General elections determine the political leadership that shapes national policies and governance for the coming years. Voter participation in these elections is crucial as it directly influences the direction of the country's future development. Discover how your vote impacts the political landscape and the key factors to consider in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
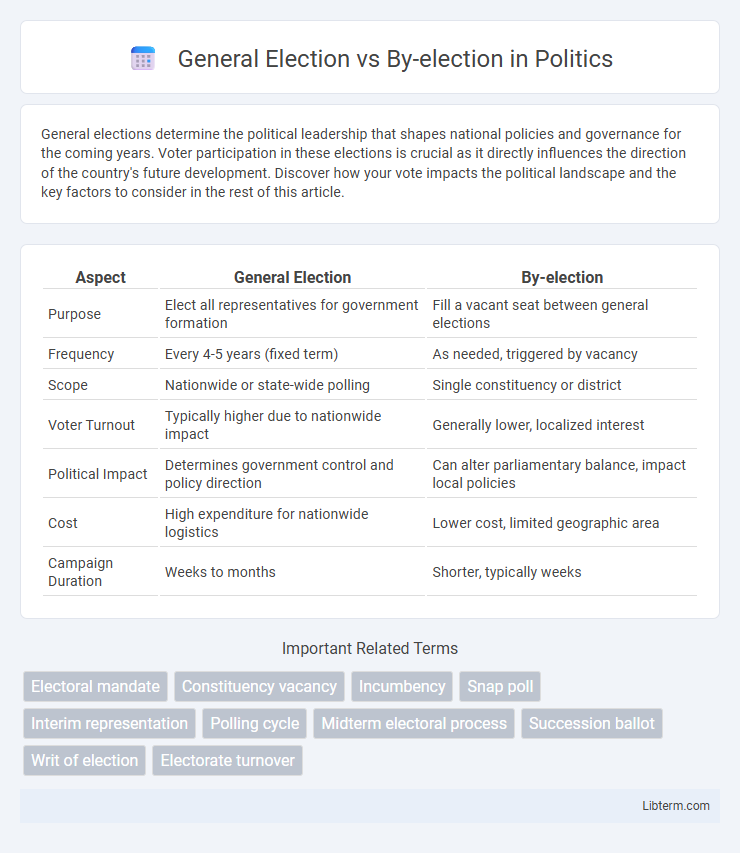
| Aspect | General Election | By-election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Elect all representatives for government formation | Fill a vacant seat between general elections |
| Frequency | Every 4-5 years (fixed term) | As needed, triggered by vacancy |
| Scope | Nationwide or state-wide polling | Single constituency or district |
| Voter Turnout | Typically higher due to nationwide impact | Generally lower, localized interest |
| Political Impact | Determines government control and policy direction | Can alter parliamentary balance, impact local policies |
| Cost | High expenditure for nationwide logistics | Lower cost, limited geographic area |
| Campaign Duration | Weeks to months | Shorter, typically weeks |
Introduction to General Elections and By-elections
General elections involve the selection of representatives for all or most seats in a legislative body, typically occurring at fixed intervals to establish a new government. By-elections are held to fill individual vacancies that arise between general elections due to resignation, death, or disqualification of sitting members. Both election types are fundamental components of democratic governance, ensuring continuous representation and accountability in legislative institutions.
Definition of General Election
A general election is a nationwide vote where citizens elect representatives to form the entire legislative body, such as a parliament or congress. It occurs at regular intervals according to constitutional or legal mandates, determining the government's composition and policy direction. General elections contrast with by-elections, which fill individual vacancies between general elections.
Definition of By-election
A by-election, also known as a special election, is held to fill a political office that becomes vacant between general elections due to resignation, death, or disqualification of a sitting member. Unlike a general election, which selects representatives for all constituencies simultaneously at fixed intervals, a by-election targets a specific constituency to ensure continuous representation. These elections are crucial for maintaining the balance of power in legislative bodies and addressing local political shifts.
Key Differences Between General Election and By-election
General elections involve voting for all or most members of a legislative body simultaneously, determining the overall government composition, while by-elections fill individual vacancies that occur between general elections, often affecting only one constituency. General elections are scheduled events occurring at regular intervals, typically every four to five years, whereas by-elections are unscheduled and triggered by circumstances like resignation, death, or disqualification of a sitting member. Voter turnout tends to be higher in general elections due to their broader political impact, whereas by-elections can have lower participation, reflecting their localized and often less publicized nature.
Frequency and Timing of Elections
General elections occur at fixed intervals, typically every four to five years, determining the full composition of a legislative body, while by-elections are held sporadically to fill individual vacancies arising between general elections. The timing of a by-election depends on specific circumstances such as resignation, death, or disqualification of a sitting member, making them unpredictable and irregular. Frequency of general elections ensures systematic democratic renewal, whereas by-elections address immediate representation needs without altering the entire legislature.
Purpose and Significance of Each Election Type
General elections determine the overall composition of a government by selecting representatives for all electoral constituencies simultaneously, ensuring a fresh mandate and legitimacy for the ruling body. By-elections fill vacancies in specific constituencies that arise between general elections due to resignations or deaths, maintaining continuous representation for affected areas. Each election type plays a crucial role in sustaining democratic governance, with general elections setting policy direction and by-elections preserving constituency-level accountability.
Electoral Process: General Election vs By-election
General elections involve the simultaneous voting of all eligible constituencies to elect representatives across a nation or region, typically occurring at fixed intervals. By-elections, conversely, take place in a single constituency to fill a vacancy arising between general elections due to resignation, death, or disqualification of a sitting member. The electoral process in general elections encompasses a broader logistical framework, including nationwide voter registration, ballot distribution, and vote counting, while by-elections focus on localized voter engagement and expedited election management.
Impact on Governance and Representation
General elections determine the overall composition of the government, influencing policy direction and legislative priorities for a full term, thereby ensuring comprehensive representation across all constituencies. By-elections fill individual vacancies between general elections, affecting localized governance and can shift the power balance in closely contested legislatures. The impact on governance is significant as general elections reset governmental mandates, while by-elections offer a mechanism for electoral accountability and localized political adjustments without altering the entire administration.
Examples of General Elections and By-elections
General elections occur nationwide to elect the entire legislative body, such as the 2020 United States presidential and congressional elections where all 435 House seats and 35 Senate seats were contested. By-elections, also known as special elections, fill individual vacancies between general elections, exemplified by the 2019 UK Peterborough by-election following a resignation and the 2017 Georgia's 6th district U.S. House special election after a seat became vacant. These electoral processes ensure continuous democratic representation by addressing either full legislative turnover or localized seat replacements.
Conclusion: Understanding Election Dynamics
General elections and by-elections serve distinct roles within democratic systems, with general elections determining the overall composition of legislative bodies, while by-elections fill vacancies arising between general polls. Analyzing voter turnout, candidate profiles, and electoral impact reveals that by-elections often act as barometers for public sentiment and government performance. Recognizing these differences enhances comprehension of election dynamics, voter behavior, and the broader political landscape.
General Election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com