An incumbent holds a current position or office, often in politics or business, where experience and established authority provide significant advantages. Understanding the challenges and opportunities faced by an incumbent is crucial for analyzing leadership dynamics and election outcomes. Discover more about how incumbency influences performance and strategy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
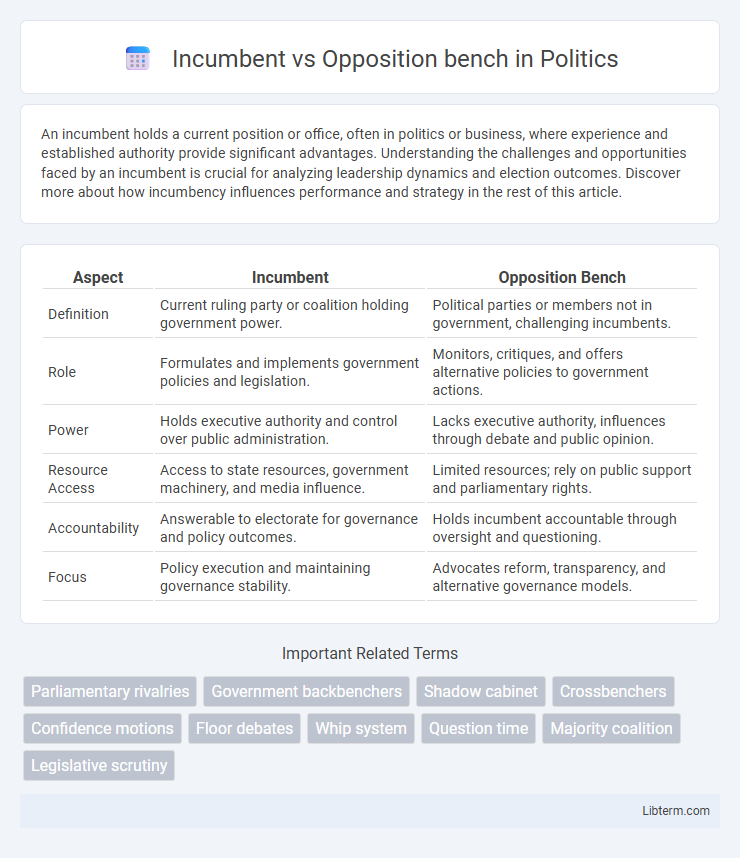
| Aspect | Incumbent | Opposition Bench |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Current ruling party or coalition holding government power. | Political parties or members not in government, challenging incumbents. |
| Role | Formulates and implements government policies and legislation. | Monitors, critiques, and offers alternative policies to government actions. |
| Power | Holds executive authority and control over public administration. | Lacks executive authority, influences through debate and public opinion. |
| Resource Access | Access to state resources, government machinery, and media influence. | Limited resources; rely on public support and parliamentary rights. |
| Accountability | Answerable to electorate for governance and policy outcomes. | Holds incumbent accountable through oversight and questioning. |
| Focus | Policy execution and maintaining governance stability. | Advocates reform, transparency, and alternative governance models. |
Understanding Incumbent and Opposition Benches
The incumbent bench consists of elected representatives or lawmakers who currently hold government positions and actively implement policies, while the opposition bench comprises members who challenge and scrutinize government actions, offering alternative viewpoints. Understanding the roles of these benches is essential to grasp how parliamentary democracy functions through debate, accountability, and legislative decision-making. The dynamic between the incumbent and opposition benches ensures balanced governance by promoting transparency and representing diverse public interests.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Incumbent
The incumbent in a parliamentary system is responsible for forming and leading the government by implementing policies, managing public administration, and ensuring law and order. They are tasked with proposing legislation, budgeting, and representing the country domestically and internationally. The incumbent also maintains accountability to the electorate through transparent governance and responding to policy challenges effectively.
Key Functions of the Opposition Bench
The Opposition Bench plays a crucial role in holding the Incumbent government accountable by critically analyzing policies and scrutinizing legislative proposals. It ensures transparency through debates, questions, and committees, providing alternative viewpoints that strengthen democratic processes. Key functions include challenging government actions, representing minority or dissenting voices, and safeguarding constitutional rights by advocating checks and balances within the parliamentary framework.
Historical Evolution of Parliamentary Benches
Parliamentary benches have historically evolved to represent the division between the government and opposition, reflecting the dynamics of majority rule and political contestation. The incumbent bench comprises members supporting the ruling party or coalition, responsible for legislative agenda and policy implementation, while the opposition bench includes parties that challenge the government's decisions and hold it accountable. This separation dates back to the British Parliament in the 18th century, where government ministers sat on the right of the Speaker and opposition members on the left, a seating arrangement that has been adopted and adapted in parliamentary systems worldwide.
Decision-Making Power: Incumbent vs Opposition
The incumbent bench wields predominant decision-making power within legislative processes due to holding the majority and controlling key committees, enabling them to set agendas and pass laws more efficiently. In contrast, the opposition bench exercises limited decision-making influence but plays a crucial role in scrutinizing government actions, debating policies, and representing alternative viewpoints. This dynamic establishes a balance in governance, where the incumbent drives policy execution while the opposition ensures accountability and transparency.
Accountability and Checks in Governance
The incumbent bench holds the primary responsibility for implementing policies and ensuring transparency in government actions, serving as the central point of accountability to the electorate. The opposition bench acts as a crucial check on power by scrutinizing government decisions, highlighting inefficiencies, and proposing alternative solutions to promote balanced governance. Effective accountability mechanisms require active engagement from both benches to maintain democratic integrity and prevent misuse of authority.
Strategies Used by Opposition Benches
Opposition benches employ strategies such as scrutinizing government policies through detailed debates and question sessions to hold the incumbents accountable. They form issue-based alliances to amplify dissent and leverage media platforms for public engagement and narrative shaping. Strategic disruptions and selective support of government initiatives enable the opposition to influence legislative outcomes and maintain political relevance.
Challenges Faced by Incumbent Governments
Incumbent governments often face challenges such as managing public expectations amid economic fluctuations and addressing policy shortcomings criticized by the opposition bench. They encounter scrutiny over transparency, governance inefficiencies, and the pressure to deliver timely social and infrastructural development. The opposition bench capitalizes on these vulnerabilities by highlighting inconsistencies and proposing alternative policy frameworks to sway public opinion.
Impact of Incumbent vs Opposition Dynamics on Policy
The dynamic between the incumbent and opposition benches significantly shapes legislative outcomes and policy development, with incumbents often driving agenda-setting due to greater control over parliamentary procedures and resources. Opposition benches play a critical role in scrutinizing, challenging, and proposing alternatives, influencing transparency and accountability in governance. This interplay affects the balance of power, policy innovation, and the responsiveness of government initiatives to public needs.
Future Trends in Parliamentary Bench Relations
The future trends in parliamentary bench relations indicate a growing emphasis on cooperative dialogue between incumbent and opposition benches to enhance legislative efficiency and democratic accountability. Advances in digital communication and data analytics are expected to facilitate bipartisan collaboration and real-time policy monitoring, reducing adversarial conflicts. Institutional reforms may prioritize transparency and inclusivity, fostering a parliamentary culture where diverse political entities contribute constructively to governance.
Incumbent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com