The Challenger space shuttle disaster remains a pivotal moment in aerospace history, highlighting critical failures in engineering and safety protocols. Understanding the causes and consequences of this tragedy offers valuable lessons for the future of space exploration. Explore the full article to learn how the Challenger incident reshaped NASA and what it means for your perspective on space missions.
Table of Comparison
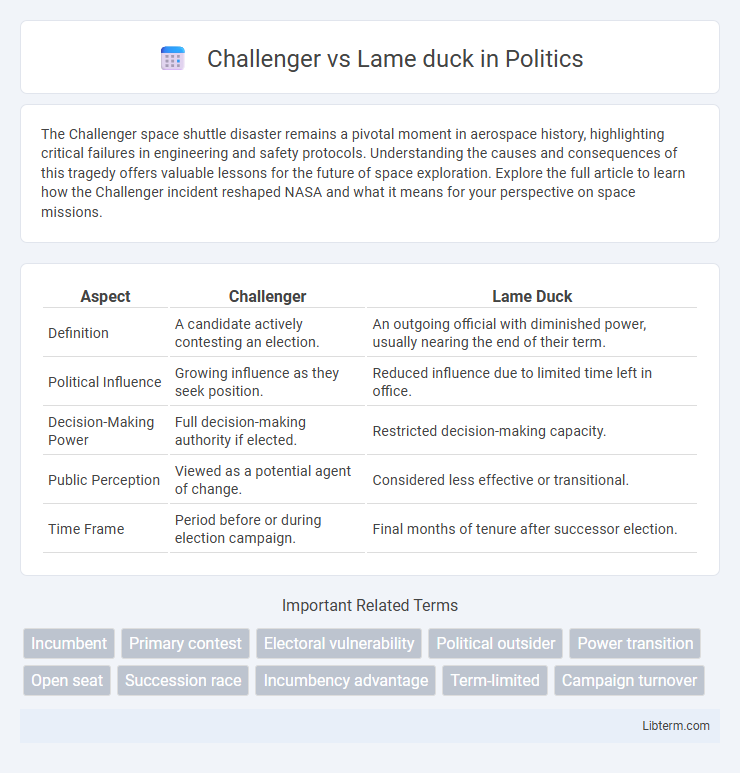
| Aspect | Challenger | Lame Duck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A candidate actively contesting an election. | An outgoing official with diminished power, usually nearing the end of their term. |
| Political Influence | Growing influence as they seek position. | Reduced influence due to limited time left in office. |
| Decision-Making Power | Full decision-making authority if elected. | Restricted decision-making capacity. |
| Public Perception | Viewed as a potential agent of change. | Considered less effective or transitional. |
| Time Frame | Period before or during election campaign. | Final months of tenure after successor election. |
Definition of Challenger and Lame Duck
A challenger is a candidate or party actively competing to win an election or political position, seeking to unseat the current officeholder. A lame duck refers to an incumbent politician who remains in office after losing an election or choosing not to run for re-election, often with diminished influence and power. The term lame duck highlights the transitional phase where the official's authority wanes until the successor assumes office.
Historical Context of Political Terms
Challenger and lame duck are political terms with distinct historical origins shaping their meanings. The term "challenger" traditionally refers to a political candidate who contests an incumbent in an election, emphasizing competitive electoral dynamics documented in U.S. presidential races such as the 1960 Kennedy-Nixon contest. "Lame duck" originated in 18th-century England to describe politicians or officials nearing the end of their term with diminished power, a concept institutionalized in U.S. politics by the 20th Amendment which reduced lame duck periods to ensure smoother transitions.
Key Differences Between Challenger and Lame Duck
The key differences between a Challenger and a Lame Duck lie in their positions and influence within political or organizational contexts. A Challenger is an active contender aiming to replace the current leader, often driving change and rallying support, whereas a Lame Duck is an outgoing official with diminishing authority, typically unable to enact significant policies or influence decisions. These roles impact power dynamics, with Challengers representing future leadership and Lame Ducks symbolizing a transitional period of reduced political efficacy.
Roles in Political Campaigns
Challengers play a critical role in political campaigns by actively seeking to unseat incumbents through aggressive strategy, policy innovation, and voter outreach efforts. Lame duck candidates often face diminished influence and limited campaign momentum due to their nearing end of term or weakened political support. The dynamic between challenger initiatives and lame duck reluctance significantly shapes campaign narratives and voter engagement.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Challenger candidates often initiate vigorous campaigns, sparking increased voter engagement and potentially shifting election outcomes by appealing to dissatisfied electorates. Lame duck incumbents, limited by diminished political capital and waning public support, may struggle to mobilize effective campaign resources, thereby reducing their chances of re-election. The dynamic between challengers and lame ducks critically influences voter turnout patterns and can lead to significant power shifts within political landscapes.
Public Perception and Media Representation
Challenger campaigns often generate heightened public interest and media coverage, portraying them as agents of change and innovation challenging the status quo. In contrast, lame duck incumbents face dwindling public support and media narratives framing them as ineffective or powerless during their final term. The media's focus on challengers' momentum versus incumbents' decline significantly shapes voter perceptions and election dynamics.
Challenges Faced by Incumbents and Lame Ducks
Incumbents face challenges such as increased scrutiny over policy decisions, voter dissatisfaction, and heightened pressure from well-funded challengers capitalizing on public desire for change. Lame duck incumbents struggle with diminished political influence, limited legislative effectiveness, and reduced ability to secure party support as their term wanes. Both groups encounter strategic obstacles in maintaining authority and advancing agendas amid shifting political dynamics.
Strategies Used by Challengers
Challengers in competitive markets employ aggressive strategies such as market penetration pricing, targeted advertising, and innovation to disrupt incumbents and capture market share. They often identify weaknesses in the lame duck's product offerings or customer service to position themselves as superior alternatives, leveraging digital marketing and social media campaigns for greater visibility. Strategic alliances and product differentiation also play critical roles in enabling challengers to gain traction against established players with declining influence.
Case Studies: Famous Challengers and Lame Ducks
Famous challengers like Barack Obama in 2008 leveraged grassroots campaigns and social media to overcome incumbent advantages, reshaping modern electoral strategies. Iconic lame duck presidents such as Jimmy Carter faced dwindling political capital during their final terms, hindering policy implementation and affecting party dynamics. Case studies reveal that challengers often thrive on change-driven narratives, while lame ducks struggle with legacy preservation amid declining public support.
Implications for Future Elections
The Challenger's success in an election often signals a public desire for change, potentially reshaping party dynamics and influencing candidate strategies in future contests. In contrast, a lame duck incumbent may struggle to maintain influence, leading parties to invest more in emerging candidates to secure electoral advantages. These dynamics impact voter engagement, campaign funding, and policy priorities, ultimately shaping the trajectory of subsequent elections.
Challenger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com