Political alliances form when parties or groups unite to achieve common goals, often enhancing their influence and electoral success. Such partnerships can reshape political landscapes by pooling resources and supporters to address shared interests or challenges. Explore the rest of the article to understand how political alliances impact governance and democracy.
Table of Comparison
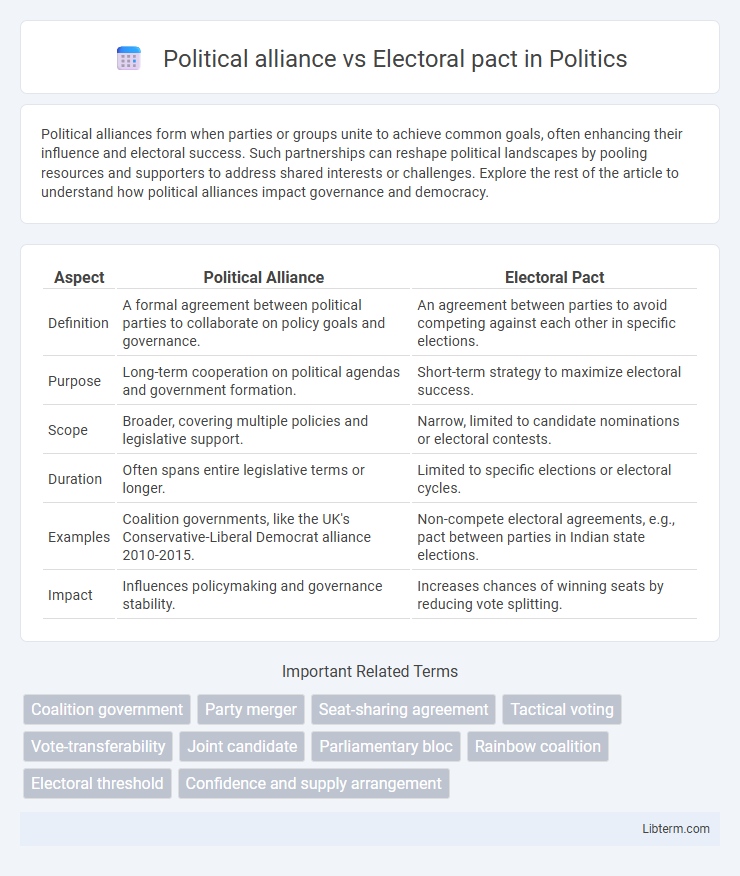
| Aspect | Political Alliance | Electoral Pact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal agreement between political parties to collaborate on policy goals and governance. | An agreement between parties to avoid competing against each other in specific elections. |
| Purpose | Long-term cooperation on political agendas and government formation. | Short-term strategy to maximize electoral success. |
| Scope | Broader, covering multiple policies and legislative support. | Narrow, limited to candidate nominations or electoral contests. |
| Duration | Often spans entire legislative terms or longer. | Limited to specific elections or electoral cycles. |
| Examples | Coalition governments, like the UK's Conservative-Liberal Democrat alliance 2010-2015. | Non-compete electoral agreements, e.g., pact between parties in Indian state elections. |
| Impact | Influences policymaking and governance stability. | Increases chances of winning seats by reducing vote splitting. |
Defining Political Alliances
Political alliances refer to formal agreements between two or more parties or organizations to cooperate on broad political objectives, often involving shared governance or policy-making frameworks. These alliances are typically long-term arrangements aimed at consolidating power, influencing legislation, or ensuring stable government coalitions. Unlike electoral pacts, which concentrate on mutual support during elections, political alliances encompass ongoing collaboration beyond voting periods.
Understanding Electoral Pacts
Electoral pacts are agreements between political parties to avoid competing against each other in specific constituencies, optimizing the chances of winning seats and preventing vote splitting. Unlike broader political alliances that may involve coordinated policy platforms and long-term cooperation, electoral pacts focus primarily on strategic collaboration during elections. Understanding electoral pacts provides insight into tactical maneuvers parties use to maximize representation without formal merging.
Key Differences Between Alliances and Pacts
Political alliances involve long-term cooperation between parties aiming for shared governance and policy goals, often including integrated decision-making structures. Electoral pacts are temporary agreements focused solely on coordinating candidates or vote shares during specific elections, without broader policy integration. Alliances emphasize sustained collaboration and mutual support, while pacts primarily seek to maximize electoral gains without formalizing long-term commitments.
Historical Examples of Political Alliances
Political alliances have historically shaped global power dynamics, as seen in the Axis Powers during World War II, where Germany, Italy, and Japan coordinated military and political strategies to achieve dominance. Similarly, the Allied Powers, including the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom, formed a robust political alliance that combined resources and tactical planning to counter Axis aggression. These collaborations differ from electoral pacts, which are typically temporary agreements focused on coordinated election strategies rather than long-term political or military cooperation.
Notable Electoral Pacts in Recent Elections
Notable electoral pacts in recent elections include the alliance between the Conservative and Liberal Democrats in the 2010 UK General Election, which prevented vote splitting and maximized seat gains against Labour. In India, the 2019 National Democratic Alliance (NDA) demonstrated strategic seat-sharing among BJP and regional parties, enhancing their parliamentary majority. These pacts emphasize tactical cooperation without formal political integration, distinguishing them from broader political alliances.
Strategic Motivations for Forming Alliances
Political alliances are formed to combine party strengths for long-term governance goals and shared ideological frameworks, enhancing collective policy influence and stability. Electoral pacts focus on short-term strategic cooperation to maximize vote shares and minimize competition in specific constituencies during elections. Both mechanisms aim to optimize electoral outcomes but differ in scope, with alliances emphasizing sustained collaboration and pacts targeting immediate electoral gains.
Advantages of Entering Electoral Pacts
Electoral pacts offer strategic advantages by consolidating votes, reducing competition among allied parties, and increasing the likelihood of winning seats in tightly contested constituencies. These agreements often enhance resource efficiency, enabling parties to pool campaign efforts and target key demographics more effectively. By minimizing vote splitting, electoral pacts can significantly influence election outcomes and strengthen coalition-building prospects post-election.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Political alliances often face challenges such as ideological conflicts and power struggles that can undermine long-term cooperation, while electoral pacts may encounter the risk of voter confusion and lack of unified messaging. Both arrangements can lead to reduced party autonomy and internal dissent, potentially weakening public trust. Managing diverse party agendas and ensuring transparent communication are critical to mitigating these risks and maintaining electoral effectiveness.
Impact on Voter Perception and Behavior
Political alliances often create a unified front among parties, enhancing voter confidence through clear policy alignment and long-term collaboration, which can increase loyalty and turnout. Electoral pacts, by contrast, focus on tactical cooperation with vote-sharing agreements that may confuse or alienate voters due to perceived opportunism or lack of ideological consistency. The impact on voter behavior varies, with alliances fostering stable support bases, while pacts might drive short-term strategic voting or abstention depending on the electorate's trust levels.
Future Trends in Political Cooperation
Political alliances are long-term collaborations between parties that share ideological goals and aim for collective governance, while electoral pacts are short-term agreements focused on minimizing competition in specific elections. Future trends indicate an increase in strategic electoral pacts leveraging data analytics and voter behavior models to maximize seat gains efficiently. Growing political polarization and the rise of coalition politics suggest more frequent formation of enduring alliances to address complex governance challenges.
Political alliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com