Political consensus is crucial for effective governance, enabling diverse groups to find common ground on key issues and implement policies that benefit society as a whole. Achieving consensus requires dialogue, compromise, and mutual respect among stakeholders to address conflicting interests and foster social stability. Discover how building political consensus can enhance democratic processes and influence policy outcomes in the full article.
Table of Comparison
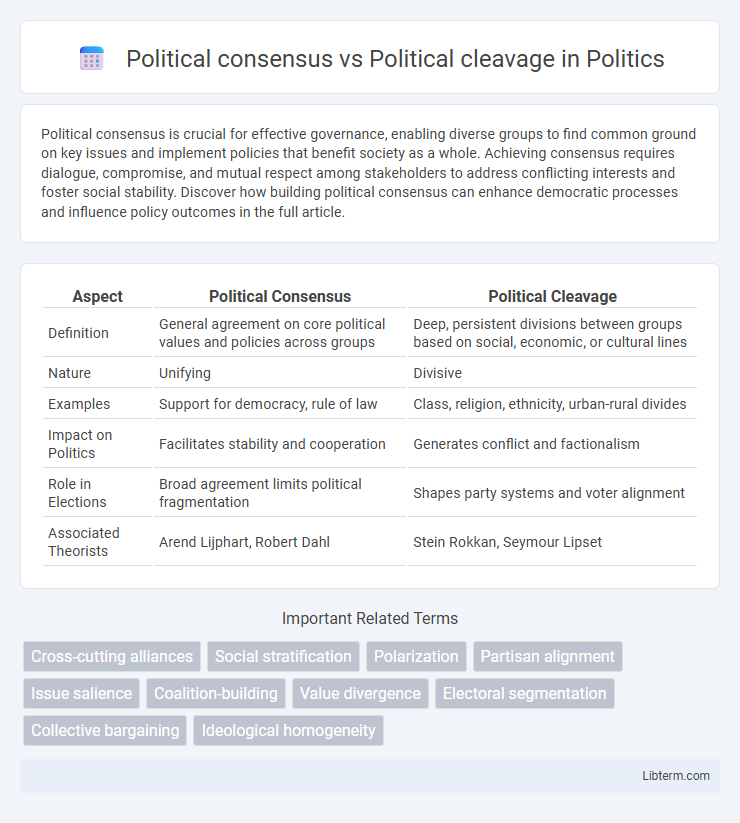
| Aspect | Political Consensus | Political Cleavage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General agreement on core political values and policies across groups | Deep, persistent divisions between groups based on social, economic, or cultural lines |
| Nature | Unifying | Divisive |
| Examples | Support for democracy, rule of law | Class, religion, ethnicity, urban-rural divides |
| Impact on Politics | Facilitates stability and cooperation | Generates conflict and factionalism |
| Role in Elections | Broad agreement limits political fragmentation | Shapes party systems and voter alignment |
| Associated Theorists | Arend Lijphart, Robert Dahl | Stein Rokkan, Seymour Lipset |
Understanding Political Consensus
Political consensus involves widespread agreement among diverse political groups on key policies, fostering stability and cooperative governance. It contrasts with political cleavage, which denotes deep divisions based on social, economic, or ideological differences that fragment society and hinder unified action. Understanding political consensus requires analyzing mechanisms of negotiation, compromise, and the role of institutional frameworks that bridge group interests and create shared objectives.
Defining Political Cleavage
Political cleavage refers to deep, persistent divisions in a society based on structural factors such as class, religion, ethnicity, or ideology that shape political alignments and voting behavior. These cleavages create distinct social groups with competing interests and identities, often influencing party systems and electoral outcomes. Unlike political consensus, which implies broad agreement and cooperation among different groups, political cleavage highlights enduring conflicts and polarized social landscapes.
Historical Roots of Consensus and Cleavage
Political consensus often traces its historical roots to shared foundational values and collective agreements during nation-building periods, fostering stability and cooperation among diverse groups. In contrast, political cleavage originates from deep-seated socio-economic, cultural, or religious divisions shaped by historical conflicts, class struggles, or colonial legacies. Understanding these historical roots is crucial for analyzing contemporary political dynamics and the persistence of party systems.
Factors Shaping Political Consensus
Political consensus emerges from shared values, effective communication, and institutional frameworks that encourage cooperation across diverse political groups. Factors shaping political consensus include common economic interests, cultural integration, and the presence of inclusive governance structures that mediate conflicts. Social trust and media influence also play critical roles in fostering agreement and minimizing political cleavage within societies.
Causes and Types of Political Cleavages
Political cleavages arise from deep-rooted social divisions such as class, ethnicity, religion, and regional identity, which create conflicting interests and alignments within a political system. Causes include economic inequality, cultural diversity, historical grievances, and institutional structures that reinforce group distinctions. Types of political cleavages include class cleavage (working class vs. elites), ethnic cleavage (majority vs. minority groups), religious cleavage (different faith communities), and urban-rural cleavage, all shaping party systems and electoral behavior.
Impacts on Governance and Policy-making
Political consensus fosters stable governance by enabling collaborative decision-making and consistent policy implementation, reducing conflict among diverse groups. In contrast, political cleavage, marked by deep divisions along ethnic, ideological, or socioeconomic lines, often leads to fragmented policymaking, stalled legislation, and weakened institutional trust. The presence of consensus facilitates coherent policies and long-term planning, whereas cleavage heightens polarization, complicating compromise and effective governance.
Consensus vs Cleavage: Influence on Political Stability
Political consensus fosters stability by promoting shared goals and cooperative governance, reducing conflicts within a society. Political cleavage, referring to deep divisions based on social, economic, or cultural lines, often leads to persistent conflict and governmental instability. Balancing consensus and cleavage is critical for maintaining political order and preventing polarization in democratic systems.
Case Studies: Consensus and Cleavage in Practice
Political consensus often emerges in stable democracies where broad agreement on fundamental policies fosters social cohesion, exemplified by post-war Germany's integration of diverse political parties into cooperative governance. In contrast, political cleavage highlights enduring divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity that shape party systems and voter behavior, as seen in Belgium's linguistic divide between Flemish and Walloon communities. Case studies reveal that successful consensus-building requires negotiation and institutional frameworks that accommodate cleavages, balancing unity with pluralism in governance.
Bridging Divides: Strategies for Reducing Cleavage
Effective strategies for reducing political cleavage involve promoting dialogue and mutual understanding among diverse groups to build political consensus. Structured deliberative forums and inclusive policy-making foster trust, allowing conflicting parties to find common ground despite ideological differences. Emphasizing shared goals and values helps bridge divides, transforming cleavage into opportunities for cooperative governance.
Future Trends in Political Consensus and Cleavage
Future trends indicate increasing political cleavage driven by growing ideological polarization, identity politics, and socio-economic disparities. Emerging global challenges such as climate change, technological disruption, and migration may both exacerbate divisions and create new grounds for political consensus around shared survival and sustainability goals. Digital platforms and data-driven political campaigns will likely play a pivotal role in shaping how consensus and cleavage evolve across diverse electorates.
Political consensus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com