Misfeasance refers to the improper performance of a lawful act, which can lead to legal liability or damages. Understanding the nuances of misfeasance is crucial for identifying when actions, though not inherently illegal, may cause harm or breach duty. Explore this article to learn more about how misfeasance impacts legal responsibilities and your rights.
Table of Comparison
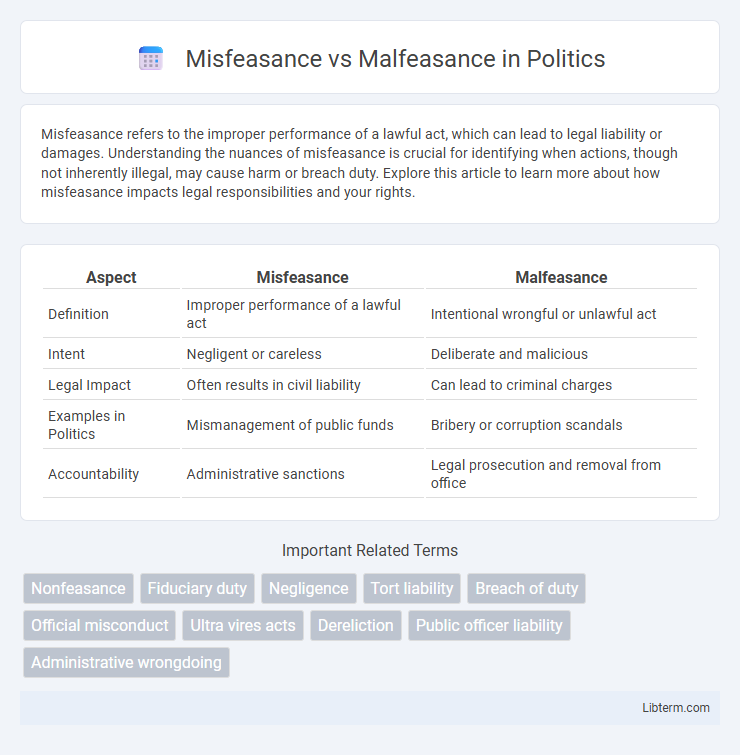
| Aspect | Misfeasance | Malfeasance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improper performance of a lawful act | Intentional wrongful or unlawful act |
| Intent | Negligent or careless | Deliberate and malicious |
| Legal Impact | Often results in civil liability | Can lead to criminal charges |
| Examples in Politics | Mismanagement of public funds | Bribery or corruption scandals |
| Accountability | Administrative sanctions | Legal prosecution and removal from office |
Introduction to Misfeasance and Malfeasance
Misfeasance refers to the improper or negligent performance of an act, resulting in harm or injury, while malfeasance involves intentional wrongdoing or illegal conduct by a public official or individual in a position of authority. Both terms are critical in legal contexts, distinguishing between accidental misdeeds and deliberate misconduct. Understanding the difference between misfeasance and malfeasance is essential for assessing liability and enforcement actions in civil and criminal law.
Defining Misfeasance
Misfeasance refers to the improper or negligent performance of a lawful act, resulting in harm or damage, often due to carelessness or error. It differs from malfeasance, which involves intentional wrongdoing or illegal actions committed by a public official or employee. Understanding misfeasance is crucial in legal contexts where duty-bound individuals fail to meet standards of care, causing unintended consequences.
Understanding Malfeasance
Malfeasance refers to wrongful or illegal conduct, especially by a public official or a person in a position of trust, involving intentional actions that cause harm or violate laws. It is distinguished from misfeasance, which involves lawful but improper or negligent performance of duties. Understanding malfeasance requires recognizing deliberate misconduct or abuse of power that results in damage or injustice.
Key Differences: Misfeasance vs Malfeasance
Misfeasance refers to the improper or negligent performance of a lawful act, whereas malfeasance involves the commission of an unlawful or wrongful act, particularly by a public official. Key differences include intent and legality: misfeasance is often attributed to carelessness or failure to exercise due care, while malfeasance indicates intentional wrongdoing or corruption. Legal consequences vary, with malfeasance typically resulting in more severe penalties due to its deliberate nature.
Legal Implications of Misfeasance
Misfeasance involves the improper performance of a lawful act, which can lead to civil liability for negligence or breach of duty. Courts often hold professionals or public officials accountable for misfeasance when their actions cause harm or financial loss to others. Legal implications include potential damages awards and injunctions to prevent further improper conduct.
Legal Consequences of Malfeasance
Malfeasance involves intentional wrongdoing or illegal acts by public officials or individuals in positions of trust, leading to serious legal consequences such as criminal charges, civil penalties, and removal from office. Courts often impose punitive damages or imprisonment to deter malicious conduct and uphold public trust. Misfeasance, by contrast, typically results in lesser legal actions focusing on negligence or improper performance without intent to harm.
Real-World Examples of Misfeasance
Misfeasance involves improper execution of a lawful act, such as a government official neglecting safety protocols during a public infrastructure project, leading to accidents. In contrast, malfeasance refers to intentional wrongdoing or illegal acts, like embezzlement by a corporate executive. Real-world cases of misfeasance include negligence by public servants in maintaining public parks or faulty administration in issuing permits that cause harm or loss to the community.
Notable Cases of Malfeasance
Notable cases of malfeasance include the Enron scandal, where executives engaged in fraudulent accounting practices to hide debt and inflate profits, leading to one of the largest corporate bankruptcies in history. The Volkswagen emissions scandal exposed deliberate manipulation of emission tests to meet regulatory standards, resulting in hefty fines and criminal charges. In the political arena, the Watergate scandal involved illegal activities such as wiretapping and obstruction of justice by government officials, culminating in President Nixon's resignation.
Preventing Misfeasance and Malfeasance in Organizations
Implementing robust internal controls and regular employee training are essential for preventing misfeasance and malfeasance in organizations. Establishing clear policies on ethical behavior, coupled with transparent reporting mechanisms such as whistleblower programs, helps detect and deter improper conduct. Regular audits and strong leadership commitment to integrity further reinforce accountability and mitigate risks of intentional or negligent wrongdoing.
Conclusion: Importance of Distinguishing Misfeasance and Malfeasance
Distinguishing misfeasance from malfeasance is crucial for accurate legal accountability and appropriate remedial measures. Misfeasance involves improper performance of a lawful act, whereas malfeasance constitutes intentional wrongdoing or illegal acts. Clear differentiation ensures proper enforcement of laws, prevents misuse of authority, and upholds justice in administrative and corporate governance.
Misfeasance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com