Government plays a crucial role in shaping policies that impact economic growth, social welfare, and national security. Understanding how different branches and levels of government function can empower you to engage effectively with civic processes. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about the essential functions and responsibilities of government.
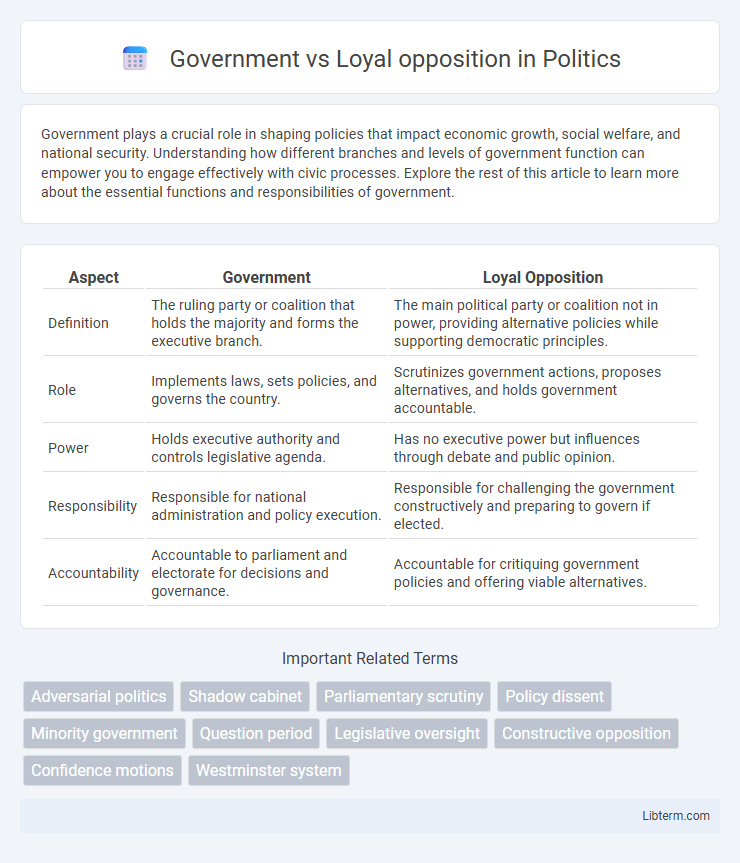
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Government | Loyal Opposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ruling party or coalition that holds the majority and forms the executive branch. | The main political party or coalition not in power, providing alternative policies while supporting democratic principles. |
| Role | Implements laws, sets policies, and governs the country. | Scrutinizes government actions, proposes alternatives, and holds government accountable. |
| Power | Holds executive authority and controls legislative agenda. | Has no executive power but influences through debate and public opinion. |
| Responsibility | Responsible for national administration and policy execution. | Responsible for challenging the government constructively and preparing to govern if elected. |
| Accountability | Accountable to parliament and electorate for decisions and governance. | Accountable for critiquing government policies and offering viable alternatives. |
Understanding the Role of Government
The role of government centers on executing laws, implementing public policies, and managing state affairs to ensure order and promote the welfare of citizens. It holds the authority to make binding decisions through elected representatives or appointed officials, maintaining stability and public services. The loyal opposition, while challenging government policies and offering alternative solutions, plays a crucial democratic role by holding the government accountable without undermining its legitimacy.
Defining the Loyal Opposition
The Loyal Opposition refers to a political group or party that opposes the current government while remaining committed to the constitutional framework and democratic principles. Unlike dissent that seeks to overthrow or undermine the state, the Loyal Opposition respects the legitimacy of the governing authority and aims to hold it accountable through debate and alternative policies. In parliamentary systems, the Loyal Opposition plays a crucial role in ensuring government transparency, fostering political pluralism, and representing diverse public interests.
Historical Origins of the Loyal Opposition
The concept of the Loyal Opposition originated in 18th-century Britain as a formal recognition that political opponents could oppose government policies without threatening the state's legitimacy. This principle emerged during the development of parliamentary democracy, ensuring that dissenting parties were accepted as essential components of a healthy political system. By institutionalizing opposition as loyal rather than rebellious, it established a foundation for modern democratic governance and political accountability.
Key Functions of the Opposition in Democracy
The key functions of the opposition in a democracy include holding the government accountable by scrutinizing policies and decisions through parliamentary debates and committees. The opposition provides alternative policies and voices public concerns, ensuring diverse perspectives are represented in governance. By challenging the ruling party, the opposition helps maintain transparency, prevents misuse of power, and strengthens democratic processes.
Government Powers and Responsibilities
The Government holds executive powers responsible for implementing laws, managing public administration, and conducting foreign affairs. It formulates policies, prepares the budget, and ensures national security while maintaining public order. These powers are balanced by the loyal opposition, which scrutinizes government actions and proposes alternatives to uphold democratic accountability.
Checks and Balances: Government vs Opposition
The government and loyal opposition play essential roles in maintaining checks and balances within a parliamentary democracy, with the government executing policies and the opposition scrutinizing decisions to hold them accountable. The opposition ensures transparency by challenging legislation and exposing potential governmental overreach, fostering a system of accountability that prevents the concentration of power. This dynamic balance facilitates effective governance and upholds democratic principles by promoting oversight, debate, and responsiveness.
Importance of Political Dissent
Political dissent plays a crucial role in a healthy democracy by ensuring that the government remains accountable and transparent. The loyal opposition provides constructive criticism and alternative policies, preventing the concentration of power and enabling diverse viewpoints. By fostering debate and challenging government decisions, political dissent strengthens democratic institutions and promotes responsive governance.
Challenges Facing the Loyal Opposition
The loyal opposition faces challenges such as limited access to resources compared to the ruling government, which restricts their ability to effectively influence policy and public opinion. They must navigate political marginalization while striving to hold the government accountable and present viable alternatives. Maintaining unity and coherence within the opposition party is essential to counteract government dominance and build public trust.
Case Studies: Successful Opposition Movements
The Indian National Congress during British colonial rule exemplified a successful opposition movement by strategically mobilizing mass protests and negotiating political reforms, ultimately contributing to India's independence. South Africa's African National Congress effectively challenged apartheid through sustained civil disobedience and international advocacy, leading to the dismantling of institutional racial segregation. In the United Kingdom, the Labour Party shifted from opposition to government by advocating workers' rights and social welfare policies, influencing the country's political landscape post-World War II.
The Future of Government-Opposition Relations
The future of government-opposition relations hinges on fostering constructive dialogue and strengthening democratic institutions to ensure accountability and responsiveness. Enhanced transparency, legal frameworks protecting opposition rights, and inclusive policy-making processes are pivotal for balanced power dynamics. Emerging technologies and social media platforms also play a critical role in shaping public discourse and enabling more effective government-opposition engagement.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com