A swing seat provides a comfortable and fun spot to relax in your backyard or garden, perfect for both children and adults. Designed with durable materials and ergonomic support, it enhances outdoor spaces by combining functionality with style. Discover how to choose the ideal swing seat for your needs and create a relaxing retreat in your outdoor area by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
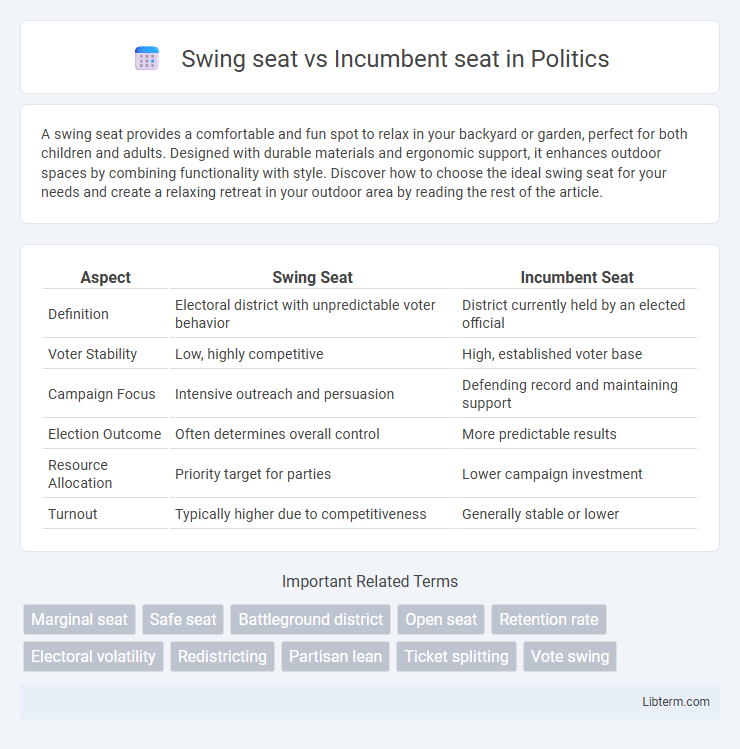
| Aspect | Swing Seat | Incumbent Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electoral district with unpredictable voter behavior | District currently held by an elected official |
| Voter Stability | Low, highly competitive | High, established voter base |
| Campaign Focus | Intensive outreach and persuasion | Defending record and maintaining support |
| Election Outcome | Often determines overall control | More predictable results |
| Resource Allocation | Priority target for parties | Lower campaign investment |
| Turnout | Typically higher due to competitiveness | Generally stable or lower |
Introduction to Swing Seats and Incumbent Seats
Swing seats refer to electoral districts where the vote can easily shift between parties, making them highly competitive and crucial in determining election outcomes. Incumbent seats are held by current officeholders who often have the advantage of name recognition, established voter base, and easier access to campaign resources. Understanding the dynamics of swing seats versus incumbent seats is essential for strategizing political campaigns and predicting election results.
Defining Swing Seats: Key Characteristics
Swing seats are electoral districts characterized by a balanced voter base that can oscillate between major political parties, making them highly competitive and pivotal in elections. These seats often have no dominant party allegiance, with past election results showing narrow victory margins typically under 10%. Voter demographics in swing seats tend to be diverse, representing a mix of urban, suburban, and rural populations, which contributes to their unpredictable voting patterns.
Understanding Incumbent Seats: What Sets Them Apart
Incumbent seats are held by current officeholders and typically benefit from name recognition, established voter bases, and access to campaign resources, creating an electoral advantage. These seats often feature lower volatility in election outcomes compared to swing seats, which represent districts where voter allegiance frequently shifts between parties. Understanding the stability and entrenched support in incumbent seats helps explain why they differ significantly from the dynamic, competitive nature of swing seats.
Political Significance of Swing Seats
Swing seats hold critical political significance due to their unpredictable voter behavior, often deciding the outcome of elections and shaping legislative majorities. Unlike incumbent seats, which generally favor sitting representatives with established voter bases, swing seats experience fluctuating party control, making them key battlegrounds in electoral strategies. Political parties invest substantial resources and tailored campaigns in these districts to sway undecided voters, recognizing their potential to shift power balances at local, state, and national levels.
Advantages of Holding an Incumbent Seat
Holding an incumbent seat provides significant advantages such as name recognition, established voter base, and easier access to campaign funding, which can deter challengers and increase re-election chances. Incumbents benefit from existing relationships with constituents and extensive experience navigating legislative processes, enhancing their effectiveness. These factors create a formidable barrier for opponents in swing seats, often shifting electoral dynamics in favor of the incumbent.
Voter Behavior in Swing vs Incumbent Districts
Voter behavior in swing seats often exhibits higher volatility due to less party loyalty and more influence from current events and candidate appeal, leading to frequent shifts in electoral outcomes. Incumbent seats typically experience more stable voter support because of established name recognition, constituent services, and perceived experience, which strengthens incumbency advantage. Campaign strategies in swing districts prioritize persuasion and turnout, whereas incumbent districts focus heavily on maintaining a reliable voter base and reinforcing past achievements.
Campaign Strategies: Swing Seats vs Incumbent Seats
Campaign strategies for swing seats prioritize targeted voter outreach, data-driven messaging, and allocating significant resources to sway undecided or moderate voters, focusing heavily on local issues and demographic trends. In contrast, campaigns for incumbent seats emphasize reinforcing the incumbent's achievements, leveraging name recognition, and mobilizing established supporter bases to maintain voter loyalty and turnout. Both strategies employ voter data analytics but differ in intensity and thematic focus to maximize election success in their respective contexts.
Historical Trends and Election Outcomes
Swing seats have historically played a pivotal role in determining election outcomes, often experiencing fluctuating party control that reflects broader political shifts. Incumbent seats tend to demonstrate higher re-election rates, with incumbents benefiting from name recognition, established voter bases, and resource advantages. Analysis of past elections reveals that swing seats frequently act as battlegrounds, attracting increased campaign investment and voter turnout, thereby influencing the overall balance of power in legislative bodies.
Challenges Faced by Swing and Incumbent Candidates
Swing seat candidates face challenges including unpredictable voter behavior, fluctuating party support, and the need to appeal to a diverse electorate. Incumbent candidates encounter obstacles such as voter fatigue, heightened scrutiny over their record, and the pressure to address unmet expectations. Both must strategically allocate resources and personalize campaigns to navigate the complex political landscape effectively.
Conclusion: Impact on the Political Landscape
Swing seats play a critical role in determining election outcomes by shifting political power and influencing party strategies, while incumbent seats typically offer stability due to established voter loyalty and name recognition. The competitive nature of swing seats encourages parties to tailor policies and campaign efforts to local issues, often leading to more dynamic political engagement and responsiveness. In contrast, the relative predictability of incumbent seats can consolidate power structures but may also reduce incentives for innovation and change within the political landscape.
Swing seat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com