Loyal voters play a crucial role in shaping election outcomes by consistently supporting their preferred candidates or parties. Understanding the behavior and motivations behind a loyal vote can offer valuable insights into political trends and campaign strategies. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your loyalty influences the democratic process and election dynamics.
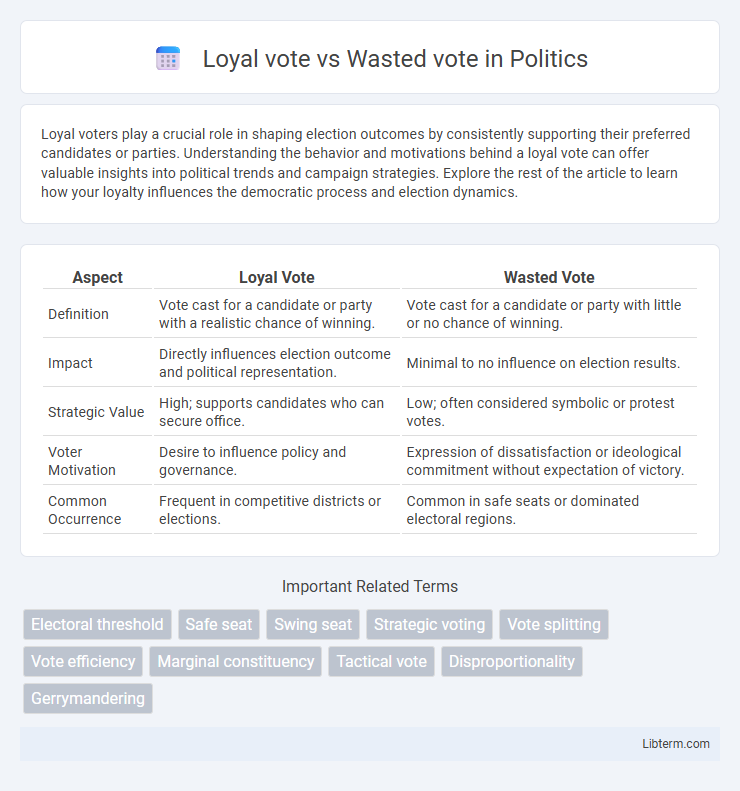
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Loyal Vote | Wasted Vote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vote cast for a candidate or party with a realistic chance of winning. | Vote cast for a candidate or party with little or no chance of winning. |
| Impact | Directly influences election outcome and political representation. | Minimal to no influence on election results. |
| Strategic Value | High; supports candidates who can secure office. | Low; often considered symbolic or protest votes. |
| Voter Motivation | Desire to influence policy and governance. | Expression of dissatisfaction or ideological commitment without expectation of victory. |
| Common Occurrence | Frequent in competitive districts or elections. | Common in safe seats or dominated electoral regions. |
Understanding Loyal Votes: What Drives Voter Loyalty?
Voter loyalty is primarily driven by consistent alignment with a party's ideology, trust in its leadership, and belief in the long-term benefits of supporting that party. Loyal votes contribute significantly to sustained political power, as these voters prioritize policy stability over short-term changes. Understanding the factors influencing loyalty helps explain why some voters resist switching even in closely contested elections, distinguishing between loyal and wasted votes.
Defining the Wasted Vote: Causes and Implications
A wasted vote occurs when a ballot does not contribute to electing a preferred candidate, often due to voting for losing candidates or excess votes beyond the winning threshold. Causes include plurality voting systems that favor major parties and discourage support for smaller or third-party candidates. This leads to voter disenfranchisement, distorted representation, and diminished incentives for political diversity.
Historical Perspectives: Loyal vs Wasted Votes in Elections
Loyal votes, often cast for major party candidates, have historically influenced election outcomes by consolidating political power and shaping party dominance, as seen in the consistent two-party systems of the United States and the United Kingdom. Wasted votes, including those for third-party or losing candidates, have frequently sparked debates about electoral reform, highlighting issues like the spoiler effect and vote splitting that undermine representative fairness. Historical elections such as the 1992 U.S. presidential race and the 2019 UK general election illustrate how loyal and wasted votes impact strategic voting, party realignment, and voter engagement over time.
The Psychology Behind Loyal Voting Behavior
Loyal voting behavior is driven by psychological factors such as identity reinforcement, cognitive consistency, and perceived in-group loyalty, which encourage voters to support their preferred party regardless of electoral outcomes. Voters often prioritize emotional attachment and social affiliation over strategic considerations like minimizing wasted votes, leading to steadfast support even in competitive districts. Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind loyal voting reveals how perceived political efficacy and social identity shape electoral participation and campaign strategies.
Electoral Systems and the Impact on Wasted Votes
Electoral systems significantly influence the distribution of loyal votes versus wasted votes, with proportional representation minimizing wasted votes by allocating seats based on vote share, while majoritarian systems often produce a higher number of wasted votes due to winner-takes-all mechanics. In plurality voting, loyal votes for losing candidates do not translate into representation, increasing the likelihood of voter dissatisfaction and decreased political engagement. Mixed-member systems attempt to balance these effects by combining district-level representation with proportional allocation, thereby reducing wasted votes and enhancing electoral fairness.
Strategic Voting: Minimizing the Risk of a Wasted Vote
Strategic voting involves selecting a candidate who has a realistic chance of winning to avoid a wasted vote that fails to influence the election outcome. Voters analyze poll data and historical trends to identify viable contenders, thereby maximizing the impact of their ballot. This approach balances personal preference with electoral pragmatism to strengthen preferred political coalitions and minimize vote dispersion.
The Role of Party Loyalty in Modern Democracies
Party loyalty in modern democracies significantly influences voter behavior, often driving loyal votes that reinforce a party's political strength and stability. Loyal votes contribute to consistent electoral support, enabling parties to implement long-term policies and represent their constituencies effectively. In contrast, wasted votes--cast for parties with little chance of winning--highlight the challenges of electoral systems and the strategic dilemmas faced by voters balancing ideological commitment with pragmatic impact.
Wasted Vote Phenomenon: Effects on Smaller Parties
The Wasted Vote phenomenon significantly impacts smaller parties by discouraging voter support due to the low probability of winning seats, leading to reduced political diversity and representation. This effect often results in strategic voting, where supporters of minor parties cast ballots for larger parties perceived as viable, further marginalizing smaller entities. Electoral systems with plurality or majoritarian rules exacerbate this issue, consolidating power among dominant parties and weakening the influence of emerging or niche political groups.
Voter Turnout: Does Fear of Wasted Votes Matter?
Voter turnout is significantly influenced by the fear of wasted votes, where individuals perceive their ballot as ineffective if cast for less popular candidates. This phenomenon often leads to strategic voting, diminishing support for third-party or independent candidates and reinforcing dominant party systems. Studies show that reducing concerns about wasted votes through electoral reforms like ranked-choice voting can increase voter participation and enhance the representation of voter preferences.
Policy Implications: Reducing Wasted Votes in Future Elections
Reducing wasted votes is critical for enhancing electoral fairness and improving democratic legitimacy by ensuring more votes contribute to the election outcome. Electoral reforms such as proportional representation and ranked-choice voting increase voter efficacy by minimizing the number of votes that do not impact seat allocation. Policymakers aiming to reduce wasted votes can foster inclusive representation, encouraging greater voter turnout and strengthening policy responsiveness.
Loyal vote Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com