Local autonomy empowers communities to govern themselves, making decisions that directly reflect their unique needs and priorities. It fosters more efficient public services, greater citizen participation, and tailored solutions that larger governments may overlook. Explore the full article to understand how local autonomy can enhance your community's development and governance.
Table of Comparison
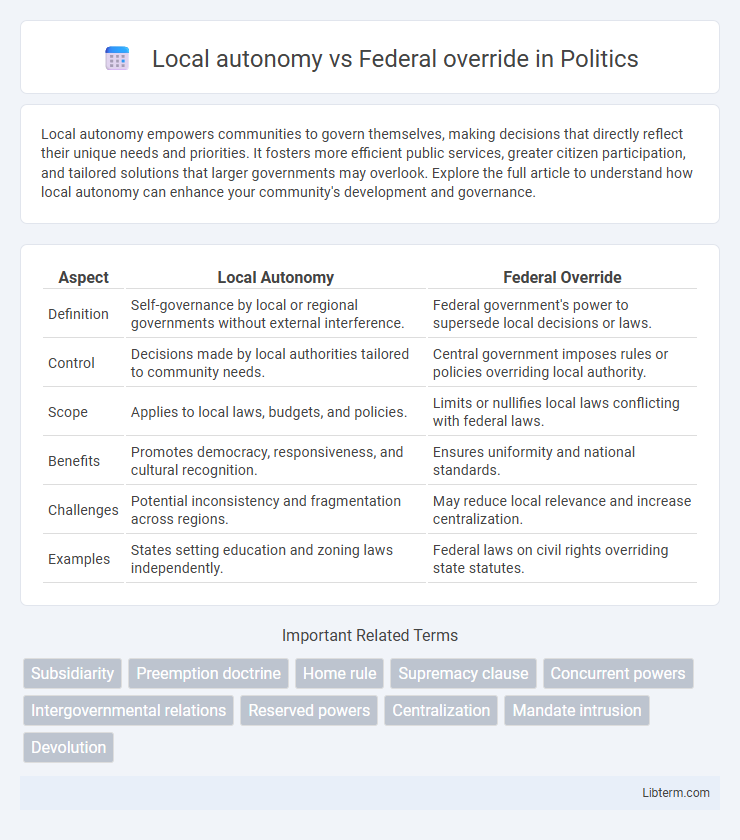
| Aspect | Local Autonomy | Federal Override |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-governance by local or regional governments without external interference. | Federal government's power to supersede local decisions or laws. |
| Control | Decisions made by local authorities tailored to community needs. | Central government imposes rules or policies overriding local authority. |
| Scope | Applies to local laws, budgets, and policies. | Limits or nullifies local laws conflicting with federal laws. |
| Benefits | Promotes democracy, responsiveness, and cultural recognition. | Ensures uniformity and national standards. |
| Challenges | Potential inconsistency and fragmentation across regions. | May reduce local relevance and increase centralization. |
| Examples | States setting education and zoning laws independently. | Federal laws on civil rights overriding state statutes. |
Understanding Local Autonomy: Definition and Scope
Local autonomy refers to the authority granted to local governments to make decisions, enact policies, and manage resources independently within their jurisdictions. This scope includes control over education, zoning, public safety, and local infrastructure, enabling tailored solutions that reflect community needs. Federal override occurs when national laws or regulations supersede local decisions, often sparking debates over the balance between local self-governance and uniform federal standards.
The Federal Override: Powers and Limitations
The federal override grants the national government the authority to supersede local decisions in areas explicitly defined by the Constitution, such as civil rights enforcement and interstate commerce. Powers under this override include enforcing federal laws, administering federal programs, and ensuring compliance with national standards, but it is limited by constitutional constraints and the Tenth Amendment, which reserves powers to states. Courts often balance these powers to prevent federal overreach, maintaining a system of checks and balances between federal and local governance.
Historical Context: Local vs Federal Authority
Local autonomy has historically been central to American governance, emphasizing community control over issues like education, law enforcement, and zoning. Federal override emerged as a mechanism to ensure national standards and protect civil rights, particularly during critical periods such as the Civil Rights Movement and the New Deal era. The tension between local authority and federal power reflects ongoing debates about the balance of power enshrined in the U.S. Constitution's Tenth Amendment and the Supremacy Clause.
Key Legal Frameworks Shaping the Debate
Key legal frameworks shaping the debate between local autonomy and federal override include the Tenth Amendment, which reserves powers not delegated to the federal government to the states or the people, and the Supremacy Clause, establishing federal law as the supreme law of the land. Landmark Supreme Court cases such as McCulloch v. Maryland and Printz v. United States have reinforced federal authority while simultaneously recognizing the importance of state sovereignty. Federal statutes like the Affordable Care Act illustrate practical instances where federal mandates challenge local decision-making, highlighting the ongoing tension between centralized control and local governance.
Case Studies: Landmark Federal Overrides
Landmark federal overrides demonstrate the tension between local autonomy and national priorities, as seen in the Supreme Court's decision in Arizona v. United States (2012), where federal immigration law preempted state statutes. The Voting Rights Act's federal oversight of state electoral practices highlights federal authority counteracting local attempts to impose discriminatory policies. California's sanctuary city policies faced federal pushback, underscoring ongoing conflicts between municipal governance and federal enforcement priorities.
Impacts on Governance and Public Policy
Local autonomy empowers municipalities to tailor governance and public policies to community-specific needs, enhancing responsiveness and innovation. Federal override can standardize regulations across states, ensuring consistency and addressing issues requiring national coordination, but may reduce local flexibility. The tension between these approaches shapes the balance of power, affecting policy effectiveness, resource allocation, and citizen engagement in governance.
Arguments for Strong Local Autonomy
Strong local autonomy promotes tailored governance, allowing communities to address unique cultural, economic, and social needs more effectively than a centralized federal system. It enhances democratic participation by empowering local citizens and governments to make decisions closely aligned with their preferences and priorities. Local autonomy also fosters innovation in policy-making, as diverse jurisdictions experiment with solutions that can be models for broader adoption.
Rationale Behind Federal Intervention
Federal intervention occurs when national interests or constitutional mandates supersede local decisions to maintain uniformity, protect civil rights, or manage resources efficiently. The rationale behind federal override often includes preventing discrimination, addressing interstate issues, and ensuring adherence to federal laws and treaties. Balancing local autonomy with federal authority aims to uphold the foundational principles of democracy while promoting national cohesion.
Balancing Rights: Finding Middle Ground
Local autonomy allows municipalities to tailor policies to community values, preserving cultural identity and addressing unique local needs. Federal override serves as a check to ensure national standards protect fundamental rights and prevent discriminatory practices. Striking a balance requires clear legal frameworks that uphold local decision-making authority while safeguarding constitutional protections across all jurisdictions.
The Future of Local-Federal Relations
Local autonomy remains essential in addressing unique community needs, but federal override powers are growing, influencing local policies on health, education, and law enforcement. Trends suggest increasing federal intervention during national crises, posing challenges for local governments seeking flexibility and self-governance. Future local-federal relations will likely balance collaborative federalism with respect for local jurisdiction, emphasizing adaptive frameworks for shared governance.
Local autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com