The policy address outlines the government's priorities and strategic plans for economic growth, public welfare, and sustainable development. It highlights key initiatives aimed at improving infrastructure, healthcare, education, and environmental protection to enhance the quality of life for all citizens. Explore the full article to understand how these policies affect your community and future opportunities.
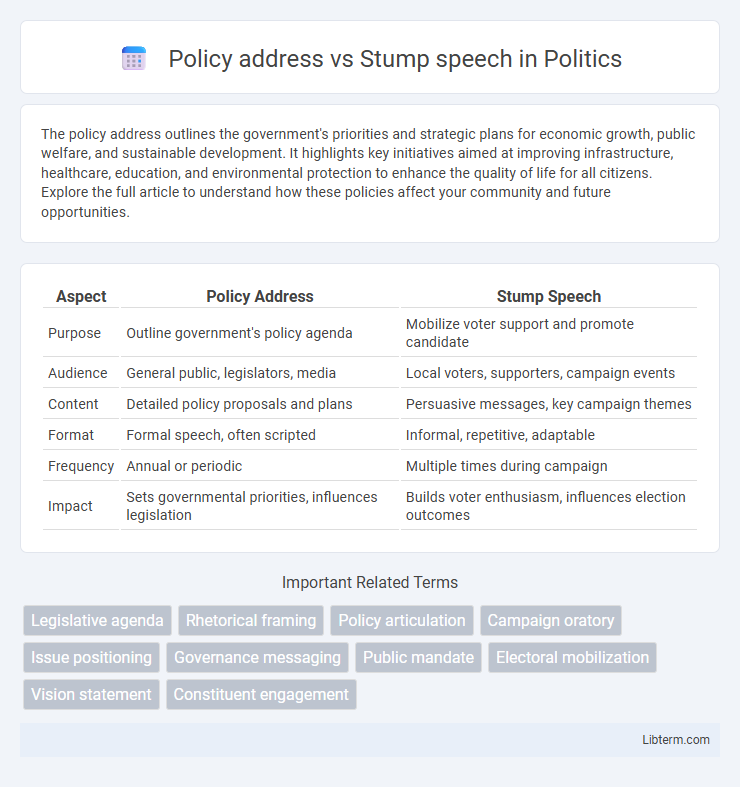
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Policy Address | Stump Speech |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Outline government's policy agenda | Mobilize voter support and promote candidate |
| Audience | General public, legislators, media | Local voters, supporters, campaign events |
| Content | Detailed policy proposals and plans | Persuasive messages, key campaign themes |
| Format | Formal speech, often scripted | Informal, repetitive, adaptable |
| Frequency | Annual or periodic | Multiple times during campaign |
| Impact | Sets governmental priorities, influences legislation | Builds voter enthusiasm, influences election outcomes |
Defining Policy Address and Stump Speech
A Policy Address is a formal speech delivered by government leaders outlining their administration's agenda, goals, and specific policy initiatives, often presented during official events like a legislative session or budget announcement. A Stump Speech is a short, repetitive campaign speech used by politicians to quickly communicate their key messages and rally voter support during election campaigns. While a Policy Address emphasizes detailed governance plans, a Stump Speech focuses on persuasive, easily memorable points tailored to engage and mobilize constituents.
Historical Origins of Both Speech Types
Policy addresses originated from formal government communications aimed at outlining legislative agendas, dating back to early parliamentary traditions in the 17th century. Stump speeches emerged in the 19th-century American political landscape, characterized by candidates delivering repetitive, impassioned talks while standing on tree stumps to engage local voters. The historical divergence reflects policy addresses as structured, top-down presentations by officials and stump speeches as grassroots, personalized political appeals.
Key Objectives: Informing vs. Persuading
Policy addresses aim to inform the public and stakeholders about government plans, priorities, and policy frameworks, providing detailed and structured information. Stump speeches focus on persuading voters and rallying support by emphasizing key messages, emotional appeal, and candidate commitments. Informing in policy addresses relies on clarity and depth, while persuading in stump speeches uses rhetoric and repetition to influence opinions.
Format and Structure Differences
A policy address is a formal, structured presentation delivered by government leaders outlining detailed plans, goals, and legislative priorities, typically following strict protocols and often supported by data and formal language. In contrast, a stump speech is a more informal, repetitive campaign speech designed to engage and persuade voters, featuring personal anecdotes, simplified messages, and a conversational tone. Policy addresses prioritize comprehensive content and official tone, while stump speeches emphasize brevity, emotional appeal, and adaptability to different audiences.
Typical Audiences and Venues
Policy addresses typically target policymakers, government officials, and stakeholders within formal settings such as legislative chambers, government conferences, or official public events. Stump speeches are aimed at general voters and supporters, delivered in informal venues like community halls, rallies, or campaign stops to energize and persuade the electorate. Both formats tailor their content and tone to suit the audience's expectations and the setting's formality.
Language and Rhetoric Employed
Policy addresses utilize formal, precise language and structured rhetoric to clearly communicate specific governmental plans and legislative priorities, aiming to demonstrate competency and transparency. Stump speeches employ more conversational, emotive language with repetitive and persuasive rhetorical devices designed to engage and mobilize a broad audience. The distinct linguistic styles reflect the differing objectives: policy addresses inform and justify policy, while stump speeches motivate and rally support.
Use of Data and Evidence
Policy addresses systematically integrate quantitative data and empirical evidence to support proposed initiatives, enhancing credibility and providing a clear rationale for policy decisions. Stump speeches rely more on anecdotal examples and emotional appeals, often using simplified or selectively chosen data to connect with the audience personally. The strategic use of comprehensive statistics in policy addresses contrasts with the narrative-driven, less data-intensive nature of stump speeches.
Timing within Political Campaigns
Policy addresses are typically delivered mid-campaign to outline detailed plans and respond to voter concerns, providing clarity and substance to a candidate's platform. Stump speeches occur frequently throughout the campaign trail, designed for consistent voter engagement and adaptable messaging to different audiences. Timing these speeches strategically enhances voter persuasion by balancing comprehensive policy explanation with repetitive, concise communication.
Impact on Public Perception and Media
Policy addresses present detailed government plans and showcase leadership competence, shaping public perception of authority and reliability while attracting in-depth media analysis. Stump speeches emphasize emotional appeal and core campaign messages, energizing supporters and generating widespread media coverage of candidate personality and voter connection. Both formats influence public opinion differently: policy addresses build trust through substance, while stump speeches drive enthusiasm through relatability and repetition.
Significance in Shaping Political Discourse
Policy addresses serve as formal communications outlining government priorities and legislative agendas, directly influencing public expectations and policy debates. Stump speeches, characterized by repetitive and persuasive rhetoric delivered during campaigns, mobilize voter support and frame electoral narratives. Both formats significantly shape political discourse by defining key issues and rallying constituencies, though policy addresses impact governance while stump speeches primarily drive electoral momentum.
Policy address Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com