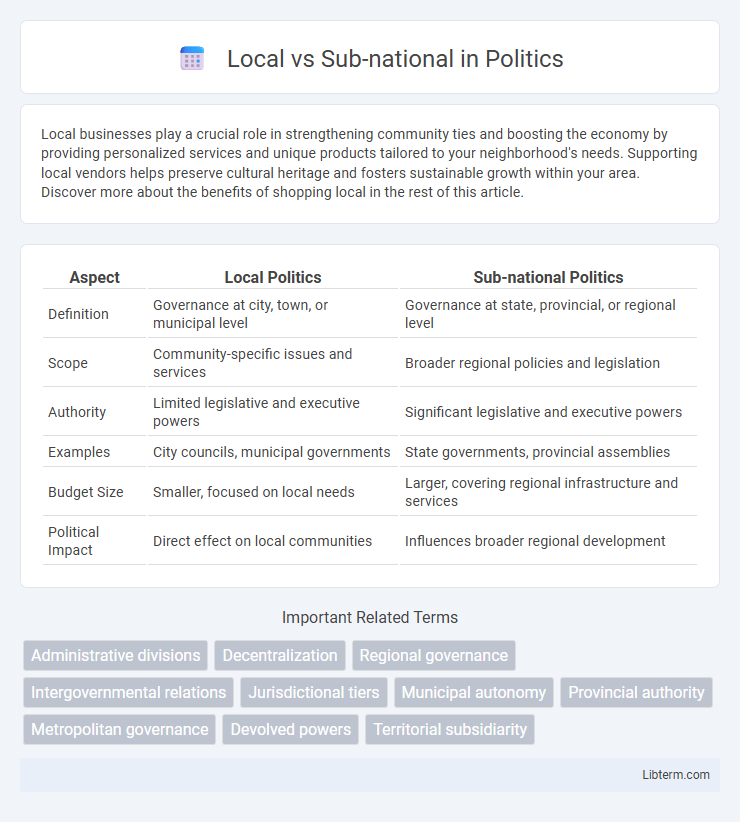
| Aspect | Local Politics | Sub-national Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance at city, town, or municipal level | Governance at state, provincial, or regional level |
| Scope | Community-specific issues and services | Broader regional policies and legislation |
| Authority | Limited legislative and executive powers | Significant legislative and executive powers |
| Examples | City councils, municipal governments | State governments, provincial assemblies |
| Budget Size | Smaller, focused on local needs | Larger, covering regional infrastructure and services |
| Political Impact | Direct effect on local communities | Influences broader regional development |
Understanding Local and Sub-national Governance
Local governance refers to administrative bodies governing cities, towns, or municipalities, directly managing community-specific services like sanitation, local policing, and urban planning. Sub-national governance encompasses a broader tier, including regions, provinces, or states with authority over policies affecting multiple localities, such as transportation infrastructure, education standards, and regional economic development. Understanding the distinction between local and sub-national governance is crucial for effective policy implementation, as local governments address immediate community needs while sub-national entities coordinate larger-scale initiatives.
Defining Local Government Structures
Local government structures encompass municipalities, towns, and cities with authority over community-level services, zoning, and public safety, whereas sub-national government includes broader administrative divisions such as states, provinces, or regions responsible for larger policy areas like education, transportation, and economic development. Defining local government structures involves understanding the specific powers granted by the sub-national unit, including taxation, law enforcement, and regulatory functions tailored to the local population's needs. Clarity in the hierarchical relationship between local and sub-national entities ensures efficient governance, resource allocation, and accountability within multi-tiered political systems.
What Constitutes Sub-national Authorities?
Sub-national authorities refer to governmental entities operating below the national level, including states, provinces, regions, and territories with defined administrative powers. These authorities manage local policies, budgets, and public services within their jurisdiction, exercising legislative, executive, or administrative functions delegated by the central government. The scope and autonomy of sub-national authorities vary widely across countries, influenced by constitutional arrangements and decentralization frameworks.
Key Differences Between Local and Sub-national Levels
Local levels represent municipal or city authorities responsible for community-specific services like zoning and public safety, whereas sub-national levels include broader administrative regions such as states or provinces overseeing larger-scale functions like education policy and infrastructure development. Local governance typically operates within smaller geographic areas with direct citizen engagement, while sub-national bodies coordinate policies across multiple localities, balancing regional priorities. Key differences lie in their scope of authority, resource allocation, and policy impact, where sub-national governments manage wider economic planning and local governments handle immediate service delivery.
Roles and Responsibilities: Local vs Sub-national
Local governments primarily manage community-specific services such as waste collection, zoning, and local law enforcement, directly addressing residents' daily needs. Sub-national entities, including states or provinces, oversee broader responsibilities like education policy, transportation infrastructure, and regional economic development to coordinate resources across multiple localities. Both levels collaborate to ensure effective governance, with local authorities implementing policies tailored to community needs while sub-national bodies provide strategic planning and regulatory frameworks.
Fiscal Powers and Budgeting Comparison
Local governments possess limited fiscal powers, mainly relying on property taxes, user fees, and intergovernmental transfers, whereas sub-national entities, such as states or provinces, wield broader taxation authority including income and sales taxes. Budgeting at the local level typically involves constrained expenditure options focused on municipal services, while sub-national governments manage larger, more complex budgets addressing infrastructure, education, and healthcare. Fiscal autonomy is significantly greater at the sub-national tier, allowing for more comprehensive financial planning and diversified revenue streams compared to local governments.
Decision-Making and Administrative Autonomy
Local governments possess decision-making authority tailored to community-specific needs, enabling direct administrative autonomy over services such as zoning, public safety, and local infrastructure. Sub-national entities, including states or provinces, exercise broader administrative autonomy with legal powers to enact legislation, manage regional budgets, and implement policies impacting multiple local jurisdictions. The distinction lies in the scope and scale of authority, where local governments focus on granular, localized decisions, while sub-national bodies coordinate larger-scale governance and resource allocation within the national framework.
Policy Implementation: Local vs Sub-national Impact
Local policy implementation directly addresses community-specific needs, allowing tailored solutions that reflect immediate social and economic conditions. Sub-national policies, encompassing regions such as states or provinces, provide broader frameworks that ensure consistency and resource allocation across multiple localities. This multi-tiered approach enhances governance efficiency by balancing targeted local actions with overarching strategic objectives at the sub-national level.
Challenges in Coordination and Overlap
Coordination between local and sub-national governments often faces significant challenges due to overlapping responsibilities and fragmented authority, leading to inefficiencies in policy implementation. Disparate administrative boundaries and varying priorities cause duplication of efforts and resource conflicts, complicating service delivery. Clear delineation of roles and improved communication mechanisms are essential to mitigate redundancy and foster effective collaboration.
The Future of Local and Sub-national Governance
Local and sub-national governance models are evolving to address increasing demands for decentralization, transparency, and citizen engagement. The integration of smart technologies and data-driven decision-making enhances the efficiency and responsiveness of local authorities while fostering collaboration across regional boundaries. Future governance structures will emphasize sustainability, inclusivity, and resilience, enabling adaptive policy frameworks that reflect diverse community needs within national contexts.
Local Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com