Loyal voters consistently support the same political party or candidate across multiple elections, playing a crucial role in shaping election outcomes. Their unwavering commitment often influences campaign strategies and policy focus. Discover how loyal voter behavior impacts democracy and what it means for your vote in upcoming elections.
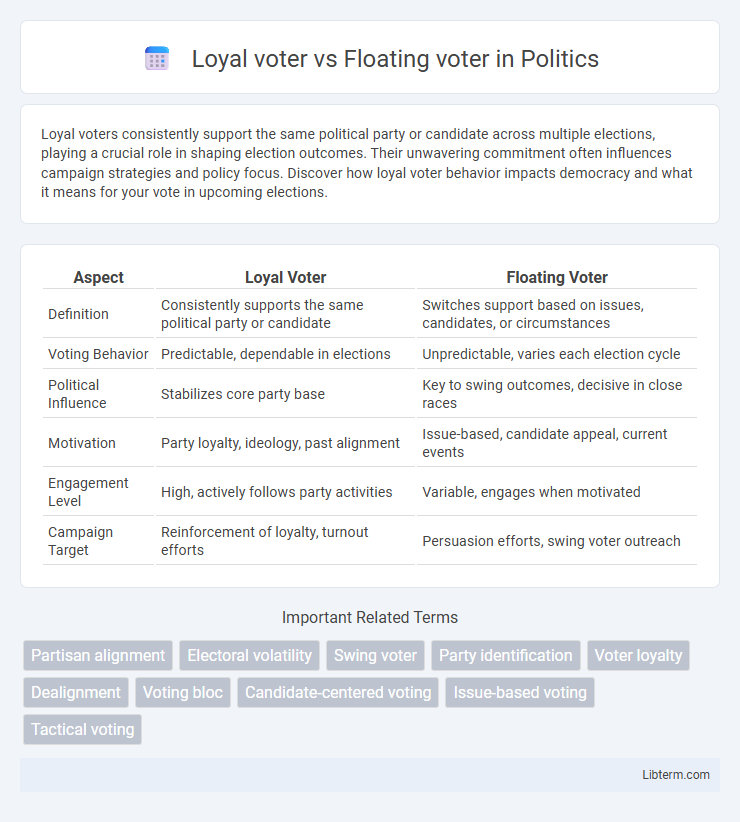
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Loyal Voter | Floating Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistently supports the same political party or candidate | Switches support based on issues, candidates, or circumstances |
| Voting Behavior | Predictable, dependable in elections | Unpredictable, varies each election cycle |
| Political Influence | Stabilizes core party base | Key to swing outcomes, decisive in close races |
| Motivation | Party loyalty, ideology, past alignment | Issue-based, candidate appeal, current events |
| Engagement Level | High, actively follows party activities | Variable, engages when motivated |
| Campaign Target | Reinforcement of loyalty, turnout efforts | Persuasion efforts, swing voter outreach |
Understanding Loyal Voters: Definition and Traits
Loyal voters consistently support the same political party or candidate across multiple elections, demonstrating strong party identification and ideological alignment. Traits of loyal voters include high political engagement, consistent voting behavior, and a tendency to rely on party cues when making decisions. This reliable voter segment often influences election outcomes by providing a stable base for political parties.
Who Are Floating Voters? Characteristics Explained
Floating voters, also known as swing voters, are individuals who do not have a fixed political allegiance and can be persuaded to support different parties or candidates in each election. They often make their decisions based on current issues, candidate appeal, and campaign effectiveness rather than party loyalty. These voters tend to be more informed, open-minded, and responsive to changing political climates, making them crucial targets for electoral strategies and opinion polling.
Historical Trends: Loyalty vs. Volatility in Voter Behavior
Historical trends reveal that loyal voters consistently support the same political party across multiple election cycles, providing a stable base of electoral support. Floating voters, on the other hand, exhibit high volatility, frequently switching allegiances based on current issues, candidate appeal, or socio-economic changes. This dynamic significantly impacts election outcomes, as parties depend on loyal voters for consistent turnout while strategizing to sway floating voters who can decisively influence closely contested races.
Factors Influencing Voter Loyalty
Voter loyalty is shaped by factors such as long-standing party identification, consistent policy alignment, and strong ideological beliefs firmly rooted in a voter's values. Demographic characteristics like age, education, and socioeconomic status contribute to a voter's likelihood of being loyal, with older and more politically engaged individuals tending to display higher loyalty. In contrast, floating voters often exhibit lower political commitment influenced by current issues, candidate appeal, and short-term economic conditions, leading to fluctuating support between election cycles.
Why Some Voters Remain Undecided
Some voters remain undecided due to a lack of strong party identification or conflicting policy priorities, making them floating voters who evaluate candidates each election cycle. Loyal voters consistently support a specific party based on deep-rooted beliefs or long-term alignment with party values, reducing their likelihood of indecision. The complexity of political platforms and fluctuating campaign dynamics often causes floating voters to delay commitment until late in the electoral process.
Impact of Loyal Voters on Election Outcomes
Loyal voters consistently support a particular political party or candidate, providing a stable base that can significantly influence election outcomes by ensuring predictable vote counts. Their unwavering commitment often shapes campaign strategies, as parties allocate resources to maximize turnout among these dependable voters. In contrast, floating voters remain undecided or switch allegiances, making loyal voters critical for establishing a foundational advantage in competitive races.
The Role of Floating Voters in Swing Elections
Floating voters, typically undecided or swing voters, play a crucial role in determining the outcome of swing elections by shifting their support between parties based on current issues and candidate appeal. Unlike loyal voters who consistently back a specific party, floating voters' decisions can be influenced by campaign strategies, economic conditions, and social trends. Their unpredictability makes them the primary target for political campaigns aiming to secure victory in closely contested electoral districts.
Campaign Strategies: Targeting Loyalty vs. Persuasion
Campaign strategies for loyal voters emphasize reinforcing party allegiance through consistent messaging, rewards, and mobilization efforts that capitalize on established trust and voter commitment. In contrast, persuading floating voters involves tailored communication, addressing their specific concerns, and highlighting policy benefits to sway their undecided stance. Successful campaigns allocate resources strategically to maintain loyalty while actively engaging swing voters with persuasive appeals and issue-based outreach.
Social and Demographic Profiles of Loyal and Floating Voters
Loyal voters typically exhibit strong party identification, higher political engagement, and consistent voting patterns, often correlating with older age groups, stable socioeconomic status, and homogeneous social networks. Floating voters display less party loyalty, higher electoral volatility, and are often younger, urban, and more diverse in education and income levels. Social factors such as occupational diversity, media consumption, and exposure to varied social groups significantly influence the demographic distinctions between loyal and floating voters.
Future Trends: Shifting Voter Allegiances in Modern Politics
Loyal voters consistently support a particular party or candidate, providing a stable foundation in elections, whereas floating voters, who may change their preferences based on current issues or candidate appeal, increasingly influence election outcomes. Future trends indicate a rise in the significance of floating voters due to growing political polarization and the impact of social media on voter information and sentiment. Political campaigns are therefore investing more in data analytics and targeted messaging to sway this unpredictable voter segment and shape modern electoral dynamics.
Loyal voter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com