Resignation is a formal declaration of an employee's intention to leave their current position, often requiring a written notice to ensure a smooth transition. Understanding the appropriate steps and timing can protect your professional reputation and maintain positive relationships with your employer. Read on to discover essential tips for handling your resignation gracefully and effectively.
Table of Comparison
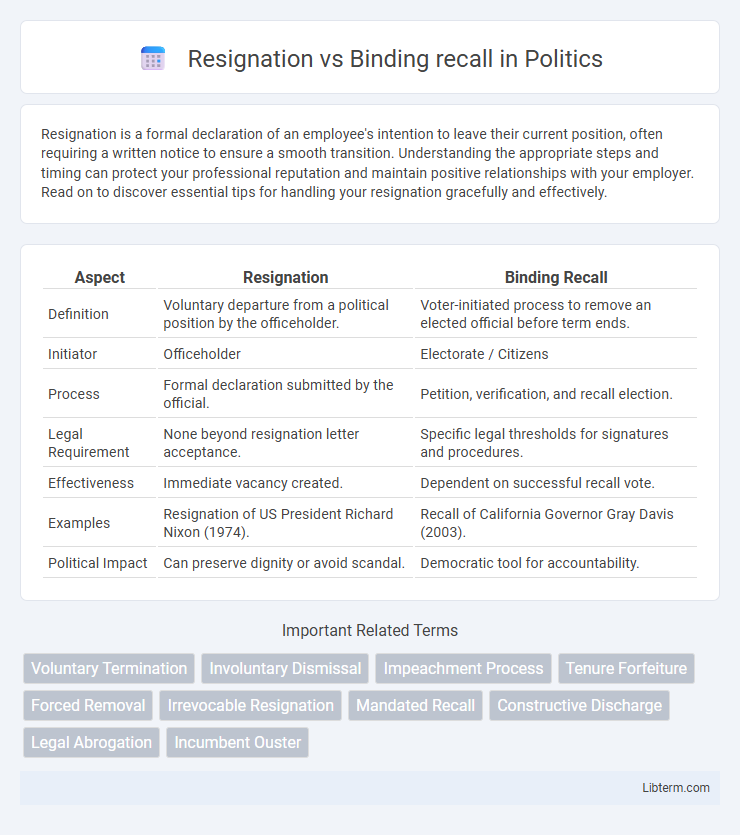
| Aspect | Resignation | Binding Recall |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary departure from a political position by the officeholder. | Voter-initiated process to remove an elected official before term ends. |
| Initiator | Officeholder | Electorate / Citizens |
| Process | Formal declaration submitted by the official. | Petition, verification, and recall election. |
| Legal Requirement | None beyond resignation letter acceptance. | Specific legal thresholds for signatures and procedures. |
| Effectiveness | Immediate vacancy created. | Dependent on successful recall vote. |
| Examples | Resignation of US President Richard Nixon (1974). | Recall of California Governor Gray Davis (2003). |
| Political Impact | Can preserve dignity or avoid scandal. | Democratic tool for accountability. |
Understanding Resignation: Definition and Scenarios
Resignation refers to an employee's voluntary decision to leave a position, often formalized through a written notice specifying the last working day. Common scenarios for resignation include seeking better career opportunities, personal reasons, or dissatisfaction with job conditions. Understanding resignation helps clarify legal implications, notice periods, and impacts on employee benefits compared to binding recall, which involves employer-driven reemployment mandates.
What is a Binding Recall? Key Principles
A Binding Recall is a formal legal mechanism allowing a company to mandatorily retrieve products from the market to protect consumer safety or comply with regulations. Key principles include its enforceability by regulatory authorities, the requirement for clear communication with consumers, and the obligation for companies to cover associated costs. Unlike voluntary resignation, a Binding Recall mandates action under legal or regulatory frameworks to ensure public safety and compliance.
Legal Frameworks Governing Resignation vs Binding Recall
Legal frameworks governing resignation establish clear protocols for voluntary termination of employment, emphasizing employee intent and contract terms to ensure lawful separation. Binding recall laws regulate the reinstatement of employees, often mandating specific conditions and timeframes under labor regulations or collective bargaining agreements to protect worker rights. Both legal constructs balance employer interests with employee protections, relying on jurisdiction-specific statutes such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) or the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) in the U.S. context.
Initiation Processes: Voluntary vs Involuntary Removal
Resignation is a voluntary removal process initiated by an individual choosing to leave a position, often requiring formal notice and documentation. Binding recall, conversely, is an involuntary removal initiated by an external authority or organization, compelling a person to vacate their role, often due to legal or contractual obligations. The initiation distinction profoundly impacts procedural requirements, legal implications, and the individual's future eligibility within the organization or industry.
Key Motivations for Resignation and Binding Recall
Key motivations for resignation often include personal career growth, job dissatisfaction, or seeking better work-life balance, driven by individual goals and external opportunities. Binding recall is primarily motivated by organizational needs to retain critical talent, ensure continuity, and respond to workforce planning challenges. Both mechanisms serve distinct strategic purposes, with resignation reflecting voluntary employee decisions and binding recall representing employer-initiated retention efforts.
Impact on Leadership and Organizational Stability
Resignation often leads to immediate leadership gaps and potential instability as organizations must quickly adjust to losing key decision-makers, whereas binding recall mechanisms ensure leadership continuity by enabling the reinstatement of experienced leaders, preserving institutional knowledge. Binding recall reinforces organizational stability by reducing turnover-related disruptions and maintaining strategic direction during turbulent periods. The choice between resignation and binding recall significantly impacts leadership effectiveness and long-term organizational resilience.
Rights and Protections: Officials in Resignation vs Recall
Officials who resign voluntarily retain limited rights, often forfeiting benefits such as severance or re-employment protections, whereas those subject to a binding recall maintain certain legal safeguards, including due process and potential reinstatement rights. Resignation typically terminates the official's contractual and statutory protections, while binding recall procedures ensure adherence to electoral laws and protect officials from arbitrary removal. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in evaluating the balance between governmental accountability and the protection of elected officials' rights.
Public Perception: Trust and Accountability
Resignation often signals acceptance of responsibility and can restore public trust by demonstrating accountability in leadership roles. Binding recall, enforced through legal or political mechanisms, empowers citizens with direct control, enhancing democratic legitimacy but sometimes fostering public skepticism if perceived as politically motivated. Both processes impact public perception differently; resignation may be viewed as a voluntary act of integrity, while binding recall reflects systemic checks on power.
Historical Cases: Resignation and Binding Recall in Practice
Historical cases demonstrate that resignation often serves as a voluntary and strategic tool for political figures to avoid prolonged conflict or legal consequences, whereas binding recall provides a formal mechanism for voters to remove officials who fail to meet public expectations. Notable examples include California's use of binding recall elections, such as the 2003 recall of Governor Gray Davis, which underscored the recall's power to reshape political leadership directly through popular vote. Resignation cases, like President Richard Nixon's 1974 departure amid the Watergate scandal, highlight personal and political pressures influencing voluntary exits absent formal recall processes.
Choosing the Right Mechanism: Key Considerations
Choosing between resignation and binding recall hinges on the desired level of control and legal implications for a company's leadership. Resignation allows a director to voluntarily step down without external pressures, preserving professional reputation and ensuring a smoother transition. Binding recall provides shareholders with the power to remove a director, emphasizing accountability but potentially triggering organizational instability or conflicts.
Resignation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com