Cohesion is the quality that makes a text logically connected and easy to follow by linking sentences and ideas smoothly. Strong cohesion uses consistent vocabulary, reference words, and transitional phrases to guide readers through the content seamlessly. Discover how mastering cohesion can enhance Your writing clarity and engagement by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
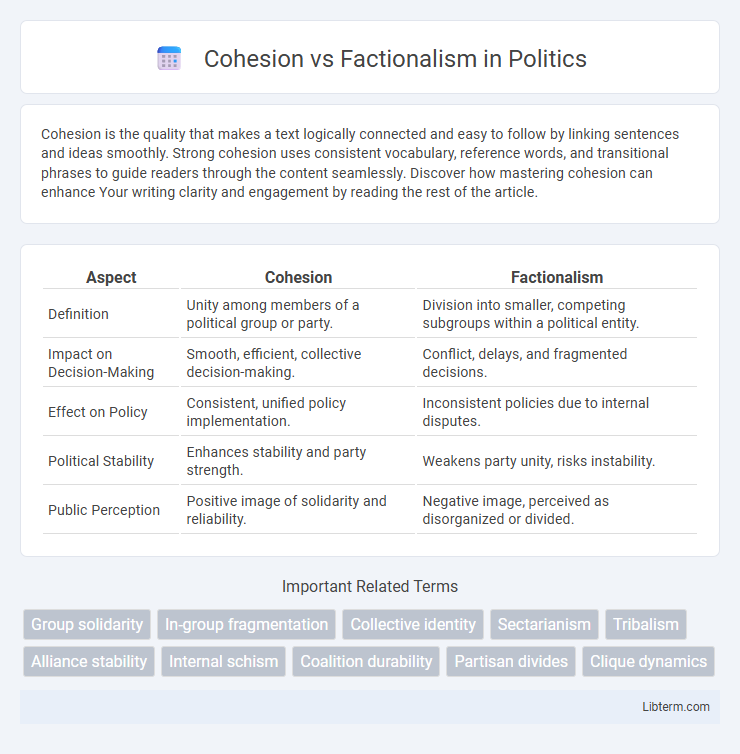
| Aspect | Cohesion | Factionalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unity among members of a political group or party. | Division into smaller, competing subgroups within a political entity. |
| Impact on Decision-Making | Smooth, efficient, collective decision-making. | Conflict, delays, and fragmented decisions. |
| Effect on Policy | Consistent, unified policy implementation. | Inconsistent policies due to internal disputes. |
| Political Stability | Enhances stability and party strength. | Weakens party unity, risks instability. |
| Public Perception | Positive image of solidarity and reliability. | Negative image, perceived as disorganized or divided. |
Understanding Cohesion and Factionalism
Cohesion refers to the unity and collective strength within a group, driven by shared values, goals, and effective communication, which enhances collaboration and stability. Factionalism, on the other hand, arises from internal divisions based on competing interests or ideologies, often leading to conflict and weakened group dynamics. Understanding these concepts is vital for managing organizational behavior and fostering an environment where cooperation prevails over discord.
Historical Context: Cohesion vs Factionalism
Historical context reveals that cohesion within societies or political groups often emerged during periods of external threats or shared struggles, fostering unity and collective identity. In contrast, factionalism tended to arise in times of political stability or social change, driven by competing interests, ideologies, or power struggles that fragmented cohesion. Key examples include the cohesive resistance movements during wartime and the factional divisions seen in revolutionary or parliamentary systems.
Key Drivers of Group Cohesion
Key drivers of group cohesion include shared goals, mutual trust, and effective communication, which foster collaboration and a strong sense of belonging among members. Social identity theory highlights the importance of perceived similarity and group loyalty in enhancing cohesion, while clear roles and consistent leadership also contribute significantly. In contrast, factionalism arises from internal conflicts, competing interests, and eroded trust, undermining group unity and productivity.
Causes and Consequences of Factionalism
Factionalism often arises from competing interests, cultural or ideological differences, and unequal access to resources or power within groups. This division weakens organizational cohesion by fostering mistrust, reducing cooperation, and escalating internal conflicts. As a result, factionalism undermines collective goals, hampers decision-making processes, and may lead to fragmentation or collapse of the group.
Cohesion’s Impact on Organizational Success
Cohesion significantly enhances organizational success by fostering trust, collaboration, and communication among team members. High cohesion leads to increased employee motivation, reduced turnover rates, and improved overall productivity. Organizations with strong cohesive cultures are better equipped to adapt to change and achieve strategic goals efficiently.
Factionalism and Its Effects on Productivity
Factionalism within organizations fosters divisions that undermine teamwork and collaboration, leading to reduced overall productivity. Persistent conflicts between internal groups drain resources, escalate tensions, and create communication barriers that hinder efficient workflow. The resulting environment of mistrust and competition slows decision-making and diminishes employee morale, significantly impacting business performance.
Navigating Internal Conflicts and Divisions
Navigating internal conflicts and divisions requires understanding the balance between cohesion and factionalism within organizations or communities. Cohesion fosters unity and shared purpose, enhancing collaboration and resilience during challenges. In contrast, factionalism often leads to fragmented goals and power struggles, undermining collective progress and creating persistent barriers to effective decision-making.
Strategies to Foster Cohesion in Teams
Promoting open communication and shared goals significantly enhances team cohesion by aligning individual efforts toward a common objective. Implementing collaborative problem-solving techniques and recognizing diverse contributions encourage trust and mutual respect among team members. Establishing clear roles and fostering inclusivity reduce factionalism, creating a unified and high-performing team environment.
Mitigating Factionalism: Best Practices
Mitigating factionalism involves cultivating open communication channels and fostering inclusive decision-making processes to enhance group cohesion. Implementing conflict resolution mechanisms and promoting shared goals align individual interests with collective objectives, reducing divisiveness. Leadership that emphasizes transparency and mutual respect further strengthens unity by addressing grievances before factions solidify.
Future Trends: Cohesion and Factionalism in Society
Future trends in society indicate a complex interplay between cohesion and factionalism, with digital platforms amplifying both collective unity and divisive group identities. Advances in AI-driven communication tools foster enhanced collaboration across diverse communities, promoting social cohesion through shared goals and values. Simultaneously, algorithmic echo chambers and polarized content risk intensifying factionalism, challenging efforts toward inclusive social integration.
Cohesion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com