Citizens' juries bring together a diverse group of individuals to deliberate on public issues, fostering informed decision-making and democratic engagement. This method allows participants to weigh evidence, discuss different perspectives, and develop recommendations that reflect community values. Discover how citizens' juries can enhance your involvement in shaping policies by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
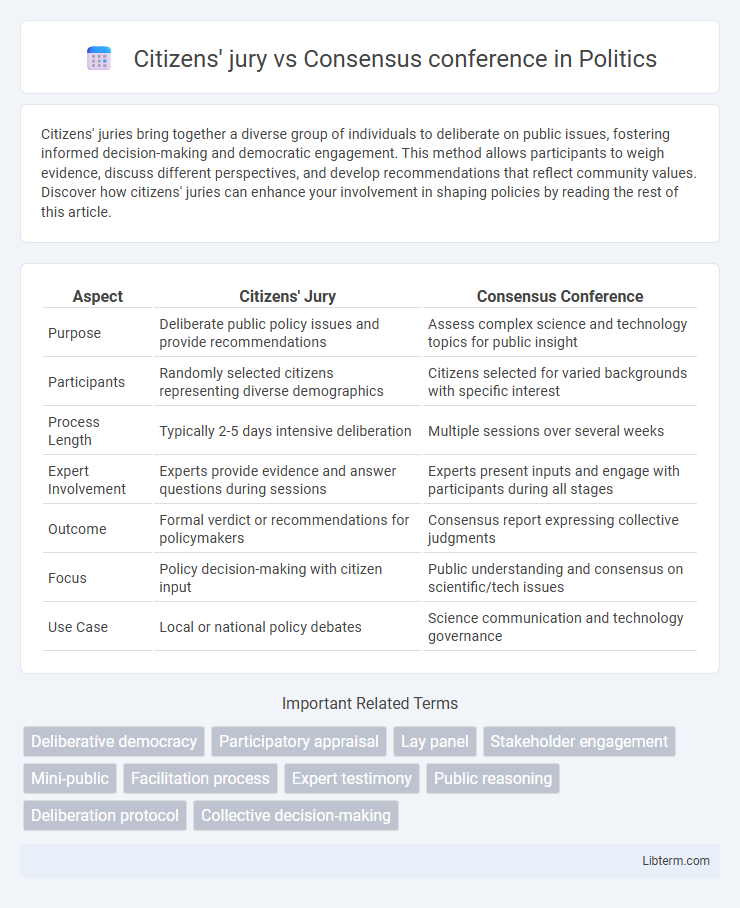
| Aspect | Citizens' Jury | Consensus Conference |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Deliberate public policy issues and provide recommendations | Assess complex science and technology topics for public insight |
| Participants | Randomly selected citizens representing diverse demographics | Citizens selected for varied backgrounds with specific interest |
| Process Length | Typically 2-5 days intensive deliberation | Multiple sessions over several weeks |
| Expert Involvement | Experts provide evidence and answer questions during sessions | Experts present inputs and engage with participants during all stages |
| Outcome | Formal verdict or recommendations for policymakers | Consensus report expressing collective judgments |
| Focus | Policy decision-making with citizen input | Public understanding and consensus on scientific/tech issues |
| Use Case | Local or national policy debates | Science communication and technology governance |
Introduction to Participatory Decision-Making
Citizens' juries and consensus conferences are prominent methods in participatory decision-making that engage diverse stakeholders to deliberate on complex policy issues. Citizens' juries involve a representative group of citizens evaluating evidence and expert testimony to reach informed judgments, while consensus conferences bring together laypersons and experts to collaboratively develop policy recommendations. Both approaches enhance democratic legitimacy by fostering transparency, inclusivity, and public empowerment in decision-making processes.
Defining Citizens' Juries
Citizens' juries are structured deliberative processes where a diverse group of citizens, typically 12 to 24, are selected to learn about, discuss, and provide recommendations on complex public policy issues. Unlike consensus conferences, which emphasize achieving collective agreement and involve more extended public engagement, citizens' juries prioritize informed, independent judgment through expert testimonies and facilitated discussions within a limited timeframe. Defining citizens' juries highlights their role in enhancing democratic legitimacy by providing policymakers with well-considered, representative citizen input grounded in evidence-based deliberation.
Understanding Consensus Conferences
Consensus conferences engage diverse citizen panels to deliberate on complex scientific or technological issues, aiming to produce well-rounded recommendations. These forums emphasize mutual understanding and consensus-building, often supported by expert presentations and open discussions. Unlike citizens' juries, which focus on decision-making and verdicts, consensus conferences prioritize exploring values and ethical implications to inform public policy.
Key Objectives and Principles
Citizens' juries prioritize deliberation among a representative group to provide informed recommendations on complex policy issues, emphasizing equal participation and transparency. Consensus conferences aim to achieve a collective agreement among diverse stakeholders, focusing on mutual understanding and collaborative problem-solving. Both methods uphold inclusivity, respect for differing viewpoints, and the goal of enhancing democratic decision-making through informed public engagement.
Selection of Participants
Citizens' juries select participants through stratified random sampling to represent a cross-section of the population, ensuring demographic and attitudinal diversity. Consensus conferences recruit laypeople primarily via voluntary applications, aiming for a balanced group with diverse perspectives relevant to the issue. Both methods emphasize inclusivity but differ in recruitment approach, impacting the representativeness and deliberative dynamics.
Procedural Differences
Citizens' juries involve a smaller group of randomly selected participants who deliberate over several days, guided by expert testimony and facilitators to reach a verdict on specific policy issues. Consensus conferences include a larger lay panel that interacts extensively with experts and stakeholders over multiple sessions, aiming to produce a collective report reflecting shared viewpoints. The procedural distinction lies in the citizens' jury's structured decision-making process culminating in a binding recommendation, while consensus conferences emphasize collaborative knowledge exchange without requiring unanimous decisions.
Stakeholder Involvement and Expert Input
Citizens' juries involve a small, diverse group of lay participants who deliberate on a specific issue with guidance from expert witnesses, ensuring direct stakeholder involvement and balanced expert input. Consensus conferences expand this model by incorporating a broader panel of stakeholders, including experts and affected community members, to collaboratively develop recommendations. Both methods emphasize transparent expert input, but consensus conferences prioritize inclusive dialogue among diverse stakeholders to reach mutual agreement.
Strengths and Limitations
Citizens' juries provide in-depth deliberation by engaging a representative group of citizens in evaluating detailed evidence, promoting informed public input with strong legitimacy in decision-making, but they demand significant time and resource investment. Consensus conferences gather diverse stakeholders to collaboratively develop shared solutions, enhancing mutual understanding and social acceptance, yet their outcomes may be influenced by group dynamics and risk producing diluted compromises. Both methods excel in fostering democratic participation and transparency, but their effectiveness depends on careful design and facilitation to balance inclusivity with depth.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Citizens' juries have been effectively used in health policy decision-making, such as in the UK's National Health Service to prioritize healthcare services based on public values. Consensus conferences, exemplified by Denmark's extensive application in technology assessment, enable diverse lay participants to evaluate emerging scientific issues and influence regulatory policies. Both methods demonstrate real-world efficacy in fostering informed public deliberation and shaping policy outcomes through structured citizen engagement.
Choosing the Right Method for Public Deliberation
Citizens' juries involve a selected group of diverse individuals who evaluate evidence and provide informed recommendations, making them ideal for complex policy issues requiring expert testimony. Consensus conferences gather laypeople to deliberate collectively, emphasizing equal participation to reach a shared understanding, suitable for exploring emerging technologies or values-based dilemmas. Choosing the right method depends on the desired depth of expertise, decision-making style, and the nature of the public issue under consideration.
Citizens' jury Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com