The Central Committee serves as the main decision-making body within many political organizations, overseeing policy implementation and strategic direction. Its members typically represent various factions and regions, ensuring diverse input in governance and organizational matters. Explore the full article to understand how the Central Committee influences political dynamics and your involvement in these processes.
Table of Comparison
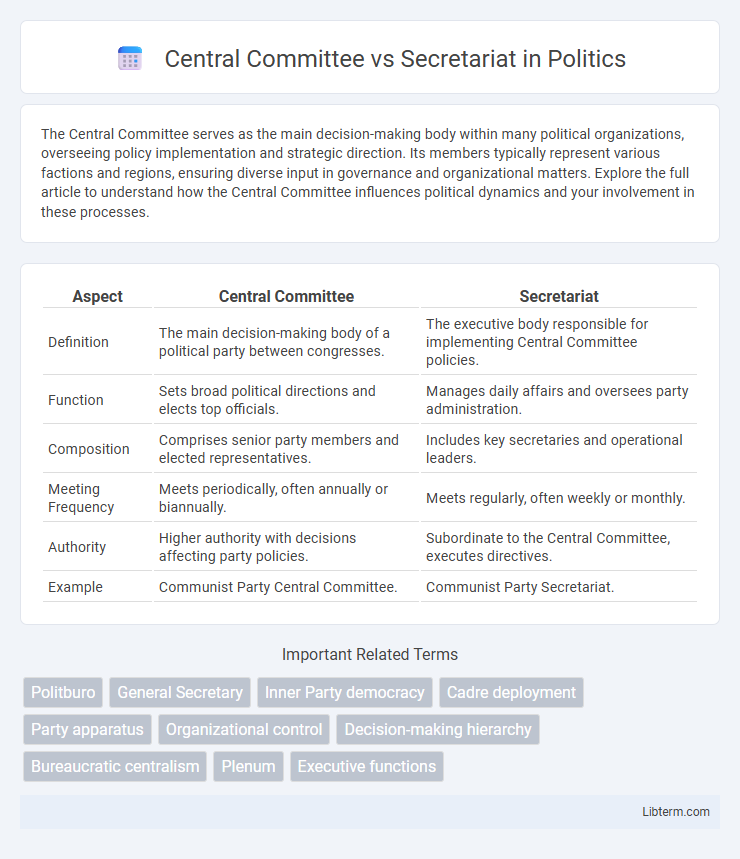
| Aspect | Central Committee | Secretariat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The main decision-making body of a political party between congresses. | The executive body responsible for implementing Central Committee policies. |
| Function | Sets broad political directions and elects top officials. | Manages daily affairs and oversees party administration. |
| Composition | Comprises senior party members and elected representatives. | Includes key secretaries and operational leaders. |
| Meeting Frequency | Meets periodically, often annually or biannually. | Meets regularly, often weekly or monthly. |
| Authority | Higher authority with decisions affecting party policies. | Subordinate to the Central Committee, executes directives. |
| Example | Communist Party Central Committee. | Communist Party Secretariat. |
Overview of the Central Committee
The Central Committee serves as the principal decision-making body within a communist party, responsible for setting major policies and overseeing party activities between congresses. It comprises key party leaders and representatives elected during the party congress, reflecting diverse regional and sectoral interests. The Secretariat, in contrast, functions as the executive arm, managing day-to-day party operations and implementing decisions made by the Central Committee.
Role and Functions of the Secretariat
The Secretariat functions as the executive arm of the Central Committee, responsible for implementing policies and managing day-to-day administrative affairs within a political party. It coordinates activities among various departments, oversees organizational discipline, and ensures communication flow between the Central Committee and lower party levels. The Secretariat's role is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency, enforcing decisions made by the Central Committee, and guiding the party's internal and external activities.
Historical Evolution of Both Bodies
The Central Committee historically functioned as the principal policymaking body within communist parties, elected at party congresses to oversee major decisions and ideological direction. The Secretariat evolved as an executive organ responsible for the daily administration and implementation of Central Committee policies, often gaining influence during periods of party consolidation. Over time, the Secretariat's role expanded, centralizing power by managing personnel appointments and party discipline, reflecting shifts in party structure from broad collective leadership to more streamlined governance.
Composition and Membership Differences
The Central Committee typically consists of several hundred members from various levels of the party, representing a broad spectrum of political, military, and regional interests. In contrast, the Secretariat is a smaller, more select body composed mainly of key party officials responsible for day-to-day administration and organizational work. Membership in the Central Committee is more extensive and inclusive, while the Secretariat's composition focuses on core leadership figures with executive authority.
Decision-Making Powers Compared
The Central Committee holds broad decision-making powers, responsible for setting major party policies, electing key leadership, and guiding long-term strategic directions. The Secretariat, by contrast, exercises executive authority in implementing the decisions of the Central Committee and managing day-to-day administrative affairs. The Central Committee's power is collective and policy-oriented, while the Secretariat's authority is more centralized and operational.
Influence on Party Policy and Direction
The Central Committee holds the primary authority for setting party policy and strategic direction during plenary sessions, influencing broad ideological and organizational decisions. The Secretariat, tasked with implementing these policies, manages daily operations and ensures adherence to party directives, wielding significant influence over routine governance and policy execution. The interplay between the Central Committee's policy formulation and the Secretariat's operational control shapes the overall trajectory and stability of party governance.
Key Responsibilities and Jurisdiction
The Central Committee serves as the principal policymaking body within a communist party, responsible for setting overall political direction and approving major decisions during party congresses. Its jurisdiction extends to supervising the implementation of party policies across all levels and electing the Secretariat to manage daily operations. The Secretariat holds executive authority over administrative functions, ensuring the execution of Central Committee decisions, managing routine affairs, and overseeing party discipline and organizational matters.
Relationship Between the Two Bodies
The Central Committee serves as the highest authority within a communist party, responsible for setting major policies and electing the Secretariat, which manages day-to-day operations and implements the Committee's decisions. The Secretariat acts as the executive arm, ensuring that the Central Committee's directives are executed efficiently across all party levels. This hierarchical relationship emphasizes the Central Committee's strategic role and the Secretariat's operational function within the party structure.
Notable Examples in Different Political Systems
The Central Committee often serves as the principal policymaking body in communist and socialist political systems, exemplified by the Communist Party of China and the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, where it shapes broad strategic decisions. The Secretariat, as seen in the Soviet Union and Vietnam, functions as an administrative arm responsible for implementing the Central Committee's decisions and managing day-to-day party affairs. In contrast, Western political systems lack a direct equivalent, but executive committees or cabinets perform similar operational roles to the Secretariat within their governance structures.
Impact on Governance and Organizational Structure
The Central Committee holds broad decision-making authority and sets long-term strategic policies, directly impacting the governance framework by representing the interests of the entire party membership. The Secretariat, tasked with executing decisions made by the Central Committee, manages daily administrative functions and ensures organizational coherence and operational efficiency. Together, the Central Committee and Secretariat create a dual-layer leadership structure that balances high-level policy direction with effective implementation across the organization.
Central Committee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com