Executive overreach occurs when government leaders exceed their legal powers, undermining checks and balances essential for democracy. This abuse can erode public trust and lead to authoritarian governance, impacting your rights and freedoms. Explore the rest of the article to understand how executive overreach shapes political landscapes and what safeguards exist to prevent it.
Table of Comparison
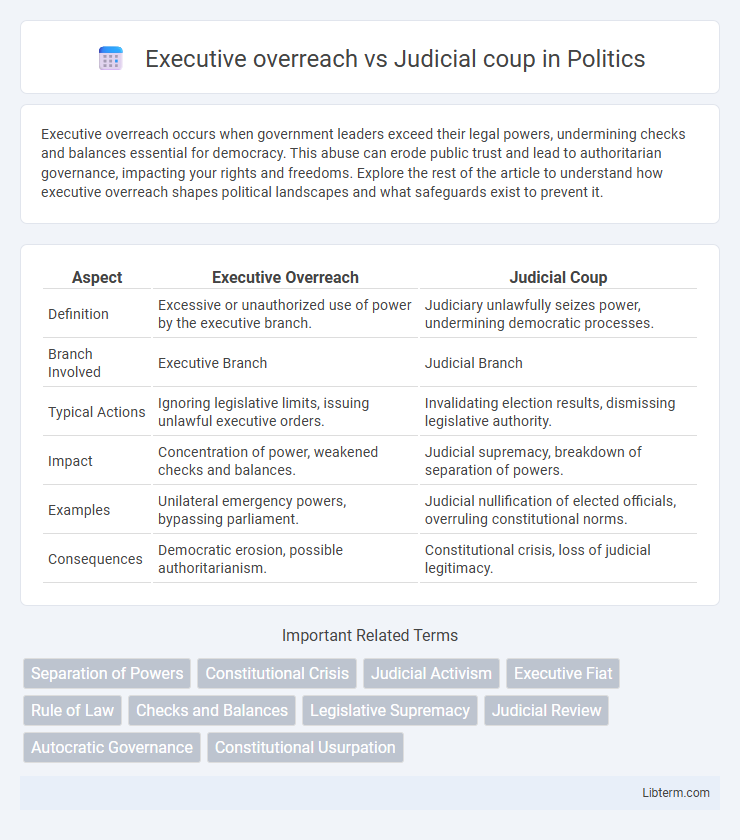
| Aspect | Executive Overreach | Judicial Coup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive or unauthorized use of power by the executive branch. | Judiciary unlawfully seizes power, undermining democratic processes. |
| Branch Involved | Executive Branch | Judicial Branch |
| Typical Actions | Ignoring legislative limits, issuing unlawful executive orders. | Invalidating election results, dismissing legislative authority. |
| Impact | Concentration of power, weakened checks and balances. | Judicial supremacy, breakdown of separation of powers. |
| Examples | Unilateral emergency powers, bypassing parliament. | Judicial nullification of elected officials, overruling constitutional norms. |
| Consequences | Democratic erosion, possible authoritarianism. | Constitutional crisis, loss of judicial legitimacy. |
Defining Executive Overreach
Executive overreach occurs when the executive branch exceeds its constitutional authority, encroaching on the powers reserved for the legislative or judicial branches. This phenomenon undermines the system of checks and balances designed to prevent concentration of power and ensures separation between branches. Legal scholars emphasize that executive overreach disrupts democratic governance by bypassing established legal frameworks and usurping legislative prerogatives.
Understanding Judicial Coup
Understanding judicial coup involves recognizing the judiciary's excessive intervention in political or legislative processes, undermining the principle of separation of powers and democratic governance. This occurs when courts overstep their constitutional role by invalidating laws or political decisions based on subjective interpretations rather than established legal frameworks. Judicial coups can destabilize political systems, erode public trust in legal institutions, and shift power balances away from elected branches toward unelected judges.
Historical Contexts of Executive Overreach
Historical contexts of executive overreach often reveal patterns where leaders expand their authority beyond constitutional limits, as seen in the authoritarian regimes of 20th-century Europe and instances like the U.S. Watergate scandal. Such overreach typically involves bypassing checks and balances, undermining legislative bodies, and suppressing judicial independence to consolidate power. These actions contrast with claims of a judicial coup, which occur when courts allegedly usurp executive functions, highlighting the tension between branches in maintaining democratic governance.
Notable Instances of Judicial Coups
Notable instances of judicial coups include Pakistan's 1997 Supreme Court decision that validated military ruler Nawaz Sharif's government after a coup, undermining democratic processes. In Turkey, the 2016 constitutional amendments expanded executive power following judicial backing, raising concerns about judicial complicity in consolidating authoritarianism. Zimbabwe's 2017 Supreme Court ruling legitimized Emmerson Mnangagwa's rise after a military takeover, exemplifying the judiciary's role in endorsing executive overreach.
Comparing Separation of Powers
Executive overreach occurs when the executive branch exceeds its constitutional authority, undermining the checks and balances fundamental to the separation of powers. Judicial coup refers to the judiciary invalidating or altering laws and executive actions beyond its interpretive role, effectively usurping legislative or executive powers. Comparing the two highlights distinct threats to democratic governance: executive overreach erodes legislative authority, while judicial coups compromise both legislative intent and executive function, disrupting the intended balance among the three branches.
Causes Behind Executive Overreach
Executive overreach occurs when the executive branch exceeds its constitutional authority, often driven by urgent political agendas, a desire to consolidate power, or perceived inefficiencies in legislative processes. Causes behind this phenomenon include weak checks and balances, emergency powers invoked during crises, and ambiguous legal frameworks that allow unilateral decision-making. This overreach can trigger judicial pushback, leading to accusations of a "judicial coup" when courts intervene to restrain executive actions.
Motivations for Judicial Intervention
Judicial intervention often stems from motivations to uphold constitutional principles and protect individual rights against executive overreach that threatens democratic norms. Courts may act to check executive power when there are perceived abuses, unlawful actions, or breaches of legal frameworks designed to maintain separation of powers. This judicial activism aims to preserve the rule of law, ensuring that the executive branch operates within its legal boundaries and respects fundamental governance principles.
Impacts on Democracy and Governance
Executive overreach erodes democratic checks and balances by concentrating power in the executive branch, undermining the separation of powers essential for accountable governance. Judicial coup refers to unelected courts overriding elected bodies, disrupting democratic legitimacy and potentially destabilizing governance structures. Both phenomena weaken institutional trust, hinder effective policy-making, and threaten the rule of law fundamental to democratic stability.
Preventative Measures and Safeguards
Preventative measures against executive overreach include robust legislative oversight, transparent administrative processes, and constitutional checks such as judicial review, which empower courts to invalidate unlawful executive actions. Judicial coups can be mitigated by ensuring judicial independence through appointment processes insulated from political pressures, enforcing ethical standards, and maintaining a clear separation of powers that prevents courts from usurping policymaking functions. Strengthening democratic institutions and promoting civic education also serve as safeguards to balance authority and protect the rule of law.
Pathways to Institutional Balance
Executive overreach undermines democratic principles by expanding executive power beyond constitutional limits, risking authoritarianism. Judicial coup occurs when courts illegitimately overturn laws or policies, disrupting the balance of power and eroding legislative authority. Pathways to institutional balance involve strengthening constitutional checks and balances, promoting judicial independence while ensuring accountability, and fostering interbranch dialogue to maintain equilibrium between executive and judiciary functions.
Executive overreach Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com