A primary election is a crucial process where political parties select their candidates for the upcoming general election. It determines which individuals will represent a party on ballots, shaping the choices available to voters in November. Explore the article to understand how primary elections impact your voting power and the overall democratic system.
Table of Comparison
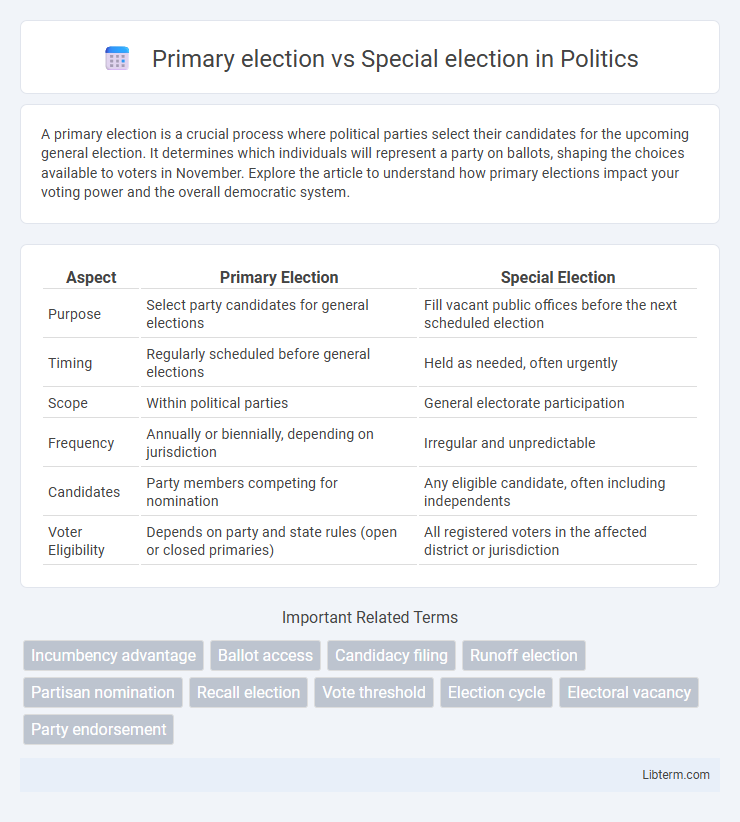
| Aspect | Primary Election | Special Election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Select party candidates for general elections | Fill vacant public offices before the next scheduled election |
| Timing | Regularly scheduled before general elections | Held as needed, often urgently |
| Scope | Within political parties | General electorate participation |
| Frequency | Annually or biennially, depending on jurisdiction | Irregular and unpredictable |
| Candidates | Party members competing for nomination | Any eligible candidate, often including independents |
| Voter Eligibility | Depends on party and state rules (open or closed primaries) | All registered voters in the affected district or jurisdiction |
Understanding Primary vs Special Elections
Primary elections determine a party's candidate for a general election by allowing registered party members to vote, whereas special elections fill unexpected vacancies in elected offices outside the regular election schedule. Primary elections follow a predetermined calendar, involving routine candidate selection, while special elections arise due to resignations, deaths, or removals from office, necessitating an immediate vote to maintain representation. Understanding the distinctions in timing, purpose, and voter eligibility clarifies the roles both types of elections play in democratic processes.
Definition of Primary Elections
Primary elections are preliminary elections in which voters select candidates to represent their political party in a subsequent general or special election. These elections determine the nominees for various offices, including local, state, and federal positions, allowing parties to present a unified candidate. Unlike special elections that fill unexpected vacancies, primary elections follow a scheduled process within the electoral calendar.
What Are Special Elections?
Special elections are held to fill unexpected vacancies in public offices due to resignation, death, or removal of an elected official, differing from primary elections that select party nominees for general elections. These elections operate outside the regular electoral calendar and often involve condensed timelines to ensure continuous representation. Special elections can significantly impact political dynamics by quickly shifting the balance of power within legislative bodies.
Key Differences Between Primary and Special Elections
Primary elections are scheduled events where political parties select their candidates for general elections, typically involving multiple contenders within the same party. Special elections occur outside the regular election calendar to fill unexpected vacancies or specific local ballot measures, often featuring fewer candidates and expedited timelines. Key differences include their timing, purpose, candidate selection process, and the scope of voter participation.
Purpose and Timing of Primary Elections
Primary elections serve to select a political party's candidate for a general election or special election, occurring on a predetermined schedule before the main election cycle. Their timing is crucial, often held months in advance to allow candidates to campaign and voters to make informed decisions. Special elections, by contrast, are held as needed to fill vacancies or address specific issues outside the regular electoral calendar.
Reasons for Holding Special Elections
Special elections occur primarily to fill unexpected vacancies in public office caused by resignation, death, or removal, ensuring uninterrupted representation. Unlike scheduled primary elections that determine party candidates before general elections, special elections address immediate electoral needs outside the regular cycle. State laws and the timing of such vacancies strongly influence the necessity and scheduling of special elections.
Voter Participation in Primary vs Special Elections
Voter participation in primary elections typically surpasses that in special elections due to scheduled timing and higher public awareness. Primary elections often coincide with general election cycles, attracting a broader electorate motivated by party nominations for major offices. Special elections, held irregularly to fill unexpected vacancies, usually experience lower turnout as voters have less time to mobilize and limited media coverage.
Impact on Political Parties
Primary elections determine party nominees for general elections, strengthening party unity by allowing members to select representatives aligned with their values. Special elections, often held to fill unexpected vacancies, can disrupt party strategies and shift power dynamics rapidly, influencing legislative agendas and party control. Both election types significantly affect political parties' ability to maintain or gain influence within government structures.
Examples of Notable Primary and Special Elections
The 2020 Democratic primary, featuring candidates like Joe Biden and Bernie Sanders, stands as a notable example of a primary election determining party nominees for the presidential race. The 2002 California gubernatorial special election, held after Gray Davis was recalled, exemplifies a special election used to fill a vacancy outside the regular election cycle. Both types of elections significantly impact political leadership but differ in timing and purpose, with primaries selecting party candidates and specials addressing unexpected vacancies.
Importance of Both Election Types in Democracy
Primary elections play a critical role in democracy by enabling political parties to select candidates who best represent the voters' interests, ensuring a competitive general election. Special elections are essential for maintaining governmental continuity and responsiveness by filling vacancies or addressing urgent issues outside the regular election cycle. Both election types uphold democratic principles by promoting voter engagement and legitimate representation in government.
Primary election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com