Civil service recruitment focuses on selecting qualified candidates to fill government positions through transparent and merit-based processes. Understanding the various stages, eligibility criteria, and examination patterns is essential for success. Explore this article to uncover key strategies and insights for navigating civil service recruitment effectively.
Table of Comparison
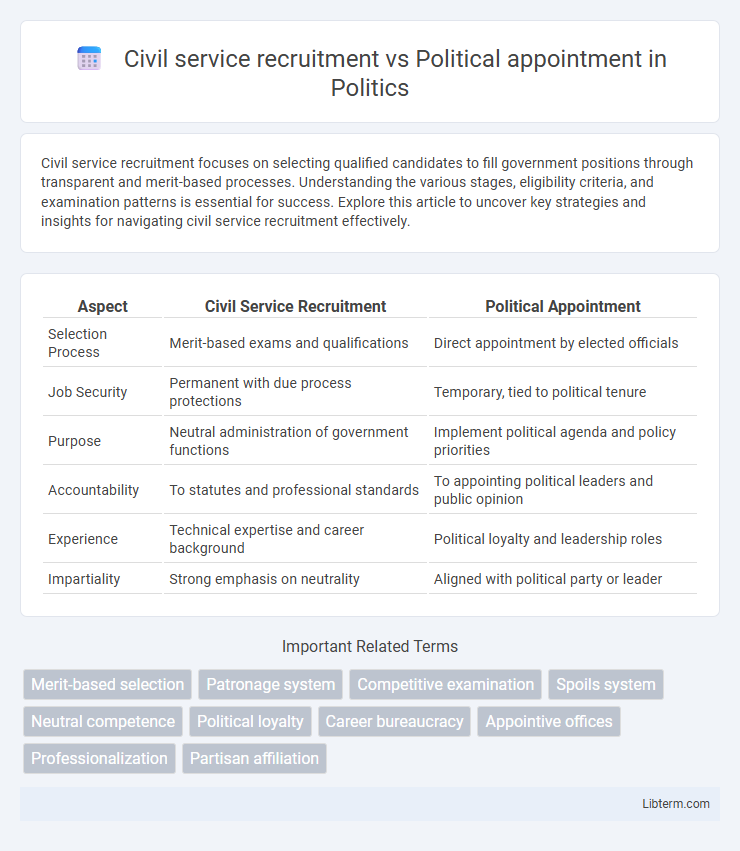
| Aspect | Civil Service Recruitment | Political Appointment |
|---|---|---|
| Selection Process | Merit-based exams and qualifications | Direct appointment by elected officials |
| Job Security | Permanent with due process protections | Temporary, tied to political tenure |
| Purpose | Neutral administration of government functions | Implement political agenda and policy priorities |
| Accountability | To statutes and professional standards | To appointing political leaders and public opinion |
| Experience | Technical expertise and career background | Political loyalty and leadership roles |
| Impartiality | Strong emphasis on neutrality | Aligned with political party or leader |
Understanding Civil Service Recruitment
Civil service recruitment emphasizes merit-based selection through competitive exams and transparent criteria to ensure qualified and professional candidates fill government roles. This system promotes stability, continuity, and non-partisan administration, distinguishing it from political appointments driven by loyalty or political affiliation. Understanding civil service recruitment highlights its role in maintaining an efficient, impartial public workforce essential for effective governance.
Defining Political Appointment
Political appointments designate individuals to government positions based on loyalty, political support, or affiliation with elected officials, rather than merit or competitive examination. These roles are often temporary and serve at the discretion of political leaders, contrasting with civil service recruitment, which emphasizes qualifications, experience, and standardized testing. Understanding political appointments involves recognizing their purpose in implementing administration policies and ensuring alignment with the current political agenda.
Key Differences Between Recruitment and Appointment
Civil service recruitment involves a merit-based, competitive process emphasizing qualifications, experience, and standardized testing to fill government positions, ensuring neutrality and professionalism. Political appointments are selections made by elected officials based on political loyalty, alignment with policy goals, or personal trust, often bypassing typical competitive procedures. The key differences lie in recruitment promoting transparency and fairness through established criteria, while appointments prioritize political considerations and may serve partisan interests.
Merit-Based Selection in Civil Service
Civil service recruitment emphasizes merit-based selection through standardized examinations, qualifications, and performance assessments to ensure qualified and competent personnel in public administration. This process fosters transparency, reduces favoritism, and promotes efficiency by prioritizing skills and expertise over political affiliations. In contrast, political appointments often prioritize loyalty and alignment with governing parties, potentially compromising impartiality and administrative professionalism.
Role of Political Influence in Appointments
Civil service recruitment relies on merit-based processes designed to ensure impartiality and competence, minimizing political influence in hiring decisions. Political appointments, in contrast, often prioritize loyalty and alignment with elected officials' agendas, embedding political influence in key governmental roles. This dynamic affects the balance between professional expertise and partisan control within public administration.
Transparency and Accountability in Hiring
Civil service recruitment emphasizes transparency and accountability through standardized exams and merit-based criteria, reducing bias and ensuring equal opportunity. Political appointments often lack such formal processes, increasing risks of favoritism and less public scrutiny. Implementing clear guidelines and public reporting enhances accountability in both systems, promoting trust in government hiring practices.
Impact on Public Sector Efficiency
Civil service recruitment ensures merit-based hiring, promoting competence and stability in public sector operations, which enhances overall efficiency. Political appointments often introduce personnel aligned with current leadership priorities but may risk disruptions due to frequent changes and lack of specialized expertise. The balance between these approaches significantly shapes public service delivery and administrative effectiveness.
Job Security and Tenure Comparisons
Civil service recruitment offers greater job security with positions typically secured through competitive exams and protected by merit-based regulations, minimizing arbitrary dismissal. Political appointments, in contrast, are often tied to the tenure of the appointing administration and can be terminated with changes in political leadership. This distinction underscores the stability of civil service roles versus the contingent nature of political appointments.
Challenges and Controversies in Both Systems
Civil service recruitment faces challenges such as bureaucratic inertia, potential for nepotism despite merit-based intentions, and lengthy hiring processes that may delay critical appointments. Political appointments often provoke controversies over favoritism, lack of qualifications, and undermining institutional neutrality, leading to questions about governance integrity and policy continuity. Both systems grapple with balancing efficiency, fairness, and accountability, impacting public trust and administrative effectiveness.
Best Practices for Fair Government Staffing
Civil service recruitment relies on merit-based examinations and transparent selection criteria to ensure qualified candidates fill government positions, promoting fairness and professionalism. Political appointments often prioritize loyalty and alignment with elected officials' policies but risk undermining impartiality and long-term stability within the bureaucracy. Best practices for fair government staffing combine rigorous civil service systems with limited, well-defined political appointments to balance expertise, accountability, and democratic responsiveness.
Civil service recruitment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com