The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) establishes procedures to protect sensitive national security information during federal trials, balancing government secrecy with a defendant's right to a fair trial. It guides how classified evidence is handled in court to prevent unauthorized disclosure while maintaining judicial integrity. Discover how CIPA impacts legal cases involving classified materials and what it means for Your rights in the justice system by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
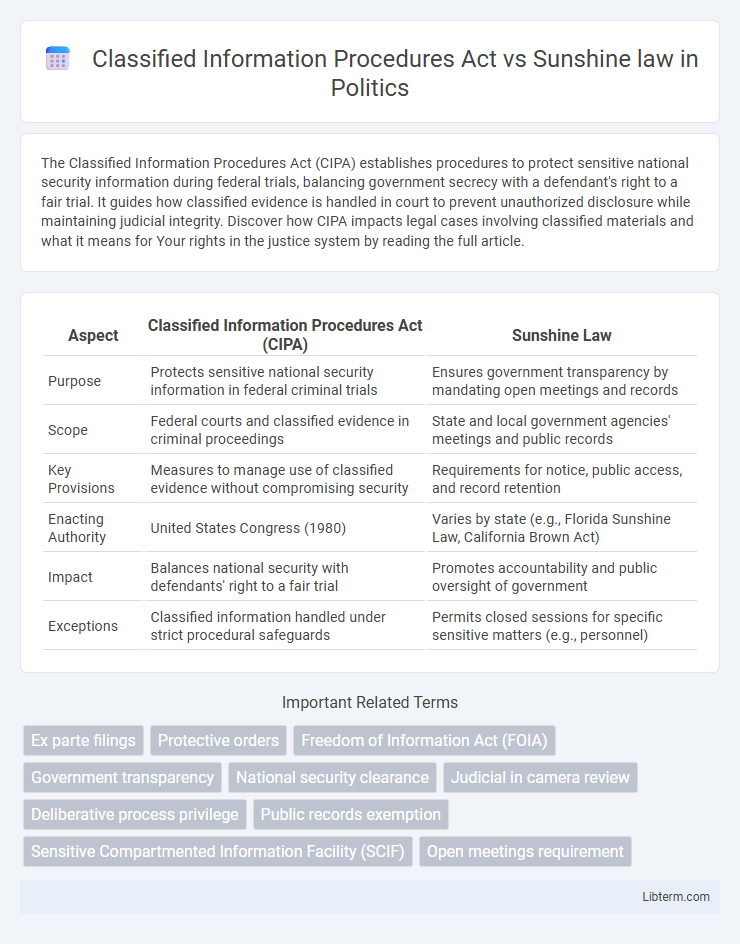
| Aspect | Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) | Sunshine Law |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects sensitive national security information in federal criminal trials | Ensures government transparency by mandating open meetings and records |
| Scope | Federal courts and classified evidence in criminal proceedings | State and local government agencies' meetings and public records |
| Key Provisions | Measures to manage use of classified evidence without compromising security | Requirements for notice, public access, and record retention |
| Enacting Authority | United States Congress (1980) | Varies by state (e.g., Florida Sunshine Law, California Brown Act) |
| Impact | Balances national security with defendants' right to a fair trial | Promotes accountability and public oversight of government |
| Exceptions | Classified information handled under strict procedural safeguards | Permits closed sessions for specific sensitive matters (e.g., personnel) |
Introduction to Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA)
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) governs the handling of sensitive government information in criminal trials to balance national security with defendants' rights. CIPA establishes procedures for pretrial hearings and protective orders to prevent unauthorized disclosure of classified data. Unlike Sunshine laws focused on transparency and public access to government meetings, CIPA prioritizes confidentiality and controlled information dissemination during judicial processes.
Overview of Sunshine Law and Its Purpose
Sunshine Laws mandate transparency by requiring government meetings and records to be accessible to the public, promoting accountability and preventing secrecy. These laws ensure that decisions and deliberations by public officials occur in an open environment to foster trust and public participation. The core purpose of Sunshine Laws is to guarantee transparency in government operations, contrasting with the Classified Information Procedures Act, which governs the handling of sensitive information in legal settings.
Key Provisions of CIPA
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) establishes procedures to protect national security information during federal criminal trials, including pretrial hearings to determine the admissibility of classified evidence and mechanisms for redacting sensitive material. CIPA's key provisions require courts to balance defendant rights with government interests by permitting substitutions or summaries of classified information to prevent disclosure. In contrast, Sunshine Laws promote transparency and public access to government meetings and records, highlighting the fundamental difference in scope and purpose between secrecy in CIPA and openness in Sunshine Laws.
Core Principles of Sunshine Law
The Sunshine Law mandates government transparency by requiring open meetings and public access to records, ensuring accountability and public participation in decision-making. In contrast, the Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) primarily protects national security by regulating the disclosure of classified information during federal criminal trials. The core principles of the Sunshine Law emphasize openness, public scrutiny, and minimizing secrecy in government operations, directly contrasting with CIPA's focus on confidentiality for security purposes.
Handling Sensitive Information: CIPA’s Approach
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) establishes a legal framework for managing sensitive national security information in criminal trials, requiring courts to balance fair trial rights with the need to protect classified data from unauthorized disclosure. Unlike Sunshine laws, which emphasize transparency and public access to government records and meetings, CIPA mandates protective measures such as in-camera proceedings, redactions, and specialized security clearances to ensure classified information remains confidential. This approach prioritizes safeguarding national security while allowing criminal prosecutions to proceed without compromising sensitive information.
Promoting Transparency: Sunshine Law in Practice
The Sunshine Law mandates open meetings and public access to government records, promoting transparency by ensuring that citizens can observe and participate in government decision-making processes. Unlike the Classified Information Procedures Act, which restricts access to sensitive information in legal cases for national security, the Sunshine Law prioritizes government openness and public accountability. This legal framework fosters trust by requiring disclosures that prevent secrecy and encourage informed civic engagement.
Legal Implications and Enforcement of CIPA
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) establishes a clear legal framework to protect sensitive government information during criminal trials, allowing courts to balance national security concerns with defendants' rights by employing protective orders and in-camera reviews. Enforcement of CIPA ensures that classified evidence is handled securely, minimizing unauthorized disclosures while maintaining the integrity of the judicial process. In contrast, Sunshine laws emphasize transparency and public access to government proceedings, creating a fundamental tension between openness and confidentiality in legal contexts involving classified information.
Public Access vs. National Security: Points of Conflict
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) restricts public access to court proceedings involving sensitive national security information to prevent unauthorized disclosures that could harm government interests. In contrast, Sunshine Laws promote transparency by ensuring the public's right to access governmental meetings and records, fostering accountability. The core conflict arises as CIPA imposes secrecy to protect national security, while Sunshine Laws demand openness, creating legal and ethical challenges in balancing public access with safeguarding classified information.
Case Studies: CIPA vs. Sunshine Law in Legal Proceedings
Case studies comparing the Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) and Sunshine Law reveal key contrasts in transparency and security during legal proceedings. CIPA safeguards national security by restricting access to sensitive information in federal criminal cases, exemplified in United States v. Reynolds where classified evidence was withheld to protect intelligence methods. Sunshine Laws promote transparency by mandating open government meetings and public access, as seen in cases like U.S. Department of Justice v. Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press, emphasizing public oversight and accountability in government actions.
Balancing Transparency and Security: Future Challenges
The Classified Information Procedures Act (CIPA) and Sunshine Laws represent contrasting approaches to handling government information, where CIPA emphasizes safeguarding national security through controlled disclosure in judicial proceedings, while Sunshine Laws promote transparency by mandating public access to government meetings and records. Future challenges will involve striking a balance between these statutes as technological advancements and evolving threats complicate the protection of sensitive data without undermining public accountability. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and clear legal frameworks will be critical to harmonizing the dual imperatives of transparency and security in an increasingly digital governance landscape.
Classified Information Procedures Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com