Political integration enhances cooperation among nations, fostering stability and unified policy responses to global challenges. This process facilitates the creation of supranational institutions that manage shared interests, promoting peace and economic growth. Discover how political integration can impact your country's future by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
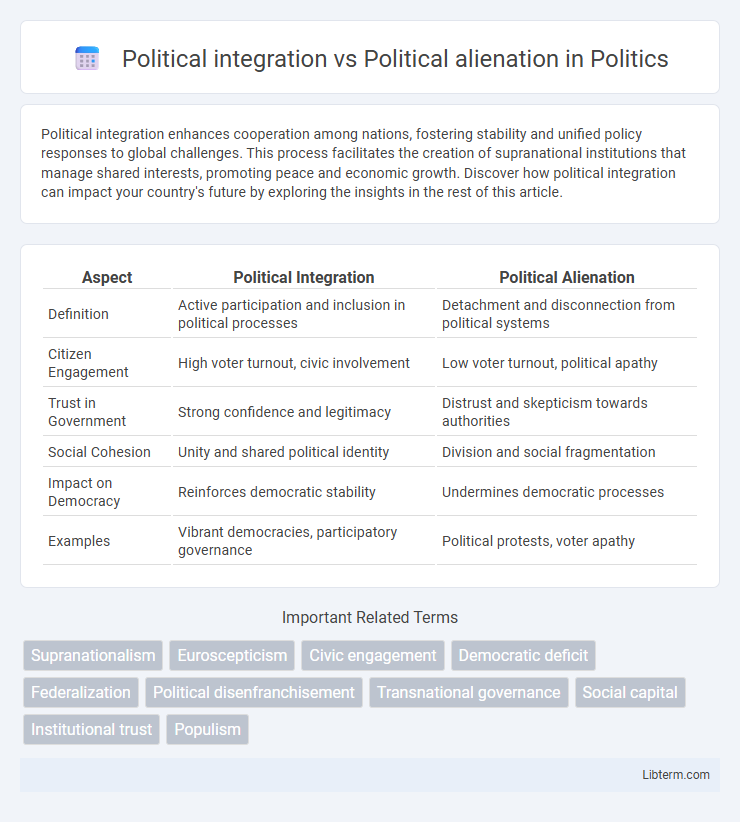
| Aspect | Political Integration | Political Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation and inclusion in political processes | Detachment and disconnection from political systems |
| Citizen Engagement | High voter turnout, civic involvement | Low voter turnout, political apathy |
| Trust in Government | Strong confidence and legitimacy | Distrust and skepticism towards authorities |
| Social Cohesion | Unity and shared political identity | Division and social fragmentation |
| Impact on Democracy | Reinforces democratic stability | Undermines democratic processes |
| Examples | Vibrant democracies, participatory governance | Political protests, voter apathy |
Defining Political Integration and Political Alienation
Political integration refers to the process by which individuals or groups become fully involved and accepted within a political system, fostering a sense of belonging and participation in governance. Political alienation describes a condition where citizens feel disconnected, powerless, or estranged from political institutions and processes, leading to disengagement and apathy. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing citizen-state relationships and the effectiveness of democratic systems.
Historical Contexts of Political Unity and Disconnection
Historical contexts of political integration often highlight the formation of empires, nation-states, and federations that unified diverse groups under centralized governance, promoting social cohesion and collective identity. Political alienation emerges prominently during periods of colonial rule, authoritarian regimes, or systemic exclusion, where marginalized populations experience disenfranchisement and disconnect from political processes. The contrasts between political unity and disconnection are evident in events like the unification of Germany in the 19th century versus the post-colonial struggles in Africa, illustrating how historical power dynamics shape citizen engagement.
Key Drivers Behind Political Integration
Key drivers behind political integration include shared values, mutual economic benefits, and effective governance structures fostering cooperation among diverse groups. Institutional frameworks like constitutions and legal systems play a crucial role in uniting different political entities under common goals. Social cohesion and inclusive policies reduce political alienation by promoting participation and trust in political processes.
Causes and Symptoms of Political Alienation
Political alienation arises from causes such as lack of trust in government, perceived inefficacy of political participation, and social exclusion. Symptoms include political apathy, low voter turnout, and disengagement from civic activities, reflecting citizens' feelings of powerlessness and disconnection from political institutions. This alienation often stems from systemic corruption, economic inequality, and unresponsiveness of political elites.
Social Impacts of Integrated Political Systems
Integrated political systems foster social cohesion by promoting inclusive governance and equal representation, which reduces feelings of alienation among diverse groups. Enhanced political participation and collaboration lead to greater social trust and collective identity, improving overall community well-being. Conversely, political integration mitigates social conflicts by addressing disparities and ensuring that marginalized voices are incorporated into decision-making processes.
Consequences of Widespread Political Alienation
Widespread political alienation erodes democratic participation, leading to lower voter turnout and weakened legitimacy of governing institutions. This alienation fosters political apathy and distrust, increasing vulnerability to populist movements and extremist ideologies. Consequently, social cohesion deteriorates, destabilizing political systems and impeding effective policy implementation.
Political Participation: Bridging Integration and Alienation
Political participation serves as a critical bridge between political integration and political alienation by enabling citizens to engage actively in democratic processes, fostering a sense of belonging and trust in governmental institutions. High levels of voter turnout, civic engagement, and involvement in public decision-making correlate with stronger political integration, reducing feelings of exclusion and disillusionment. Conversely, political alienation manifests when individuals perceive their participation as ineffective or disregarded, leading to decreased political efficacy and social cohesion.
Case Studies: Nations Experiencing Integration vs. Alienation
Societies like Germany and Canada exemplify political integration through inclusive governance and federal structures that accommodate diverse cultural identities, fostering unity and stability. Conversely, regions such as Catalonia in Spain and Kashmir in India demonstrate political alienation as marginalized groups experience exclusion and limited political representation, leading to unrest and demands for autonomy. These case studies reveal the critical role of equitable political participation in preventing alienation and sustaining national cohesion.
Policy Strategies to Foster Political Integration
Policy strategies to foster political integration prioritize inclusive governance, equitable resource distribution, and civic education to enhance citizen engagement and trust in political institutions. Implementing transparent decision-making processes and promoting participatory democracy help mitigate political alienation by giving marginalized groups a voice in shaping policies. Strengthening social cohesion through community-building initiatives and addressing systemic inequalities ensures more effective political integration and reduces feelings of disenfranchisement.
Future Perspectives: Overcoming Political Alienation
Future perspectives on overcoming political alienation emphasize enhancing civic education and promoting inclusive governance to rebuild trust between citizens and political institutions. Digital platforms and participatory democracy initiatives are expected to create more responsive political systems that engage diverse populations effectively. Strengthening community networks and fostering dialogue can mitigate alienation by making political processes more transparent and accessible.
Political integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com