The minority leader plays a crucial role in shaping legislative agendas and representing the interests of their party within a legislative body. This position involves strategic negotiation, organizing party members, and providing a unified voice against the majority party's policies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the minority leader influences political dynamics and impacts decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
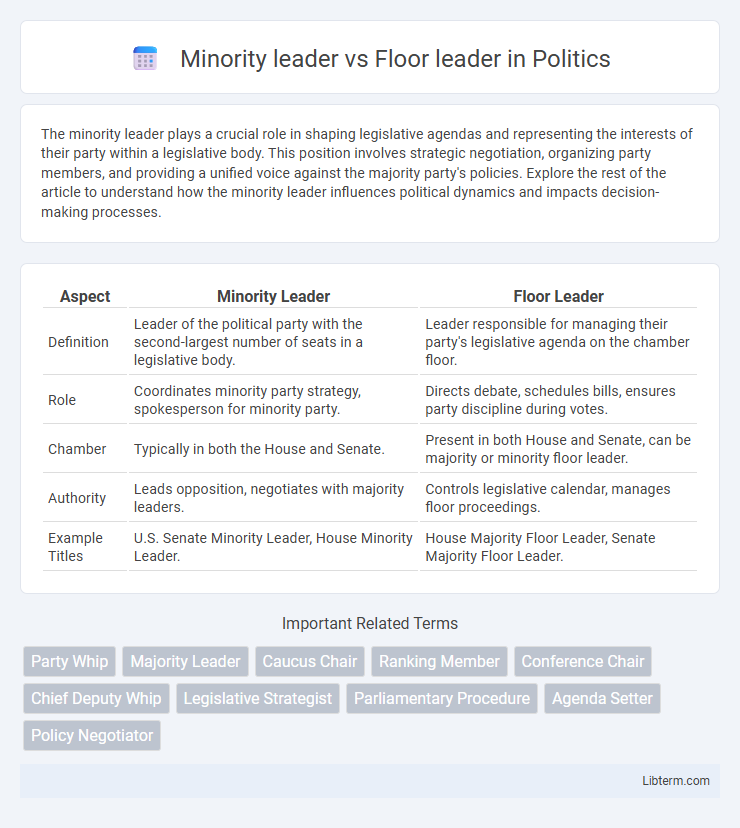
| Aspect | Minority Leader | Floor Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leader of the political party with the second-largest number of seats in a legislative body. | Leader responsible for managing their party's legislative agenda on the chamber floor. |
| Role | Coordinates minority party strategy, spokesperson for minority party. | Directs debate, schedules bills, ensures party discipline during votes. |
| Chamber | Typically in both the House and Senate. | Present in both House and Senate, can be majority or minority floor leader. |
| Authority | Leads opposition, negotiates with majority leaders. | Controls legislative calendar, manages floor proceedings. |
| Example Titles | U.S. Senate Minority Leader, House Minority Leader. | House Majority Floor Leader, Senate Majority Floor Leader. |
Definition of Minority Leader
The Minority Leader is the head of the political party with the second-largest number of seats in a legislative body, responsible for strategizing and coordinating the party's legislative agenda. Unlike the Floor Leader, whose role centers on managing the legislative floor operations and debates, the Minority Leader focuses on opposing the majority party's policies and representing the interests of the minority party. This leadership position plays a critical role in shaping legislative discussions and ensuring minority party influence within the legislative process.
Definition of Floor Leader
The Floor Leader is a key legislative position responsible for managing and strategizing the legislative agenda on the floor of the legislative body, representing their party's interests during debates and coordinating voting efforts. In contrast, the Minority Leader specifically leads the minority party, focusing on voicing opposition and organizing minority party strategies. The Floor Leader's role emphasizes active management of legislative processes, while the Minority Leader prioritizes leadership within the minority party.
Historical Origins of Leadership Roles
The Minority Leader and Floor Leader positions trace their origins to the early legislative systems where distinct political factions required organized representation within parliamentary procedures. The Minority Leader historically emerged as the chief spokesperson for the opposition party, shaping legislative strategy and articulating dissent within forums like the U.S. Congress since the 19th century. Floor Leaders developed as key organizers responsible for managing their party's legislative agenda on the chamber floor, coordinating debates and votes to steer policymaking efficiently.
Key Responsibilities of Minority Leaders
Minority leaders primarily coordinate and represent the interests of the minority party within legislative bodies, strategizing opposition or support for bills and policy initiatives. They organize party members, negotiate with the majority leadership, and manage legislative agendas to influence decision-making processes effectively. Minority leaders also serve as the spokesperson for their party's positions, ensuring cohesive communication and unified action on key legislative issues.
Key Responsibilities of Floor Leaders
Floor leaders play a crucial role in managing legislative agendas, coordinating party strategies, and maintaining order during debates on the house floor. They are responsible for scheduling the legislative calendar, facilitating communication between party members, and ensuring the passage of key bills aligned with party goals. Unlike minority leaders, floor leaders represent the majority party's interests and lead the execution of party policies within the legislative chamber.
Powers and Limitations
The Minority Leader holds significant influence in shaping the agenda, coordinating party strategy, and serving as the principal spokesperson for the minority party, yet faces limitations in setting the legislative calendar and controlling floor debates dominated by the majority party. The Floor Leader, often the Majority Leader, possesses powers to schedule legislation, manage floor proceedings, and facilitate the passage of bills but must navigate internal party dynamics and accommodate various factions within the majority. Both leaders wield pivotal roles in legislative negotiation, yet their effectiveness is constrained by the chamber's rules and their party's numerical strength.
Selection and Appointment Process
The Minority Leader is typically selected by the members of the minority party through internal party elections or caucuses, reflecting the collective choice of the minority caucus. In contrast, the Floor Leader designation often corresponds to the leadership role assigned by party rules or legislative bodies, sometimes overlapping with the Majority Leader if the majority party holds that title. The appointment process for both positions emphasizes party consensus and strategic leadership alignment within the legislative framework.
Influence on Legislative Agenda
The Minority Leader holds significant sway over the legislative agenda by representing the opposition party and strategizing to block or modify bills unfavorable to their party's interests. The Floor Leader, often the Majority Leader, controls the scheduling of debates and floor actions, directly shaping which bills advance and when. Both roles are pivotal in steering legislative priorities, with the Minority Leader influencing opposition tactics and the Floor Leader managing the flow and timing of legislative business.
Notable Minority and Floor Leaders in History
Notable Minority Leaders such as Nancy Pelosi, who served as the first female Speaker of the U.S. House and a prominent Democratic Minority Leader, have significantly influenced legislative strategies and party cohesion. Floor Leaders like Harry Reid, former Senate Majority and Minority Leader, played crucial roles in managing floor debates and guiding key legislative agendas. The distinction lies in Minority Leaders leading the opposition party's overall strategy, while Floor Leaders focus on day-to-day legislative management and floor procedures.
Comparing Minority Leader and Floor Leader Roles
The Minority Leader serves as the head of the party with the second-highest number of seats in a legislative chamber, responsible for coordinating party strategy, articulating opposition policies, and leading debates against the majority party. The Floor Leader, often synonymous with either the Majority or Minority Leader depending on party status, manages the legislative agenda on the chamber floor and ensures party discipline during votes. While both focus on party leadership, the Minority Leader specifically represents the minority party's interests, whereas the Floor Leader oversees the smooth conduct of legislative business regardless of majority or minority status.
Minority leader Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com