Partisan politics often leads to increased polarization, impacting legislative effectiveness and public trust in government. Understanding how party loyalty shapes policy decisions can reveal underlying motivations behind political actions. Explore the rest of the article to learn how partisan dynamics influence your everyday political environment.
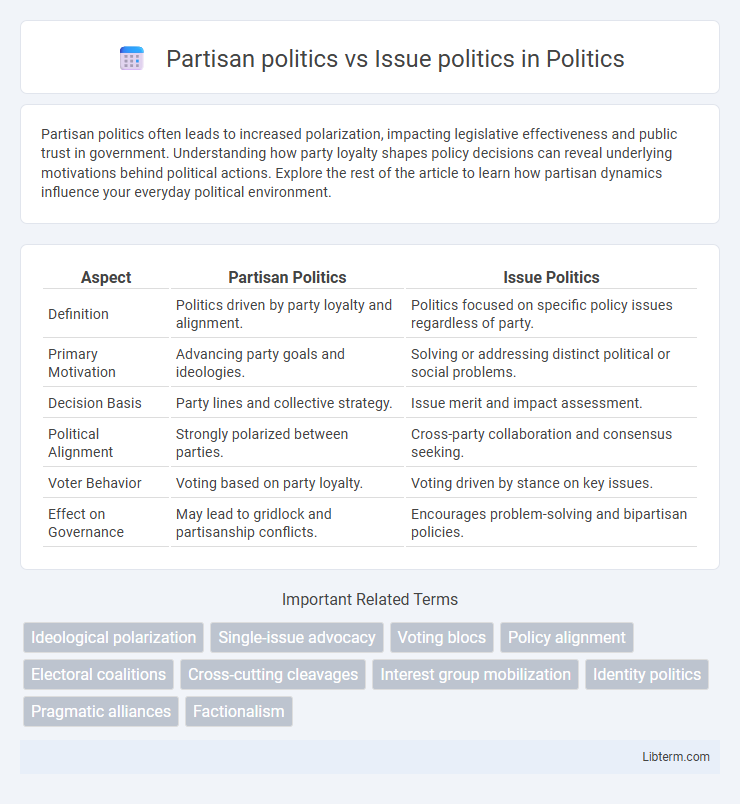
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Partisan Politics | Issue Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Politics driven by party loyalty and alignment. | Politics focused on specific policy issues regardless of party. |
| Primary Motivation | Advancing party goals and ideologies. | Solving or addressing distinct political or social problems. |
| Decision Basis | Party lines and collective strategy. | Issue merit and impact assessment. |
| Political Alignment | Strongly polarized between parties. | Cross-party collaboration and consensus seeking. |
| Voter Behavior | Voting based on party loyalty. | Voting driven by stance on key issues. |
| Effect on Governance | May lead to gridlock and partisanship conflicts. | Encourages problem-solving and bipartisan policies. |
Understanding Partisan Politics: Definition and Dynamics
Partisan politics refers to the alignment and loyalty to a specific political party, influencing decision-making and policy preferences based on party ideology rather than individual issues. This dynamic fosters group identity, often leading to polarized debates and a focus on winning elections rather than bipartisan solutions. Understanding partisan politics involves analyzing how party affiliation shapes voter behavior, legislative collaboration, and political discourse in democratic systems.
What Is Issue Politics? Core Concepts and Characteristics
Issue politics centers on specific policy concerns or social problems rather than party loyalty, emphasizing pragmatic solutions to pressing matters like healthcare, climate change, or education reform. This approach prioritizes evidence-based decision-making and encourages cross-party collaboration based on shared values or goals linked to the issue at hand. Core concepts include agenda-setting around defined policy challenges, stakeholder engagement, and the use of data-driven advocacy to influence public opinion and legislative outcomes.
Historical Evolution: Partisan vs Issue Politics
Partisan politics, rooted in early democratic systems, evolved through structured party organizations emphasizing loyalty and collective agendas, while issue politics emerged prominently during the 20th century as voters and politicians began prioritizing specific policy concerns over party identity. The rise of mass media and social movements in the 1960s and 1970s accelerated the shift toward issue-based politics by amplifying single-issue advocacy and public debate. Historical milestones such as the Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War protests highlight the increasing influence of issue politics, challenging traditional partisan alignments and reshaping political engagement.
Motivations: Party Loyalty vs Policy Goals
Partisan politics centers on party loyalty where individuals prioritize alignment with their political party to maintain unity and electoral strength. Issue politics drives motivations by focusing on specific policy goals, encouraging voters and politicians to support causes based on principles rather than party affiliation. This divergence shapes political behavior, influencing legislative decision-making and voter engagement patterns.
Impact on Voter Behavior and Engagement
Partisan politics often polarizes voter behavior, leading to increased loyalty toward political parties rather than specific policies, which can diminish critical evaluation of issues. Issue politics encourages voters to focus on policy details and candidate positions, fostering higher engagement and informed decision-making. Studies show that issue-based voters are more likely to participate consistently in elections and civic activities, enhancing democratic responsiveness.
Media Influence: Shaping Narratives and Perceptions
Media influence plays a critical role in shaping narratives and perceptions in both partisan politics and issue politics by framing stories to align with audience biases or highlight specific policy impacts. Partisan media outlets often reinforce ideological divides through selective coverage and emotionally charged language, deepening political polarization. Conversely, issue-oriented media aims to provide detailed analysis and diverse perspectives, fostering informed public debate on policy solutions.
Effects on Policy Making and Governance
Partisan politics often leads to polarization, resulting in gridlock that slows legislative processes and complicates consensus-building among policymakers. Issue politics emphasizes specific policy problems, fostering more pragmatic solutions and bipartisan cooperation that facilitate effective governance. The focus on party loyalty in partisan politics can prioritize electoral gains over public interest, whereas issue-centered approaches tend to promote evidence-based policymaking and responsive governance.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Both Approaches
The 2020 U.S. Presidential Election exemplifies partisan politics, with candidates rallying strongly around party platforms and ideological divisions. In contrast, the 2018 Irish Referendum on Abortion showcased issue politics, where voters prioritized the specific topic over party loyalty, leading to a decisive social change. These cases illustrate how partisan and issue-based strategies drive political outcomes differently, influencing voter behavior and policy decisions worldwide.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Each Political Approach
Partisan politics fosters party loyalty and simplifies voter choices by aligning policies with clear ideological platforms, but it often leads to polarization and hinders bipartisan cooperation. Issue politics emphasizes policy-specific debates and encourages cross-party alliances based on shared interests, enhancing problem-solving but potentially causing voter confusion and dilution of coherent party identity. Each approach balances the trade-off between ideological consistency and flexible, pragmatic governance.
The Future: Bridging Partisan and Issue-Based Politics
The future of American politics hinges on bridging the divide between partisan loyalty and issue-based decision-making by fostering dialogue centered on shared goals like healthcare reform and climate change. Emerging platforms that prioritize transparent data and nuanced policy discussions empower voters to look beyond party lines and focus on evidence-based solutions. Integrating technology-driven civic engagement tools can further enhance collaborative governance, reducing polarization while promoting consensus on critical national issues.
Partisan politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com