Political efficacy refers to the belief that your participation in the political process can influence government actions and policies. High political efficacy encourages greater voter turnout and civic engagement, shaping a more responsive and accountable democracy. Explore the article to understand how political efficacy impacts your role in the political landscape.
Table of Comparison
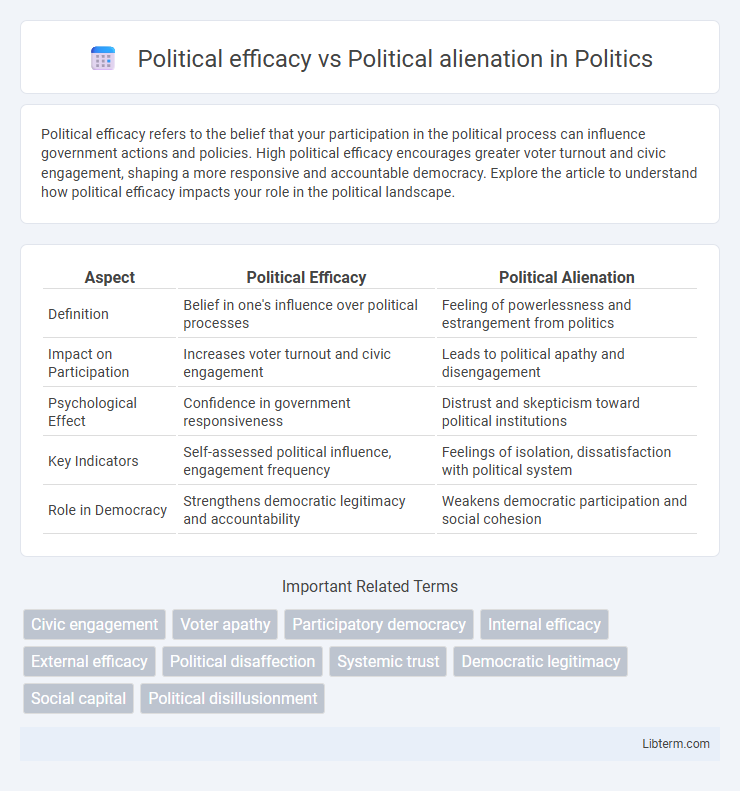
| Aspect | Political Efficacy | Political Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in one's influence over political processes | Feeling of powerlessness and estrangement from politics |
| Impact on Participation | Increases voter turnout and civic engagement | Leads to political apathy and disengagement |
| Psychological Effect | Confidence in government responsiveness | Distrust and skepticism toward political institutions |
| Key Indicators | Self-assessed political influence, engagement frequency | Feelings of isolation, dissatisfaction with political system |
| Role in Democracy | Strengthens democratic legitimacy and accountability | Weakens democratic participation and social cohesion |
Defining Political Efficacy
Political efficacy refers to citizens' belief in their ability to influence political processes and government decisions, reflecting confidence in the responsiveness of political systems. It encompasses both internal efficacy, which is an individual's confidence in their political knowledge and skills, and external efficacy, the perception that the political system will respond to citizens' demands. High political efficacy encourages civic engagement and participation, while political alienation denotes feelings of powerlessness and disconnection from political institutions.
Understanding Political Alienation
Political alienation reflects a citizen's sense of powerlessness and disenchantment with political processes, often leading to disengagement and reduced voter turnout. It contrasts sharply with political efficacy, which embodies an individual's belief in their ability to influence political decisions effectively. Understanding political alienation requires analyzing factors such as distrust in government, perceived corruption, and lack of representation, all of which diminish public participation and democratic legitimacy.
Historical Perspectives on Political Engagement
Historical perspectives reveal that political efficacy, the belief in one's ability to influence politics, often flourished during periods of social movements and democratic expansion, such as the civil rights era or the expansion of suffrage in the early 20th century. In contrast, political alienation, characterized by feelings of powerlessness and disconnection from political institutions, became more pronounced during times of political scandal, government distrust, and social upheaval, exemplified by the Vietnam War protests and Watergate crisis. These fluctuating attitudes have significantly shaped voter turnout patterns and participation in political activism across different eras.
Key Factors Influencing Political Efficacy
Political efficacy is shaped by factors such as access to political information, education level, and personal experiences with government responsiveness, which enhance an individual's belief in their ability to influence political processes. In contrast, political alienation often stems from feelings of powerlessness, distrust in political institutions, and social marginalization, reducing engagement and motivation to participate. The interaction of socio-economic status, media exposure, and civic education plays a critical role in determining the degree of political efficacy or alienation within populations.
Causes and Consequences of Political Alienation
Political alienation stems from causes such as perceived government corruption, lack of political representation, and limited civic engagement opportunities, leading to feelings of powerlessness and distrust in the political system. The consequences of political alienation include decreased voter turnout, diminished public participation, and increased social fragmentation. These effects undermine democratic legitimacy and hinder effective governance by reducing accountability and responsiveness.
Comparing Political Efficacy and Alienation
Political efficacy reflects an individual's belief in their ability to influence political processes, fostering engagement and trust in government institutions. In contrast, political alienation signifies a sense of powerlessness and estrangement from political systems, often leading to apathy or disengagement. Comparing both concepts reveals that high political efficacy correlates with active participation, whereas political alienation typically results in political withdrawal and skepticism toward authorities.
Political Participation: Motivators and Barriers
Political efficacy significantly influences political participation by enhancing individuals' belief in their ability to impact government decisions, thereby motivating active engagement in voting, campaigning, or civic discussions. In contrast, political alienation acts as a barrier, causing feelings of powerlessness and distrust in political institutions, which diminishes voter turnout and discourages involvement in collective political actions. Research highlights that increasing political efficacy through education and transparent governance can counteract alienation, fostering higher participation rates in democratic processes.
Societal Impacts of Efficacy and Alienation
Political efficacy fosters active citizen participation, promoting democratic stability and social cohesion by encouraging trust in government institutions. In contrast, political alienation leads to disengagement, reducing voter turnout and weakening community bonds, which can increase social unrest and exacerbate inequalities. Societal impacts of efficacy include enhanced policy responsiveness and civic engagement, while alienation often results in political polarization and diminished public accountability.
Strategies to Foster Political Efficacy
Enhancing political efficacy involves education programs that increase citizens' understanding of governmental processes and their ability to influence political outcomes. Community engagement initiatives and participatory platforms empower individuals to take part in decision-making, reducing feelings of political alienation. Transparent communication and responsive governance further build trust, encouraging active political involvement and fostering a sense of efficacy.
Building Inclusive and Responsive Political Systems
Political efficacy refers to citizens' belief in their ability to influence political processes, while political alienation reflects feelings of powerlessness and disengagement from politics. Building inclusive and responsive political systems requires enhancing political efficacy through transparent governance, citizen participation mechanisms, and equitable representation. Strengthening these aspects reduces political alienation, fostering trust and active engagement in democratic institutions.
Political efficacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com