An adjournment motion is a parliamentary procedure used to temporarily suspend a meeting or session, allowing members to pause discussions and reconvene later. This motion helps manage time effectively and address urgent matters without closing the session entirely. Explore the article to understand how you can strategically use adjournment motions in your legislative or organizational meetings.
Table of Comparison
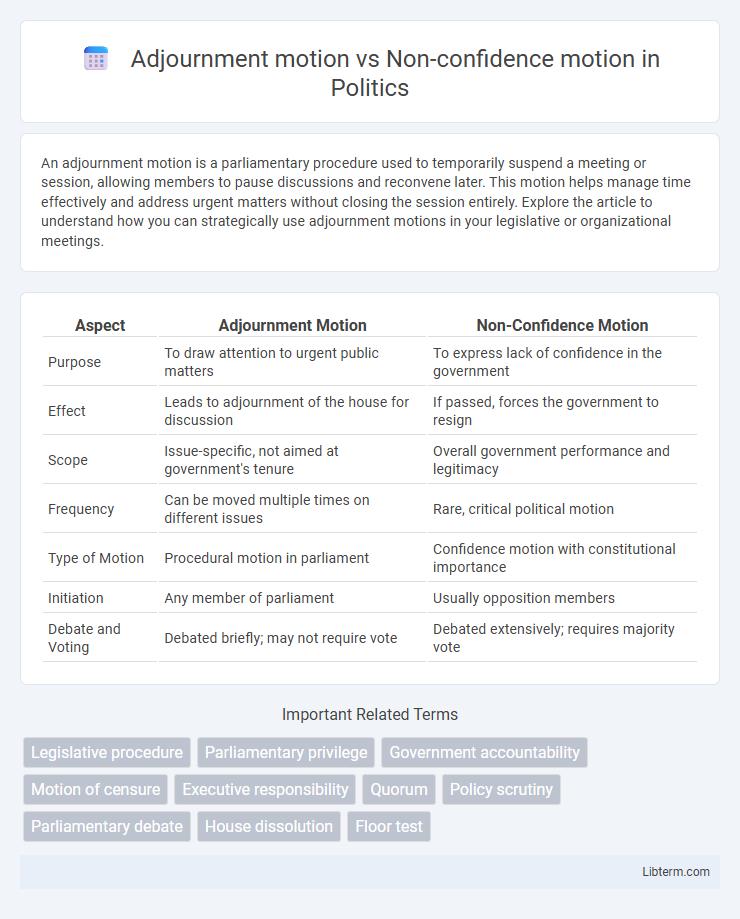
| Aspect | Adjournment Motion | Non-Confidence Motion |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To draw attention to urgent public matters | To express lack of confidence in the government |
| Effect | Leads to adjournment of the house for discussion | If passed, forces the government to resign |
| Scope | Issue-specific, not aimed at government's tenure | Overall government performance and legitimacy |
| Frequency | Can be moved multiple times on different issues | Rare, critical political motion |
| Type of Motion | Procedural motion in parliament | Confidence motion with constitutional importance |
| Initiation | Any member of parliament | Usually opposition members |
| Debate and Voting | Debated briefly; may not require vote | Debated extensively; requires majority vote |
Introduction to Parliamentary Motions
Parliamentary motions serve distinct functions: an adjournment motion is used to temporarily halt proceedings, often to allow debate on urgent matters, while a non-confidence motion challenges the government's legitimacy, potentially leading to its collapse. Adjournment motions are procedural tools aimed at managing the legislative agenda without affecting government stability. Non-confidence motions hold significant political weight, as their passage signals parliamentary withdrawal of support from the executive branch, triggering possible elections or government reformation.
Definition of Adjournment Motion
An adjournment motion is a parliamentary procedure used to temporarily suspend or postpone a sitting session to discuss urgent matters requiring immediate attention. It allows members to raise specific issues not included in the agenda, facilitating prompt debate on pressing concerns without delaying ongoing legislative business. Unlike a non-confidence motion, which challenges the government's legitimacy, an adjournment motion focuses on procedural suspension for targeted discussion.
Definition of Non-confidence Motion
A Non-confidence motion, also known as a vote of no confidence, is a formal parliamentary procedure where members express that they no longer support the current government or executive leadership, potentially leading to its resignation or dissolution. It serves as a critical mechanism to hold the administration accountable, ensuring that the government maintains the confidence of the legislative body. Unlike an adjournment motion, which aims to temporarily suspend proceedings to discuss urgent matters, a Non-confidence motion directly challenges the legitimacy and continuation of the ruling government.
Constitutional Basis for Both Motions
Adjournment motion is rooted in parliamentary procedure under rules of procedure and conduct of business, allowing members to raise urgent public matters not covered in the agenda, but it lacks an explicit constitutional provision. Non-confidence motion holds a constitutional basis, as it is linked to Article 75 of the Indian Constitution, empowering the Lok Sabha to withdraw support from the Council of Ministers, leading to its resignation or dissolution. The key distinction lies in the constitutional sanction, with non-confidence motions having the authority to affect the government's tenure, while adjournment motions serve primarily as tools for immediate debates without constitutional consequences.
Objectives of Adjournment Motion
An Adjournment Motion aims to draw attention to a specific urgent matter of public importance that requires immediate debate in the legislature, thereby temporarily suspending the regular business. Its objective is to highlight issues not included in the scheduled agenda, facilitating timely discussion and scrutiny by members. Unlike a Non-confidence Motion, which challenges the government's legitimacy and seeks to unseat it, the Adjournment Motion focuses solely on addressing urgent topics needing prompt legislative attention.
Objectives of Non-confidence Motion
A non-confidence motion primarily aims to demonstrate that the sitting government no longer commands the support of the majority in the legislature, which can lead to its resignation or dissolution of the assembly. This motion is a critical tool for holding the executive accountable and ensuring that the administration maintains the confidence of elected representatives. Unlike an adjournment motion that seeks to temporarily halt proceedings to discuss urgent matters, the non-confidence motion targets the legitimacy and continuation of the entire government.
Key Differences Between Adjournment and Non-confidence Motions
An adjournment motion is primarily used in parliamentary proceedings to request the suspension or postponement of a session to allow further discussion or investigation on a specific issue. In contrast, a non-confidence motion is a formal proposal indicating that the legislature has lost confidence in the government or a minister, potentially leading to their resignation or dissolution of the assembly. Key differences include their objectives--adjournment motions aim to address urgent matters temporarily, while non-confidence motions challenge the government's legitimacy and stability.
Procedural Requirements and Process
An adjournment motion requires notice and is used to temporarily suspend a sitting to discuss urgent matters, often requiring a simple majority to pass. A non-confidence motion demands a formal proposal indicating loss of majority support in the legislature, typically following stricter procedural rules, including advance notice and quorum verification. The non-confidence motion leads to government resignation or dissolution if passed, while the adjournment motion primarily emphasizes debate on specific issues without immediate governmental consequences.
Implications and Outcomes of Each Motion
An adjournment motion temporarily suspends parliamentary proceedings to address urgent matters, often leading to short-term delays without altering the government's stability. In contrast, a no-confidence motion challenges the government's legitimacy and, if passed, mandates its resignation or dissolution of parliament, directly impacting political power dynamics. The adjournment motion serves as a procedural tool for debate, while the no-confidence motion has significant constitutional and political consequences.
Comparative Analysis and Practical Examples
An adjournment motion is a procedural tool used in parliamentary systems to temporarily suspend proceedings for urgent matters, often requiring immediate attention but not necessarily challenging the government's authority. A non-confidence motion directly tests the government's legitimacy by seeking a parliamentary vote to confirm whether the executive retains majority support, potentially leading to resignation or elections if lost. For example, in India's Lok Sabha, adjournment motions have been employed to debate urgent issues like price hikes, whereas in the UK Parliament, non-confidence motions have led to significant political changes, such as the fall of Margaret Thatcher's government in 1990.
Adjournment motion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com