Affirmative action policies aim to promote equal opportunities by addressing historical inequalities and discrimination in education and employment. These initiatives focus on creating a diverse and inclusive environment that benefits society as a whole. Explore the rest of the article to understand how affirmative action impacts your community and workplace.
Table of Comparison
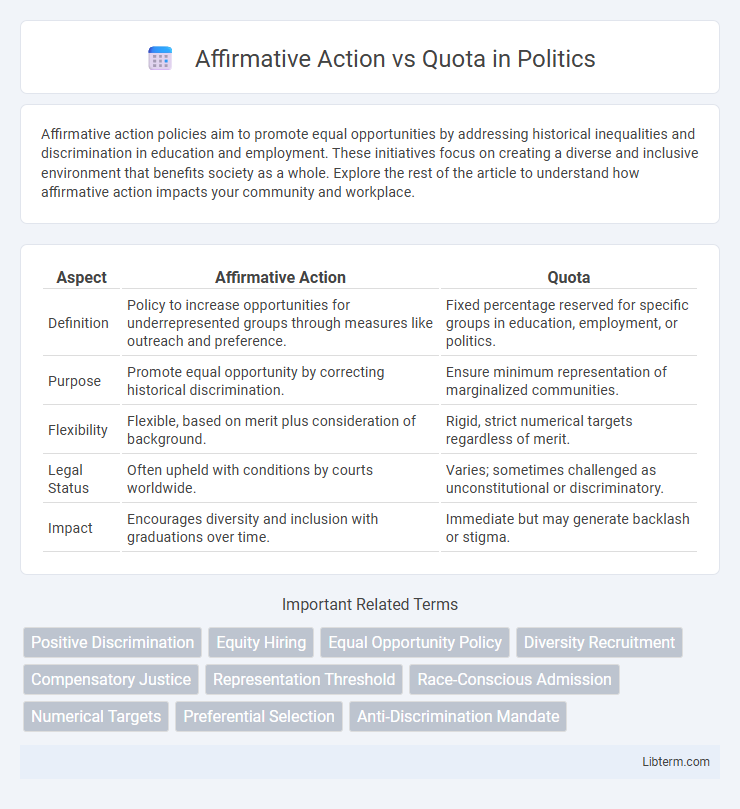
| Aspect | Affirmative Action | Quota |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy to increase opportunities for underrepresented groups through measures like outreach and preference. | Fixed percentage reserved for specific groups in education, employment, or politics. |
| Purpose | Promote equal opportunity by correcting historical discrimination. | Ensure minimum representation of marginalized communities. |
| Flexibility | Flexible, based on merit plus consideration of background. | Rigid, strict numerical targets regardless of merit. |
| Legal Status | Often upheld with conditions by courts worldwide. | Varies; sometimes challenged as unconstitutional or discriminatory. |
| Impact | Encourages diversity and inclusion with graduations over time. | Immediate but may generate backlash or stigma. |
Understanding Affirmative Action: Definition and Goals
Affirmative Action refers to policies designed to increase opportunities in education, employment, and other areas for historically marginalized groups by addressing systemic inequalities. Its primary goals include promoting diversity, ensuring equal access, and rectifying past discrimination without rigid numerical requirements. Unlike quota systems that set specific limits or targets, Affirmative Action emphasizes flexible, merit-based consideration to foster inclusive environments.
Quota Systems Explained: Key Features and Purpose
Quota systems allocate a fixed percentage of opportunities or resources to specific groups, aiming to ensure representation and address historical inequalities. These systems often apply in education, employment, and political sectors to promote diversity and inclusion. Key features include mandatory minimums, group-based eligibility, and legal enforcement mechanisms designed to balance social disparities.
Historical Context: The Origins of Both Approaches
Affirmative action emerged in the 1960s United States as a policy tool aimed at remedying past discrimination by promoting equal opportunities in education and employment for marginalized groups. Quotas, by contrast, have historic roots in various global contexts as fixed numerical targets to ensure minority representation, often sparked by legal mandates or social movements demanding immediate inclusion. Both approaches reflect evolving strategies to tackle systemic inequality but differ fundamentally in flexibility and implementation, shaped by their distinct historical and cultural origins.
Legal Framework: Global Perspectives on Affirmative Action and Quotas
Affirmative action policies and quotas operate within diverse legal frameworks worldwide, reflecting varying approaches to remedy historical discrimination and promote equality. In the United States, affirmative action is regulated through constitutional scrutiny and landmark Supreme Court rulings balancing diversity goals with anti-discrimination principles. Contrastingly, India enforces legally mandated quotas for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes under its constitutional provisions, exemplifying a statutory quota system embedded in public sector employment and education.
Key Differences Between Affirmative Action and Quota Systems
Affirmative action refers to policies aimed at increasing opportunities for historically marginalized groups through measures like outreach and holistic evaluation, while quota systems mandate fixed numerical targets or percentages for minority representation. Affirmative action emphasizes flexibility and considers multiple factors to promote diversity, whereas quota systems enforce strict, legally binding requirements that guarantee specific levels of inclusion. The key difference lies in affirmative action's broader, case-by-case approach versus quota systems' rigid, predetermined allocation of positions.
Advantages of Affirmative Action Policies
Affirmative action policies promote diversity and inclusion by providing opportunities based on merit while considering historical disadvantages, enhancing social equity without rigid numerical constraints. These policies foster a more dynamic and adaptable environment, encouraging individual achievement and reducing stereotypes associated with quotas. Emphasizing tailored support and outreach, affirmative action helps bridge gaps in education and employment, contributing to sustainable socioeconomic progress.
Drawbacks of Quota-Based Systems
Quota-based systems often lead to reverse discrimination, undermining meritocracy by prioritizing demographic characteristics over qualifications. These systems can cause social fragmentation, fostering resentment among groups excluded or perceived as unfairly treated. Rigid quotas may also limit flexibility in talent selection, reducing overall efficiency in education and employment sectors.
Impact on Diversity and Inclusion: Comparative Analysis
Affirmative action promotes diversity and inclusion by considering a broad range of factors such as race, gender, and socioeconomic background without rigid numerical limits, fostering a more diverse candidate pool. Quota systems mandate fixed percentages for underrepresented groups, which may increase representation but can lead to perceptions of tokenism and undermine merit-based selection. Comparative analysis shows affirmative action tends to create sustainable inclusion through holistic evaluation, while quotas achieve immediate diversity gains but risk legal and social challenges.
Real-World Case Studies: Successes and Controversies
Affirmative action policies, such as in the United States, have shown success in increasing diversity in higher education and workplaces, evidenced by Harvard University's proactive admissions strategies. However, quota systems, like India's reservation policy, have sparked controversies regarding meritocracy and social division, leading to prolonged legal battles such as the Supreme Court's scrutiny of the 27% OBC quota. Both approaches reveal complex outcomes where social equity gains coexist with debates over fairness, efficiency, and long-term integration.
Future Trends in Diversity Policies: What Lies Ahead
Future trends in diversity policies indicate a shift from rigid quotas towards more flexible affirmative action strategies that emphasize individual qualifications alongside demographic representation. Organizations increasingly adopt holistic approaches integrating technology and data analytics to track progress and identify unconscious biases. Emphasis on inclusive culture-building and equity-driven initiatives is expected to dominate diversity frameworks, fostering sustainable and meaningful workforce diversity.
Affirmative Action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com