Maintaining independence fosters personal growth and self-confidence, allowing you to make decisions that align with your values and goals. It strengthens problem-solving skills and encourages responsibility in both personal and professional areas. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for enhancing your independence.
Table of Comparison
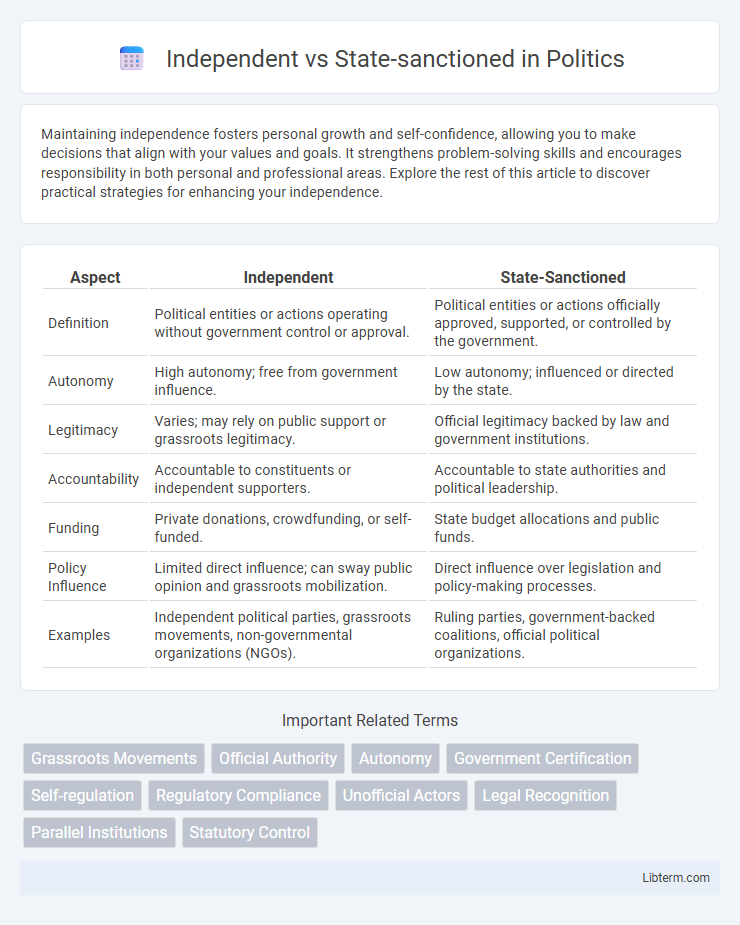
| Aspect | Independent | State-Sanctioned |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political entities or actions operating without government control or approval. | Political entities or actions officially approved, supported, or controlled by the government. |
| Autonomy | High autonomy; free from government influence. | Low autonomy; influenced or directed by the state. |
| Legitimacy | Varies; may rely on public support or grassroots legitimacy. | Official legitimacy backed by law and government institutions. |
| Accountability | Accountable to constituents or independent supporters. | Accountable to state authorities and political leadership. |
| Funding | Private donations, crowdfunding, or self-funded. | State budget allocations and public funds. |
| Policy Influence | Limited direct influence; can sway public opinion and grassroots mobilization. | Direct influence over legislation and policy-making processes. |
| Examples | Independent political parties, grassroots movements, non-governmental organizations (NGOs). | Ruling parties, government-backed coalitions, official political organizations. |
Introduction to Independent vs State-Sanctioned
Independent organizations operate autonomously from government control, allowing for unbiased decision-making and innovation in various sectors. State-sanctioned entities function under governmental authority or regulations, ensuring alignment with public policies and national objectives. The distinction affects governance, accountability, and the scope of influence within political and social frameworks.
Defining Independent Organizations
Independent organizations operate autonomously without direct control or influence from government entities, allowing for unbiased decision-making and diverse perspectives. These entities often rely on private funding, volunteer support, and transparent governance structures to maintain independence. Differentiating independent organizations from state-sanctioned ones hinges on their operational freedom, accountability mechanisms, and ability to advocate without governmental restrictions.
Understanding State-Sanctioned Entities
State-sanctioned entities operate under government authority, receiving official approval and often funding to perform specific functions aligned with national policies. These organizations are typically accountable to regulatory frameworks and must adhere to state-mandated standards and objectives. Understanding their role involves recognizing their influence on public administration, law enforcement, and essential services within the controlled legal and social environment established by the government.
Historical Overview: Independence and State Control
Independent movements throughout history have often emerged as grassroots efforts challenging established authority, driven by social, political, or economic grievances. State-sanctioned initiatives typically reflect centralized power structures aiming to maintain control and stability through official policies and regulations. Historical examples include the American Revolution as an independent uprising and the Soviet Union's state-controlled cultural programs exemplifying institutional control over expression.
Key Differences in Operation and Governance
Independent organizations operate autonomously without direct control from government entities, allowing greater flexibility in decision-making and resource allocation. State-sanctioned entities function under government oversight, adhering to specific regulations, policies, and often relying on public funding. Governance in independent bodies tends to be self-regulated with diverse stakeholder involvement, while state-sanctioned organizations are subject to bureaucratic processes, accountability standards, and political influence.
Advantages of Independence
Independence offers organizations greater flexibility in decision-making, enabling faster adaptation to market changes without bureaucratic constraints. Independent entities can maintain impartiality and avoid political influence, which often enhances credibility and trust among stakeholders. Financially, they may access diverse funding sources, reducing reliance on government budgets and fostering innovation through competitive practices.
Benefits and Drawbacks of State Sanctioning
State-sanctioned entities benefit from legal protection, government funding, and formal recognition, enabling scalability and stability in operations. However, state sanctioning often limits autonomy, imposing regulatory constraints and potential political interference that may hinder innovation and responsiveness. Balancing state support with independence is crucial for sustainable effectiveness and credibility.
Case Studies: Independent vs State-Sanctioned Examples
Case studies reveal distinct outcomes in independent versus state-sanctioned initiatives, highlighting variations in autonomy and impact. Independent projects, such as grassroots environmental campaigns in Brazil, often foster innovation and community engagement but face regulatory challenges. Conversely, state-sanctioned programs like China's social credit system demonstrate extensive reach and enforcement capability but raise concerns about surveillance and civil liberties.
Public Trust and Accountability
Independent organizations often foster higher public trust due to perceived impartiality and reduced political influence, enhancing accountability through transparent governance structures. State-sanctioned entities may face challenges in maintaining credibility as their actions can be viewed as extensions of government agendas, potentially undermining public confidence. Effective accountability mechanisms must be clearly defined and rigorously enforced in both contexts to ensure legitimacy and sustained public trust.
Future Trends: Independence or State Oversight?
Future trends reveal a growing tension between Independent entities and State-sanctioned authorities regarding governance and regulation. Technological advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and decentralized systems empower independent organizations to operate autonomously, challenging traditional state oversight mechanisms. Governments explore hybrid regulatory frameworks integrating AI-driven monitoring tools to balance innovation with public accountability, signaling evolving models of cooperation rather than absolute control or independence.
Independent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com