Public welfare encompasses government programs designed to support individuals and families in need, promoting economic stability and social well-being. These services include healthcare, housing assistance, food aid, and unemployment benefits, all aimed at reducing poverty and enhancing quality of life. Explore this article to understand how public welfare can impact your community and the resources available to you.
Table of Comparison
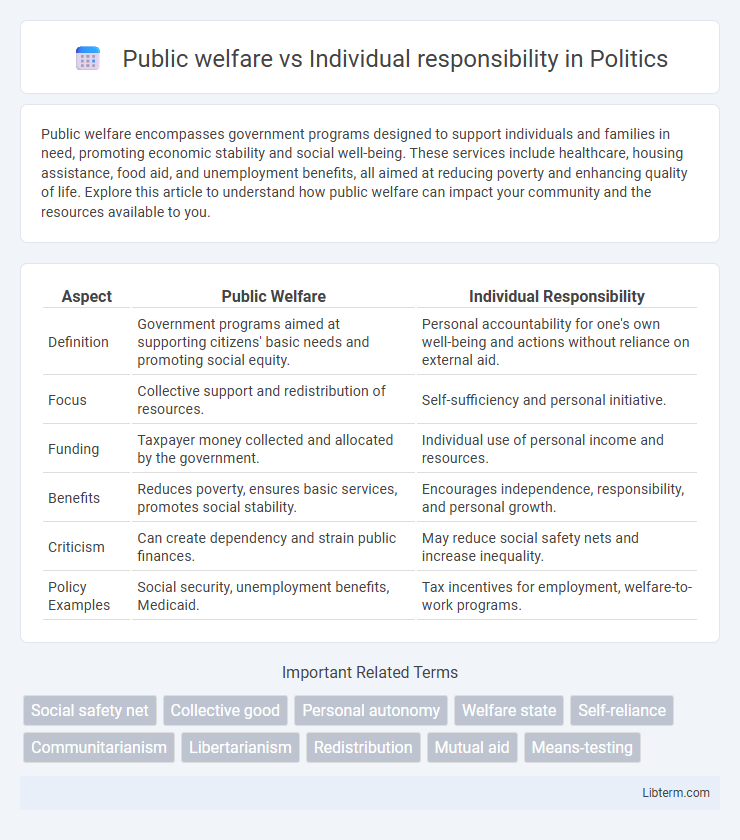
| Aspect | Public Welfare | Individual Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government programs aimed at supporting citizens' basic needs and promoting social equity. | Personal accountability for one's own well-being and actions without reliance on external aid. |
| Focus | Collective support and redistribution of resources. | Self-sufficiency and personal initiative. |
| Funding | Taxpayer money collected and allocated by the government. | Individual use of personal income and resources. |
| Benefits | Reduces poverty, ensures basic services, promotes social stability. | Encourages independence, responsibility, and personal growth. |
| Criticism | Can create dependency and strain public finances. | May reduce social safety nets and increase inequality. |
| Policy Examples | Social security, unemployment benefits, Medicaid. | Tax incentives for employment, welfare-to-work programs. |
Introduction to Public Welfare and Individual Responsibility
Public welfare encompasses government programs and policies designed to support the well-being of all citizens, including healthcare, education, and social security. Individual responsibility emphasizes personal accountability in managing one's health, finances, and social obligations without over-reliance on public systems. The balance between these concepts shapes social policy, influencing how resources are allocated to promote economic stability and social equity.
Defining Public Welfare: Scope and Objectives
Public welfare encompasses government programs and policies designed to support the health, education, and economic security of the population, targeting vulnerable groups such as the unemployed, elderly, and low-income families. The primary objectives include reducing poverty, improving public health, and ensuring equitable access to essential services. This framework balances societal support mechanisms with promoting individual responsibility to foster self-sufficiency and social stability.
Understanding Individual Responsibility in Society
Individual responsibility in society involves actively contributing to communal well-being through personal actions, ethical behavior, and accountability. Emphasizing self-reliance and informed decision-making fosters social trust and reduces dependency on public welfare systems. Balancing individual duties with collective support ensures sustainable progress and equitable resource distribution.
Historical Perspectives on Welfare and Personal Accountability
Historical perspectives on welfare reveal a complex interplay between public welfare systems and individual responsibility, highlighting shifts from charitable aid in ancient societies to more structured social safety nets in modern states. Early welfare models often emphasized community support, but industrialization and urbanization prompted governments to formalize welfare programs, balancing state intervention with expectations of personal accountability. The evolution of these frameworks reflects ongoing debates over the roles of government and individuals in addressing poverty, social risks, and economic inequality.
The Role of Government in Public Welfare
Government plays a crucial role in public welfare by implementing policies that ensure equitable access to healthcare, education, and social services, thereby reducing socioeconomic disparities. Through taxation and public spending, governments allocate resources to support vulnerable populations and promote social safety nets that protect individuals from poverty and unemployment. Balancing public welfare with individual responsibility requires government frameworks that encourage self-sufficiency while providing necessary assistance to maintain community well-being.
Balancing Personal Freedom with Collective Good
Balancing personal freedom with collective good requires navigating the tension between individual rights and societal obligations, ensuring that public welfare policies do not unduly restrict personal autonomy while promoting social equity and safety. Effective governance implements measures that protect vulnerable populations and provide essential services without imposing excessive control over personal choices, fostering a cooperative environment where personal responsibility aligns with communal benefit. This equilibrium supports sustainable development by encouraging citizens to contribute to the common good while preserving their freedoms.
Ethical Considerations in Welfare Policies
Ethical considerations in welfare policies balance public welfare with individual responsibility by emphasizing fairness, autonomy, and social justice. Policies must ensure equitable resource distribution while respecting personal agency and avoiding dependency. Striking this balance promotes societal well-being and upholds moral accountability among citizens.
Economic Impacts: Public Welfare vs. Individual Initiative
Public welfare programs can stimulate economic growth by providing safety nets that increase consumer spending and reduce poverty-related costs. In contrast, emphasizing individual responsibility encourages entrepreneurship and innovation, which may lead to higher productivity and economic resilience. Balancing government support with personal initiative is key to sustaining a dynamic and inclusive economy.
Case Studies: Welfare Systems Around the World
Examining welfare systems in countries like Sweden and the United States reveals distinct approaches to public welfare and individual responsibility. Sweden's comprehensive social safety net emphasizes universal healthcare, unemployment benefits, and education aimed at reducing inequality, while the U.S. welfare model prioritizes targeted assistance programs emphasizing personal accountability and work requirements. Case studies highlight the impact of these varying frameworks on poverty rates, social mobility, and economic stability, providing valuable insights for policymakers balancing collective support with individual initiative.
Future Trends: Evolving Concepts of Responsibility and Welfare
Future trends in public welfare emphasize a hybrid approach that redefines the balance between societal support and personal accountability, driven by technological advancements and shifting economic landscapes. Emerging models prioritize adaptive welfare policies integrating automation and AI to enhance efficiency while fostering individual empowerment through digital literacy and personalized assistance programs. Data-driven strategies and collaborative governance are reshaping responsibility concepts, promoting sustainable welfare ecosystems that address disparities and encourage proactive citizen engagement.
Public welfare Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com