Globalism drives interconnected economies and cultures, promoting trade, communication, and collaboration across borders. It shapes political policies and business strategies, offering opportunities and challenges for economic growth and social integration. Discover how globalism influences your world and what it means for the future by exploring the full article.
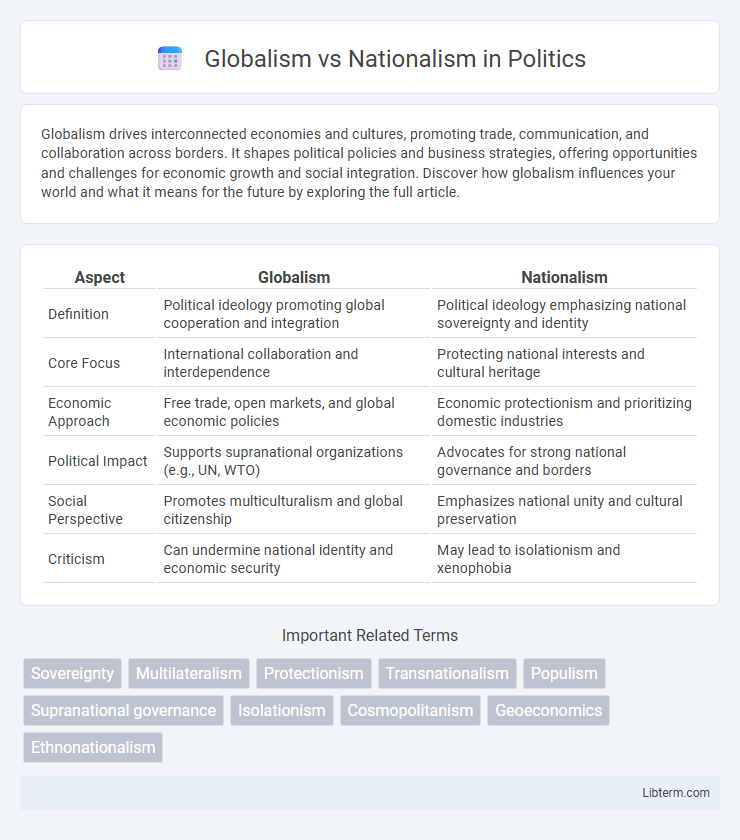
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Globalism | Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political ideology promoting global cooperation and integration | Political ideology emphasizing national sovereignty and identity |
| Core Focus | International collaboration and interdependence | Protecting national interests and cultural heritage |
| Economic Approach | Free trade, open markets, and global economic policies | Economic protectionism and prioritizing domestic industries |
| Political Impact | Supports supranational organizations (e.g., UN, WTO) | Advocates for strong national governance and borders |
| Social Perspective | Promotes multiculturalism and global citizenship | Emphasizes national unity and cultural preservation |
| Criticism | Can undermine national identity and economic security | May lead to isolationism and xenophobia |
Introduction: Defining Globalism and Nationalism
Globalism emphasizes the interconnectedness of nations through economic integration, cultural exchange, and political cooperation, promoting global governance and shared challenges like climate change. Nationalism centers on prioritizing a country's sovereignty, cultural identity, and economic independence, often advocating for protective policies and strict immigration controls. These contrasting ideologies shape international relations by influencing trade policies, security strategies, and diplomatic alliances.
Historical Background of Globalism and Nationalism
Globalism traces its roots to the Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries, when European powers expanded trade routes and cultural exchanges worldwide, laying the groundwork for interconnected economies. Nationalism emerged prominently in the 18th and 19th centuries during the decline of monarchies and the rise of nation-states, fueled by revolutions such as the American and French Revolutions that emphasized sovereignty, identity, and self-determination. Both ideologies evolved through historical events like the Industrial Revolution, World Wars, and decolonization, shaping the modern political and economic landscape.
Key Principles of Globalism
Globalism emphasizes interconnectedness through open trade, multilateral cooperation, and the promotion of international institutions like the United Nations and World Trade Organization. It advocates for economic integration, cultural exchange, and global governance mechanisms to address transnational issues such as climate change and security. Core principles include the belief in a borderless world economy, collective problem-solving, and the advancement of human rights on a global scale.
Core Tenets of Nationalism
Nationalism emphasizes the sovereignty and self-determination of a nation, prioritizing the interests, culture, and identity of a specific national group over global integration. It advocates for strong national borders, preservation of traditional values, and political independence from supranational organizations. Core tenets include patriotism, cultural unity, and the promotion of national identity as central to political legitimacy and social cohesion.
Drivers Behind the Resurgence of Nationalism
Economic disparities and cultural identity concerns drive the resurgence of nationalism globally, as communities react to perceived threats from globalization and immigration. Political actors leverage nationalist rhetoric to mobilize support by emphasizing sovereignty and protection of local industries. Technological advancements and social media amplify nationalist messages, increasing visibility and influence in public discourse.
Impact of Globalism on National Economies
Globalism drives economic integration by promoting cross-border trade, investment, and technology exchange, which can enhance national productivity and growth. However, it also poses challenges such as increased competition for domestic industries and vulnerability to global market fluctuations. Countries engaged in globalism often experience shifts in labor markets, requiring adaptive policies to balance economic benefits with social stability.
Nationalism and Its Effects on International Relations
Nationalism emphasizes sovereignty and prioritizes a nation's interests, often leading to stricter immigration policies and trade protectionism. This approach can heighten diplomatic tensions and reduce cooperation on global issues such as climate change and security. As nationalist policies gain traction, international alliances may weaken, resulting in fragmented multilateral efforts and a shift toward bilateral agreements.
Cultural Identity in a Globalized World
Globalism promotes interconnectedness and cultural exchange, fostering a hybrid cultural identity shaped by diverse influences across borders. Nationalism emphasizes preserving distinct cultural traditions and heritage, asserting the importance of local identities in the face of global homogenization. The tension between these forces shapes contemporary debates on cultural sovereignty, social cohesion, and the balance between universal values and particularistic identities.
Challenges and Controversies: Balancing Global and National Interests
Globalism promotes interconnected economies and cultural exchange but faces challenges in addressing national sovereignty and identity concerns. Nationalism emphasizes protecting domestic industries and maintaining cultural uniqueness, often leading to trade barriers and political isolation. Balancing these forces requires nuanced policies that foster international cooperation while respecting the autonomy and priorities of individual nations.
The Future of Globalism and Nationalism: Trends and Predictions
The future of globalism and nationalism will be shaped by the interplay between technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and economic interdependence. Rising digital connectivity supports global cooperation, while increasing political populism and protectionist policies fuel nationalist sentiments. Experts predict a hybrid system where selective global partnerships coexist with strong national identity and sovereignty assertions.
Globalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com