Establishment refers to the founding or creation of an organization, institution, or system, marking the beginning of its structured existence. It encompasses all foundational activities necessary to set up operations, define goals, and establish governance frameworks. Explore the rest of the article to understand how effective establishment impacts your project's success and growth.
Table of Comparison
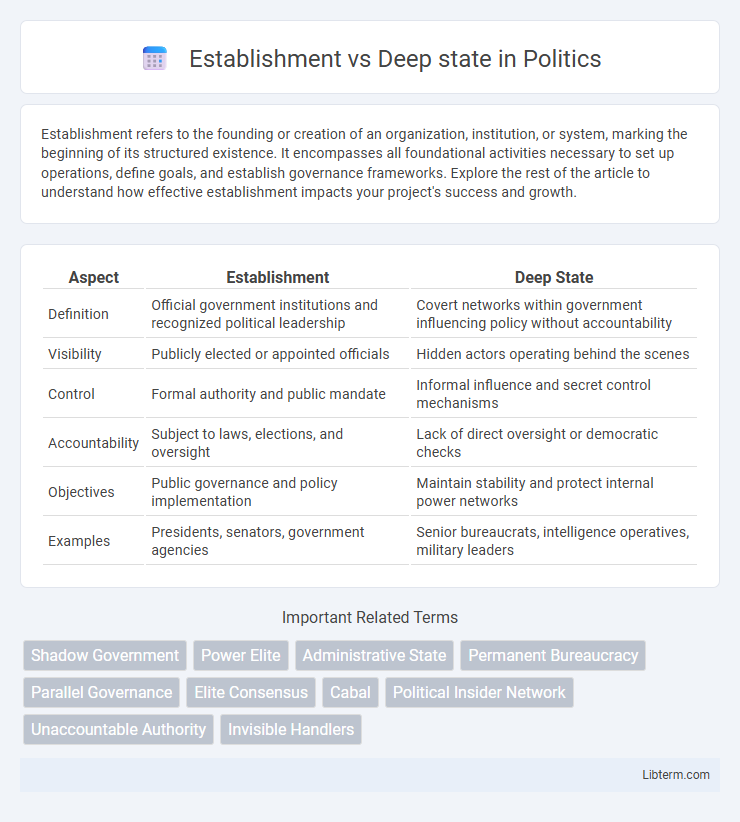
| Aspect | Establishment | Deep State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official government institutions and recognized political leadership | Covert networks within government influencing policy without accountability |
| Visibility | Publicly elected or appointed officials | Hidden actors operating behind the scenes |
| Control | Formal authority and public mandate | Informal influence and secret control mechanisms |
| Accountability | Subject to laws, elections, and oversight | Lack of direct oversight or democratic checks |
| Objectives | Public governance and policy implementation | Maintain stability and protect internal power networks |
| Examples | Presidents, senators, government agencies | Senior bureaucrats, intelligence operatives, military leaders |
Understanding the Establishment: Definition and Origins
The Establishment refers to the dominant groups and elite institutions that hold power in a society, shaping policies and maintaining social order through traditional political, economic, and cultural influence. Originating from historical hierarchies and entrenched networks, the Establishment includes politicians, business leaders, media moguls, and other key stakeholders who sustain systemic control. Understanding the Establishment involves recognizing its role in reinforcing existing power structures and influencing governance beyond formal democratic processes.
What is the Deep State? Unpacking the Concept
The Deep State refers to a network of influential members within government agencies, military, intelligence, and bureaucracies who operate independently of elected officials, often shaping policy covertly. This concept highlights the tension between visible, democratic institutions and hidden power structures that may prioritize their own agendas over public accountability. Understanding the Deep State involves analyzing its role in undermining or influencing governance through secretive operations and entrenched institutional interests.
Key Differences Between the Establishment and Deep State
The Establishment refers to the official, visible power structures such as government officials, political parties, and institutional leaders who operate within the rules and transparency of democracy. In contrast, the Deep State encompasses covert networks, including intelligence agencies, military insiders, and unelected bureaucrats, who exert hidden influence and often operate beyond public accountability. Key differences lie in legitimacy, transparency, and public awareness, with the Establishment functioning openly and the Deep State working in the shadows to shape policy and maintain control.
Historical Examples: Establishment vs Deep State in Action
Historical examples of Establishment versus Deep State conflicts include Turkey's 1990s era, where the military and intelligence agencies covertly undermined elected governments to preserve secularism. In Egypt, the military's removal of President Morsi in 2013 reflected the Deep State's influence overriding the political establishment. The United States during the Vietnam War saw intelligence agencies clash with elected officials, revealing tensions between bureaucratic power and democratic leadership.
The Role of Bureaucracy in Both Entities
Bureaucracy serves as the operational backbone of both the Establishment and the Deep State, facilitating policy implementation and maintaining institutional continuity. In the Establishment, bureaucratic agencies function within legal frameworks, executing elected officials' directives and supporting democratic governance. Conversely, the Deep State utilizes bureaucratic networks to exert covert influence, often bypassing formal political channels to shape decisions behind the scenes.
Political Influence: How the Establishment Shapes Policy
The Establishment wields significant political influence by shaping policy through institutional control, lobbying networks, and long-standing relationships within government agencies. This influence ensures the continuity of preferred economic and social agendas, often prioritizing elite interests over public demands. By contrast, the Deep State operates covertly, using bureaucratic power to subtly steer policy implementation beyond elected officials' oversight.
Deep State Allegations: Fact vs Fiction
Deep state allegations often blur the line between legitimate government operations and covert networks manipulating policy beyond public scrutiny, generating widespread debate about transparency and accountability. While some claims cite documented instances of intelligence agency overreach, many theories exaggerate the influence of unseen actors or lack concrete evidence, leading to misinformation. Critical analysis distinguishes factual concerns about bureaucratic inertia or political influence from unfounded conspiracies lacking empirical support.
Media Representation: Establishment and Deep State Narratives
Media representation often frames the Establishment as the recognized power structure consisting of elected officials and mainstream institutions, while the Deep State is portrayed as a covert network operating behind the scenes to influence or undermine official policies. News outlets aligned with the Establishment tend to emphasize transparency and legitimacy in governance, whereas alternative and conspiracy-focused media highlight secrecy, manipulation, and hidden agendas attributed to the Deep State. This dichotomy in narratives shapes public perception by reinforcing trust in traditional authorities or fueling skepticism about hidden political machinations.
Public Perception: Trust, Suspicion, and Conspiracy Theories
Public perception of the Establishment often centers on trust in official institutions such as government, media, and judiciary, reflecting confidence in their legitimacy and authority. In contrast, the Deep State is associated with suspicion and conspiracy theories alleging hidden networks of power manipulating policies behind the scenes, eroding public trust. This dichotomy fuels polarized narratives where trust in transparency collides with fears of covert influence, shaping societal debates on governance and accountability.
The Impact on Democracy: Risks and Safeguards
The establishment, composed of official institutions and influential elites, can shape policy direction within democratic frameworks, while the deep state refers to covert networks operating independently of elected authority, often undermining transparency and accountability. Such clandestine power structures pose significant risks to democracy by eroding public trust, enabling unchecked decision-making, and subverting electoral processes. Implementing robust oversight mechanisms, fostering institutional transparency, and empowering independent watchdogs are critical safeguards to protect democratic integrity from undue influence by entrenched or hidden powers.
Establishment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com