Direct democracy empowers citizens to participate actively in decision-making by voting on laws and policies without intermediaries. This system enhances transparency and accountability, ensuring that Your voice directly influences government actions. Explore the rest of this article to understand how direct democracy shapes governance worldwide.
Table of Comparison
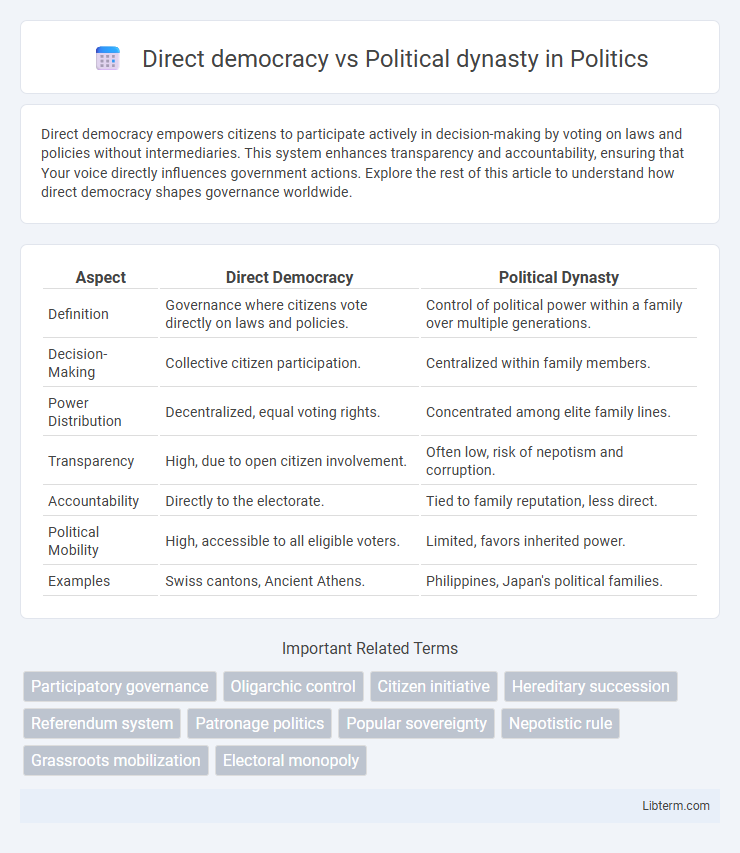
| Aspect | Direct Democracy | Political Dynasty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance where citizens vote directly on laws and policies. | Control of political power within a family over multiple generations. |
| Decision-Making | Collective citizen participation. | Centralized within family members. |
| Power Distribution | Decentralized, equal voting rights. | Concentrated among elite family lines. |
| Transparency | High, due to open citizen involvement. | Often low, risk of nepotism and corruption. |
| Accountability | Directly to the electorate. | Tied to family reputation, less direct. |
| Political Mobility | High, accessible to all eligible voters. | Limited, favors inherited power. |
| Examples | Swiss cantons, Ancient Athens. | Philippines, Japan's political families. |
Introduction: Defining Direct Democracy and Political Dynasty
Direct democracy empowers citizens to participate directly in decision-making processes through referendums and initiatives, bypassing elected representatives. Political dynasties, in contrast, concentrate power within specific families or groups, often limiting broader public influence on governance. Understanding these concepts highlights the tension between citizen-driven policy-making and entrenched familial political control.
Origins and Historical Context
Direct democracy traces its origins to ancient Athens in the 5th century BCE, where citizens participated personally in legislative decisions, reflecting early principles of equal political involvement. Political dynasties emerged predominantly in monarchies and aristocratic societies, where power concentrated within families to maintain control over resources and governance across generations. Historical contexts show direct democracy thriving in small, relatively homogenous communities, whereas political dynasties have often flourished in hierarchical, stratified societies with limited political participation.
Core Principles and Mechanisms
Direct democracy centers on empowering citizens to make decisions through referendums and initiatives, ensuring political sovereignty resides with the people. Political dynasties operate through familial control of power, often leveraging patronage and inherited influence to maintain authority across generations. The core principle of direct democracy is active participation and equal voting power, whereas political dynasties rely on entrenched power structures and limited political competition.
Impacts on Political Participation
Direct democracy enhances political participation by empowering citizens to vote on laws and policies directly, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. In contrast, political dynasties often limit broader engagement as power is concentrated within a few families, reducing opportunities for diverse voices and grassroots involvement. This concentration can lead to voter apathy, weakening democratic participation over time.
Representation and Accountability
Direct democracy enhances citizen representation by allowing individuals to vote directly on policies, ensuring that public decisions closely reflect the electorate's will. In contrast, political dynasties often concentrate power within specific families, which can limit diverse representation and create accountability challenges due to entrenched interests. Accountability in direct democracy is maintained through transparent voting processes and active civic participation, whereas political dynasties may face reduced accountability as power is perpetuated within a select few, potentially undermining democratic responsiveness.
Governance Efficiency and Transparency
Direct democracy enhances governance efficiency by enabling citizens to make decisions directly, reducing bureaucratic delays and increasing accountability. Political dynasties often hinder transparency due to concentrated power and potential conflicts of interest, leading to governance inefficiencies and favoritism. Empirical studies show that regions with active direct democratic processes report higher transparency indices and lower corruption rates compared to those dominated by political dynasties.
Socioeconomic Effects and Inequality
Direct democracy empowers citizens to participate in decision-making processes, promoting equitable policy outcomes and reducing the concentration of political power that often exacerbates socioeconomic inequalities. Political dynasties tend to consolidate wealth and influence within a limited elite, perpetuating unequal access to resources and opportunities, which intensifies social stratification and hinders inclusive economic development. Research indicates that regions with stronger direct democratic practices experience lower levels of income disparity and improved public service delivery compared to areas dominated by entrenched political families.
Case Studies: Global Examples and Lessons
Direct democracy empowers citizens to influence policy decisions through referendums and initiatives, as demonstrated by Switzerland's frequent use of popular votes to shape legislation directly. In contrast, political dynasties, such as the Kennedy family in the United States or the Nehru-Gandhi family in India, often concentrate power within select families, raising concerns about reduced political competition and accountability. Comparative analysis reveals that while direct democracy enhances citizen participation and transparency, political dynasties may hinder democratic diversification but can also provide political stability and experience in governance.
Contemporary Challenges and Criticisms
Direct democracy faces challenges such as scalability issues and the risk of populism, which can undermine informed decision-making in large populations. Political dynasties often provoke criticism for perpetuating nepotism, limiting political competition, and hindering democratic diversity. Both systems raise concerns about effective representation and accountability in contemporary governance.
Future Prospects and Reform Strategies
Direct democracy offers the potential to reduce the influence of political dynasties by empowering citizens to participate directly in decision-making processes, fostering transparency and accountability. Reform strategies include implementing digital platforms for citizen voting, establishing term limits for elected officials, and enhancing civic education to encourage informed participation. Future prospects highlight the integration of technology-based direct democracy tools that diminish entrenched family political power while promoting inclusive governance.
Direct democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com