Independent thinking empowers you to make decisions based on your values and critical analysis rather than external pressures. Cultivating independence strengthens confidence and fosters personal growth in various aspects of life. Explore the full article to discover practical strategies for developing your independent mindset.
Table of Comparison
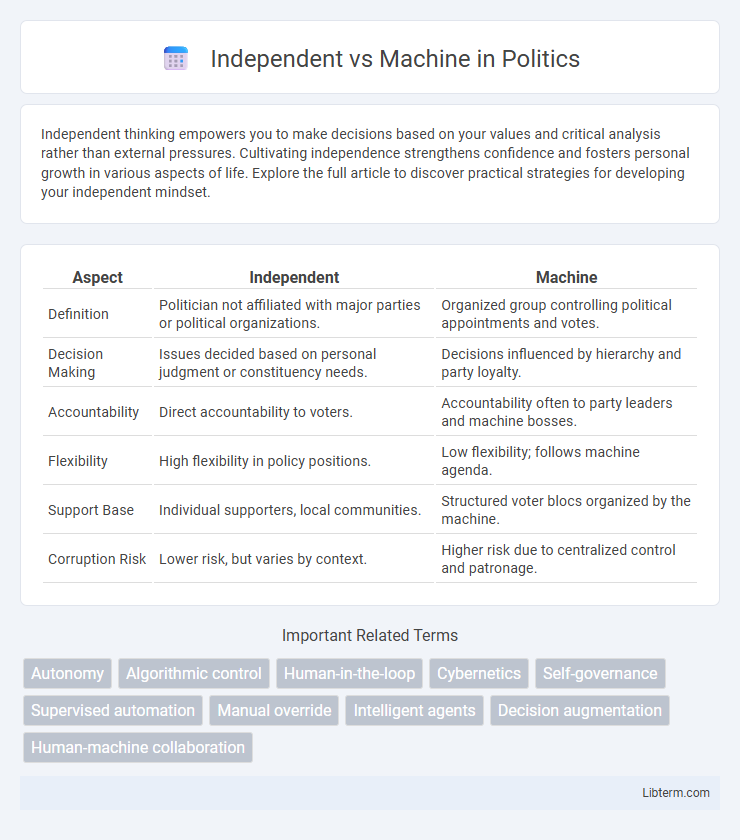
| Aspect | Independent | Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Politician not affiliated with major parties or political organizations. | Organized group controlling political appointments and votes. |
| Decision Making | Issues decided based on personal judgment or constituency needs. | Decisions influenced by hierarchy and party loyalty. |
| Accountability | Direct accountability to voters. | Accountability often to party leaders and machine bosses. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in policy positions. | Low flexibility; follows machine agenda. |
| Support Base | Individual supporters, local communities. | Structured voter blocs organized by the machine. |
| Corruption Risk | Lower risk, but varies by context. | Higher risk due to centralized control and patronage. |
Defining Independent Work and Machine Automation
Independent work involves tasks performed by individuals relying on personal expertise, creativity, and decision-making without constant supervision, enabling flexibility and innovation. Machine automation refers to the use of technology, such as robots, AI, and software systems, to execute repetitive or complex processes with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Defining independent work emphasizes human agency and adaptability, whereas machine automation highlights programmed operational precision and scalability.
Historical Evolution of Independence and Automation
The historical evolution of independence and automation reflects a shift from manual, individual control to increasing reliance on machine-driven processes. Early industrial advances introduced mechanization, gradually replacing human labor with automated systems to enhance efficiency and precision. Over time, the development of artificial intelligence and robotics has expanded machine autonomy, reducing dependence on human intervention while raising new questions about control and ethical governance.
Core Differences: Human Judgment vs Algorithmic Processing
Independent decision-making relies on human judgment, incorporating intuition, experience, and ethical considerations to navigate complex, ambiguous situations. Machine decision-making uses algorithmic processing, analyzing large datasets with speed and consistency but often lacking contextual understanding and emotional intelligence. The core difference lies in humans' ability to interpret nuance and adapt dynamically, while machines excel in pattern recognition and scalable data-driven efficiency.
Key Benefits of Independent Decision-Making
Independent decision-making enhances creativity by enabling individuals to explore diverse solutions uninhibited by machine constraints, fostering innovative problem-solving. It bolsters accountability, as decisions reflect personal judgment and responsibility, which machines cannot replicate. Furthermore, independent choices adapt fluidly to nuanced contexts and ethical considerations beyond algorithmic capabilities.
Machine Advantages: Speed, Scale, and Consistency
Machine-driven processes outperform independent efforts by delivering unparalleled speed, enabling rapid task completion that humans cannot match. These systems operate at scale, efficiently handling vast volumes of data and transactions without loss of performance. Consistency is another key advantage, as machines execute operations uniformly, minimizing errors and ensuring reliable outcomes.
Challenges of Human Independence in Modern Work
Human independence in modern work faces challenges such as increased reliance on machine automation, which can reduce individual decision-making and creativity. The integration of artificial intelligence and algorithms often limits human autonomy by standardizing tasks and imposing rigid workflows. Balancing the efficiency of machines with the need for human judgment remains a critical issue for maintaining independence in contemporary workplaces.
Limitations and Risks of Relying on Machines
Relying on machines presents inherent limitations such as vulnerability to technical malfunctions, cybersecurity threats, and the inability to replicate human intuition or ethical judgment. Machine errors can lead to significant operational failures, compromising safety and data integrity in critical systems. Dependence on automated processes risks reducing human oversight, potentially escalating errors and limiting adaptability in unpredictable scenarios.
When to Choose Human Oversight vs Automation
Human oversight is essential when tasks require nuanced judgment, ethical considerations, or complex decision-making that artificial intelligence may misinterpret. Automation excels in processing large volumes of data rapidly, ensuring consistency, and reducing human error in routine, repetitive operations. Choose human involvement for strategic, creative, or sensitive scenarios, while deploying machine automation for tasks demanding speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Future Trends: Hybrid Models and Collaborative Systems
Future trends in Independent vs Machine systems emphasize the rise of hybrid models combining human intuition with machine precision to enhance decision-making accuracy. Collaborative systems leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms alongside human expertise to optimize efficiency and adaptability in complex environments. These integrated approaches promise advancements in automation, predictive analytics, and real-time problem-solving across industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
Ethical Considerations: Balancing Independence and Automation
Balancing ethical considerations in independent versus machine-driven systems requires assessing autonomy, accountability, and transparency to ensure responsible decision-making. Independent human judgment often prioritizes moral values, while machine automation demands robust algorithmic fairness and bias mitigation to uphold ethical standards. Striking the optimal balance involves integrating human oversight with automated processes to maintain trust and social responsibility.
Independent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com