Party loyalty shapes political landscapes by influencing voter behavior and policy decisions, often solidifying support for particular ideologies. Understanding how loyalty affects candidate selection and legislative outcomes can reveal the dynamics within your preferred party. Explore the full article to uncover key insights about party loyalty and its impact on politics.
Table of Comparison
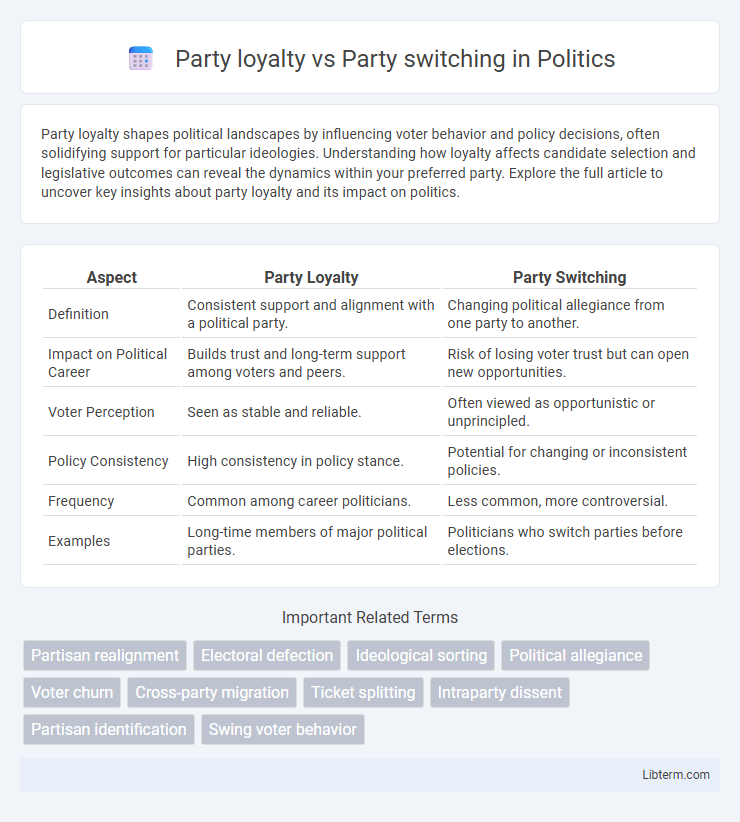
| Aspect | Party Loyalty | Party Switching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent support and alignment with a political party. | Changing political allegiance from one party to another. |
| Impact on Political Career | Builds trust and long-term support among voters and peers. | Risk of losing voter trust but can open new opportunities. |
| Voter Perception | Seen as stable and reliable. | Often viewed as opportunistic or unprincipled. |
| Policy Consistency | High consistency in policy stance. | Potential for changing or inconsistent policies. |
| Frequency | Common among career politicians. | Less common, more controversial. |
| Examples | Long-time members of major political parties. | Politicians who switch parties before elections. |
Understanding Party Loyalty: Definition and Importance
Party loyalty refers to the consistent support and allegiance voters or politicians exhibit towards a particular political party over time. It is crucial in maintaining political stability, enabling parties to implement their platforms effectively and fostering trust among constituents. High levels of party loyalty contribute to cohesive policy-making and predictability in electoral outcomes.
Historical Perspective on Party Allegiance
Historical perspective on party allegiance reveals that party loyalty was often deeply rooted in ideological alignment and social identity, particularly during the 19th and early 20th centuries when party platforms clearly defined political divisions. Instances of party switching occurred mainly due to significant shifts in policy stances, such as the realignment during the Civil Rights Movement when many Southern Democrats transitioned to the Republican Party. This historical pattern demonstrates that party allegiance has been influenced by evolving political landscapes and key national events that reshaped voter priorities and party identities.
Motivations Behind Party Switching
Motivations behind party switching often stem from ideological realignment, personal political ambitions, or shifts in constituency preferences. Politicians may switch parties to align better with their evolving policy views or to increase their chances of electoral success in changing political landscapes. External factors such as party leadership disputes, changing party platforms, or strategic considerations also significantly influence the decision to switch parties rather than maintain party loyalty.
Key Factors Influencing Party Loyalty
Voter demographic characteristics such as age, education, and socioeconomic status significantly influence party loyalty, with older and more educated voters tending to exhibit stronger allegiance to a single party. Political socialization, including family influence, community environment, and media exposure, reinforces consistent party identification over time. The perceived alignment between a party's platform and an individual's core values and policy priorities also plays a critical role in sustaining party loyalty or prompting party switching.
Prominent Cases of Party Switching
Prominent cases of party switching, such as Senator Arlen Specter's move from Republican to Democrat in 2009, highlight strategic realignments influenced by ideological shifts and electoral advantages. Another notable example is former Congressman Parker Griffith, who switched from Democrat to Republican in 2009, citing policy disagreements as key factors. These high-profile instances underscore the complex interplay between political loyalty, personal conviction, and changing party dynamics in American politics.
Impact of Party Switching on Political Careers
Party switching often disrupts established voter trust and can lead to diminished political influence due to perceived opportunism or ideological inconsistency. Many politicians experience short-term gains in strategic positioning but face long-term challenges, such as loss of key endorsements and decreased party funding. Electoral success after party switching depends heavily on timing, constituency alignment, and the ability to convincingly communicate the reasons behind the switch.
Party Loyalty in Modern Electoral Politics
Party loyalty remains a critical factor in modern electoral politics, serving as a foundation for stable voter bases and consistent policy platforms. Strong party alignment influences voter behavior, candidate selection, and legislative collaboration, reinforcing ideological coherence within political systems. Maintaining party loyalty enhances electoral predictability and strengthens democratic institutions by promoting accountability and clear policy mandates.
Public Perception: Loyalty vs Switching
Public perception often favors party loyalty as a sign of consistency, trustworthiness, and ideological commitment, enhancing a politician's credibility among constituents. Party switching can be viewed with skepticism, raising doubts about opportunism, political ambition, or instability in core beliefs. Voter trust and media framing heavily influence how party loyalty or switching impacts political reputation and electability.
Consequences for Political Parties
Party loyalty strengthens political parties by ensuring consistent support, enhancing organizational stability, and promoting unified policy platforms. Party switching undermines party cohesion, disrupts legislative agendas, and can weaken voter trust, leading to decreased party influence. Consequences for political parties include altered power dynamics, challenges in candidate selection, and potential shifts in policy direction.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Party Affiliation
Future trends in party affiliation indicate a growing fluidity as voters increasingly prioritize issue-based politics over traditional party loyalty, driven by generational shifts and digital media influence. Data from recent elections show a rise in independent and unaffiliated voters, reflecting a departure from strict party identity towards more personalized political alignments. Political analysts predict that this evolution will force parties to adapt by broadening their platforms and embracing more inclusive, dynamic engagement strategies to retain and attract members.
Party loyalty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com