Stronghold offers a strategic gaming experience where players build fortified castles and manage resources to defend against invading forces. Mastering its complex mechanics enhances your tactical thinking and planning skills. Dive into the article to uncover expert tips and strategies to dominate your stronghold.
Table of Comparison
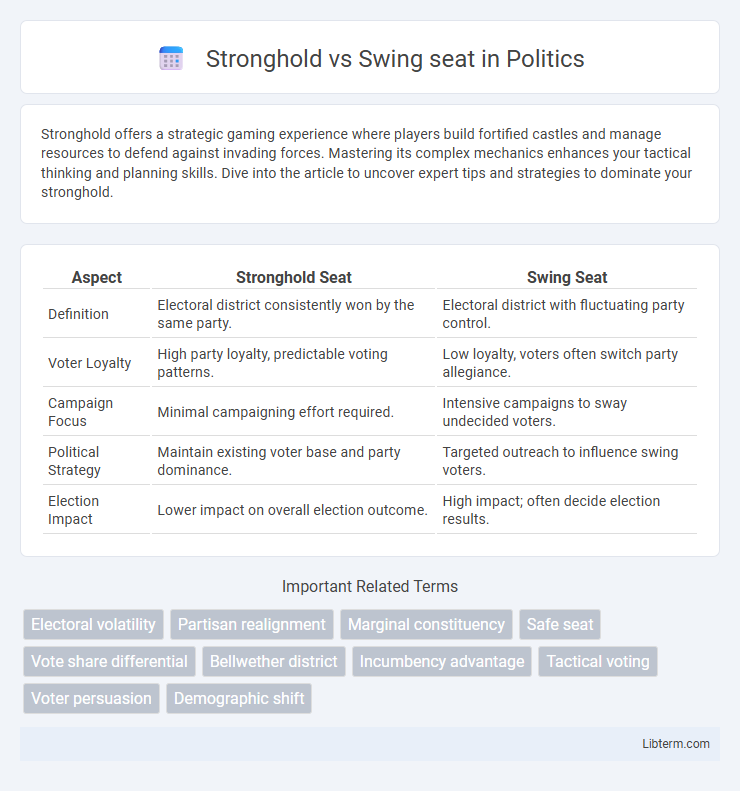
| Aspect | Stronghold Seat | Swing Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electoral district consistently won by the same party. | Electoral district with fluctuating party control. |
| Voter Loyalty | High party loyalty, predictable voting patterns. | Low loyalty, voters often switch party allegiance. |
| Campaign Focus | Minimal campaigning effort required. | Intensive campaigns to sway undecided voters. |
| Political Strategy | Maintain existing voter base and party dominance. | Targeted outreach to influence swing voters. |
| Election Impact | Lower impact on overall election outcome. | High impact; often decide election results. |
Understanding Stronghold and Swing Seats
Stronghold seats are electoral districts consistently won by the same political party, characterized by strong party loyalty and predictable voting patterns. Swing seats, also known as marginal seats, frequently change party control between elections and are crucial battlegrounds that can determine overall election outcomes. Understanding the demographic, economic, and social factors influencing voter behavior in these seats is essential for effective campaign strategies and resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Stronghold and Swing Seats
Stronghold seats are fixed and provide consistent, immovable support designed for maximum stability, often used in heavy-duty applications like gaming chairs or office seating. Swing seats, in contrast, are suspended and allow for gentle movement, enhancing comfort and relaxation in settings such as outdoor swings or nursery rocking chairs. The key differences lie in stability versus mobility, with stronghold seats prioritizing a rigid seating experience and swing seats offering dynamic motion.
Historical Background of Stronghold and Swing Seats
Stronghold seats have their origins in longstanding political dominance, often characterized by consistent party control established over decades, reflecting deep-rooted voter loyalty and historical voting patterns. Swing seats, conversely, gained prominence in electoral analysis as battleground districts where voter behavior is less predictable, often shifting between parties and thus playing a critical role in determining overall election outcomes. The historical background of strongholds highlights entrenched political cultures, while the evolution of swing seats underscores the dynamic nature of voter sentiment and demographic changes.
Political Importance of Stronghold Seats
Stronghold seats hold significant political importance as they guarantee consistent electoral victories for a party, providing stability and a reliable voter base crucial during tightly contested elections. These constituencies allow parties to prioritize resources on swing seats, which are competitive and can change party control, making them pivotal for overall election outcomes. The political strategy often hinges on maintaining strongholds to secure parliamentary presence while targeting swing seats to expand influence.
The Role of Swing Seats in Elections
Swing seats play a crucial role in election outcomes by representing constituencies where voter support can shift between competing parties, making them highly contested and strategically significant in campaigns. Unlike stronghold seats, which consistently favor one party, swing seats often determine the balance of power, as winning these key battlegrounds can secure a parliamentary majority or government control. Political parties allocate substantial resources and tailor policies to appeal to swing seat voters, recognizing their potential to influence overall election results.
Factors Influencing Swing Seats
Swing seats are primarily influenced by demographic shifts, local economic conditions, and the effectiveness of targeted campaigning strategies, whereas strongholds maintain consistent voting patterns due to stable party loyalty and entrenched community values. Voter turnout variability and swing voter behavior are critical in determining swing seat outcomes, contrasting with strongholds where voter allegiance remains relatively predictable. Data from recent elections indicate that swing seats often hinge on micro-level issues such as employment rates, healthcare access, and education funding, highlighting the importance of tailored political messaging.
Electoral Strategies for Stronghold vs Swing Seats
Stronghold electoral strategies focus on voter retention through targeted grassroots mobilization and reinforcing party loyalty by addressing local issues and maintaining strong community ties. Swing seat campaigns prioritize persuasive messaging and demographic analysis to attract undecided or swing voters, often tailoring policy promises and outreach efforts to reflect the specific concerns of fluctuating electorates. Effective resource allocation distinguishes both approaches, with strongholds emphasizing sustained engagement and swing seats concentrating on intensive, short-term voter persuasion to maximize electoral gains.
Case Studies: Stronghold vs Swing Seats in Recent Elections
Recent elections reveal Stronghold seats consistently deliver high vote margins for dominant parties, exemplified by Labour's sustained control over constituencies like Liverpool Walton. Swing seats such as the 2019 general election's work in Mid Worcestershire demonstrate volatility, with narrow margins and frequent shifts between parties, highlighting their pivotal role in determining overall parliamentary majorities. Case studies indicate targeted campaign investments and micro-targeting in swing seats significantly influence voter turnout and election outcomes.
Impact on Voter Turnout and Engagement
Stronghold seats typically show higher voter turnout due to consistent party loyalty, reinforcing stable engagement patterns over multiple election cycles. Swing seats, characterized by competitive margins, often experience fluctuating voter turnout driven by intensified campaign efforts and heightened voter interest. The strategic importance of swing seats stimulates targeted mobilization, increasing voter engagement through persuasive messaging and resource allocation.
Future Trends: Shifting from Stronghold to Swing Seats
Future electoral trends indicate a gradual shift from traditional stronghold constituencies to more volatile swing seats, driven by changing voter demographics and increased political polarization. Data analytics and targeted campaigning strategies are increasingly applied to swing seats, reflecting their growing importance in national elections. This evolving dynamic challenges parties to adapt rapidly, focusing resources on mobilizing undecided voters rather than relying solely on loyal bases.
Stronghold Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com